Exercise 1.6Z: Ergodic Probabilities
From LNTwww
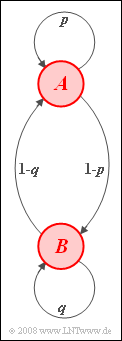
We consider a homogeneous stationary first-order Markov chain with events A and B and transition probabilities corresponding to the adjacent Markov diagram:
For subtasks (1) to (4), assume:
- Event A is followed by A and B with equal probability.
- After B: The event A is twice as likely as B.
From subtask (5) on, p and q are free parameters, while the ergodic probabilities Pr(A)=2/3 and Pr(B)=1/3 are fixed.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Markov Chains.
- You can check your results with the (German language) interactive SWF applet
- Ereigniswahrscheinlichkeiten einer Markov-Kette erster Ordnung ⇒ "Event Probabilities of a First Order Markov Chain".
Questions
Solution
(1) According to the instruction, p=1−p ⇒ p=0.500_ and q=(1−q)/2, ⇒ q=0.333_ holds.
(2) For the event probability of A holds:
- Pr(A)=Pr(A|B)Pr(A|B)+Pr(B|A)=1−q1−q+1−p=2/32/3+1/2=47≈0.571_.
- This gives Pr(B)=1−Pr(A)=3/7≈0.429_.
(3) No statement is made about the time ν−1 .
- At this time A or B may have occurred. Therefore holds:
- Pr(Bν|Aν−2)=Pr(A|A)⋅Pr(B|A)+Pr(B|A)⋅Pr(B|B)=p⋅(1−p)+q⋅(1−p)=5/12≈0.417_.
(4) According to Bayes' theorem:
- Pr(Aν−2|Bν)=Pr(Bν|Aν−2)⋅Pr(Aν−2)Pr(Bν)=5/12⋅4/73/7=5/9≈0.556_.
Reasoning:
- The probability Pr(Bν|Aν−2)=5/12 has already been calculated in subsection (3).
- Due to stationarity, Pr(Aν−2)=Pr(A)=4/7 and Pr(Bν)=Pr(B)=3/7 holds.
- Thus, the value of 5/9 is obtained for the sought inference probability according to the above equation.
(5) According to subtask (2) with p=1/2 for the probability of A in general:
- Pr(A)=1−q1.5−q.
- Thus from Pr(A)=2/3 follows q=0_.
(6) In the case of statistical independence, for example, it must hold:
- Pr(A|A)=Pr(A|B)=Pr(A).
- From this follows p=Pr(A)=2/3_ and accordingly q=1−p=1/3_.