Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.4: "Pointer diagram" and "Locality Curve""
From LNTwww
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „ {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulationsverfahren/ Allgemeines Modell der Modulation}} [[File:|right|]] ===Fragebogen=== <quiz display=simple> {Multiple-Choic…“) |
m |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/General_Model_of_Modulation}} |
| + | [[File:P_ID966__Mod_A_1_4_neu.png|right|frame|A given analytical signal in the complex plane]] | ||
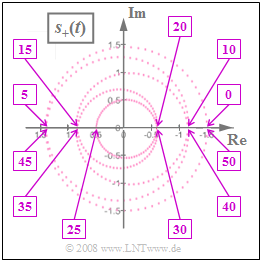
| + | The accompanying graph shows the analytical signal $s_+(t)$ in the complex plane. | ||
| + | *The numbers shown in the rectangles indicate the time points in microseconds. | ||
| + | *For all multiples of $5 \ \rm µ s$ , $s_+(t)$ is always real with the following values: | ||
| + | :$$s_+(t = 0) =s_+(t = 50\;{\rm µ s})= 1.500\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$s_+(t = 5\;{\rm µ s}) = s_+(t = 45\;{\rm µ s})= -1.405\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$s_+(t = 10\;{\rm µ s}) = s_+(t = 40\;{\rm µ s})= 1.155\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$\text{.....................................} $$ | ||
| + | :$$s_+(t = 25\;{\rm µ s}) = -0.500\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | It is assumed that the corresponding physical signal has the following form: | ||
| + | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \left(\omega_{\rm T}\cdot t\right) + {A_0}/{2}\cdot \cos\left(\left(\omega_{\rm T} + \omega_{\rm 0}\right)\cdot t \right) + {A_0}/{2}\cdot \cos\left(\left(\omega_{\rm T} - \omega_{\rm 0}\right)\cdot t \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *The frequency of the carrier signal is given as $f_{\rm T} = 100\text{ kHz}$. | ||
| + | *The three further parameters $f_0$, $A_{\rm T}$ and $A_0$ are to be determined. | ||
| − | |||
| + | Reference will also be made to the [[Modulation_Methods/General_Model_of_Modulation#Describing_the_physical_signal_using_the_equivalent_low-pass_signal|equivalent lowpass signal]] $s_{\rm TP}(t)$, with the following relationship to the analytical signal: | ||
| + | :$$s_{\rm TP}(t) = s_+(t) \cdot {\rm e}^{-{\rm j}\hspace{0.03cm} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | === | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Hints: | ||
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/General_Model_of_Modulation|General Model of Modulation]]. | ||
| + | *Particular reference is made to the page [[Modulation_Methods/General_Model_of_Modulation#Describing_the_physical_signal_using_the_equivalent_low-pass_signal|Describing the physical signal using the equivalent low-pass signal]]. | ||
| + | *You will find further information on these topics in these chapters of the book "Signal Representation": | ||
| + | ::(1) [[ Signal_Representation/Harmonic_Oscillation|Harmonic Oscillation]], | ||
| + | ::(2) [[Signal_Representation/Analytical_Signal_and_Its_Spectral_Function|Analytical Signal and its Spectral Function]], | ||
| + | ::(3) [[Signal_Representation/Equivalent_Low-Pass_Signal_and_its_Spectral_Function| Equivalent Low-Pass Signal and its Spectral Function]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In our tutorial $\rm LNTwww$, the plot of the analytical signal $s_+(t)$ n the complex plane is sometimes referred to as the "pointer diagram", while the "locus curve" gives the time course of the equivalent lowpass signal $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ . We refer you to the corresponding interactive Applets | ||
| + | ::(1) [[Applets:Physical_Signal_%26_Analytic_Signal|Physical and analytic signal]], | ||
| + | ::(2) [[Applets:Physical_Signal_%26_Equivalent_Lowpass_Signal|Physical signal and equivalent low-pass signal]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Using $s(t)$, give the equation for $s_+(t)$ and simplify it. Which equation is valid for the equivalent low-pass signal? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
| − | - | + | - $s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_0 · {\rm e}^{–{\rm j}ω_0t}.$ |
| − | + | + | - $s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_{\rm T} + A_0 · {\rm e}^{+{\rm j}ω_0t}.$ |
| + | + $s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_{\rm T} + A_0 · \cos(ω_0t).$ | ||
| + | {Determine the signal parameter $f_0$. | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | $f_0 \ = \ $ { 20 3% } $\ \text{kHz}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Determine the additional signal parameters $A_{\rm T}$ and $A_0$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\ | + | $A_{\rm T} \ = \ $ { 1 3% } |
| + | $A_0 \ = \ $ { 0.5 3% } | ||
| + | {Calculate the values of the analytical signal $s_+(t)$ at times $t = 15 \;{\rm µ s}$ and $t = 20\;{\rm µ s}$. | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | $s_+(t = 15 \ \rm µ s) \ = \ $ { -0.865--0.825 } | ||
| + | $s_+(t = 20 \ \rm µ s) \ = \ $ { 0.595 3% } | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''1 | + | '''(1)''' Convert all cosine functions to corresponding complex exponential functions: |
| − | '''2 | + | :$$s_+(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} + \frac{A_0}{2}\cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}(\omega_{\rm T} + \omega_{\rm 0})\hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} + \frac{A_0}{2}\cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}(\omega_{\rm T} - \omega_{\rm 0})\hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} = {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} \cdot \left[ A_{\rm T}+ \frac{A_0}{2} \cdot \left( {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} + {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}-{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t}\right)\right]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | '''3 | + | *Using the equation ${\rm e}^{{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}· \hspace{0.05cm}α} + {\rm e}^{-{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}·\hspace{0.05cm} α} = 2 · \cos(α)$ it further follows that: |
| − | ''' | + | :$$s_+(t) = {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} \cdot \left[ A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot t) \right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | *Thus, for the equivalent lowpass signal, we obtain: | |
| − | ''' | + | :$$s_{\rm TP}(t) = s_+(t) \cdot {\rm e}^{-{\rm j}\hspace{0.03cm} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | Therefore the <u>last answer</u> is correct. | |
| + | *In the chapter "Envelope Demodulation" of the present book we will see that we are dealing with "DSB-AM of a cosine signal with a cosine carrier". | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' The period of the analytical signal $s_+(t)$ is $T_0 = 50$ μs. | ||
| + | *The physical signal $s(t)$ has the same period duration. | ||
| + | *Assuming that $f_{\rm T}$ is an integer multiple of $f_0$ (which always first needs confirming, but is true for this example), this results in | ||
| + | :$$f_0 = 1/T_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 20 \ \rm kHz}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' At the given times (multiples of $5$ μs), the following applies to the complex rotating pointer of the carrier: | ||
| + | :$${\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} 2 \pi \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} {100\,{\rm kHz}}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}(k \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} 5\,{\rm \mu s})} = {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}k \hspace{0.03cm} \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} \pi } = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} +1 \\ -1 \\ \end{array} \right. \begin{array}{*{10}c} {\rm{if}} \\ {\rm{if}} \\ \end{array}\begin{array}{*{20}c} k \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm even} , \\ k \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm odd} . \\ \end{array}$$ | ||
| + | *Therefore, it follows from the equation calculated in Question '''(1)''': | ||
| + | :$$k = 0 \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} s_{\rm +}(t = 0) = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot 0) = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$k = 5 \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} s_{\rm +}(t = 25\;{\rm µ s}) = - \left[ A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot {T_0}/{2}) \right] = -A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *A comparison with the first and last equation on the sheet shows: | ||
| + | :$$ s_{\rm +}(t = 0) = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0}=1.5 \hspace{0.05cm}, $$ | ||
| + | :$$ s_{\rm +}(t = 25\;{\rm \mu s}) = -A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} = -0.5 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *This gives $A_{\rm T} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1}$ and $A_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0.5}$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(4)''' At time $t = 15$ μs $(k = 3$, odd$)$ it holds that: | ||
| + | :$$ s_{\rm +}(t = 15\;{\rm µ s}) = - \left[ 1+ 0.5 \cdot \cos (2 \pi \cdot 20\,{\rm kHz} \cdot 0.015\,{\rm ms}) \right] \hspace{0.05cm} = -1- 0.5 \cdot \cos (108^{\circ})\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -0.845} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *In contrast, for time $t = 20$ μs $(k = 4$, even$)$: | ||
| + | :$$ s_{\rm +}(t = 20\;{\rm µ s}) = 1 + 0.5 \cdot \cos (144^{\circ})\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.595} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | At all these considered time points, the physical signal $s(t) = {\rm Re}[s_+(t)]$ is exactly as large. | ||
| + | |||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Modulation Methods: Exercises|^1.3 General Model of Modulation ^]] |
Latest revision as of 13:19, 24 March 2022
The accompanying graph shows the analytical signal $s_+(t)$ in the complex plane.
- The numbers shown in the rectangles indicate the time points in microseconds.
- For all multiples of $5 \ \rm µ s$ , $s_+(t)$ is always real with the following values:
- $$s_+(t = 0) =s_+(t = 50\;{\rm µ s})= 1.500\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$s_+(t = 5\;{\rm µ s}) = s_+(t = 45\;{\rm µ s})= -1.405\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$s_+(t = 10\;{\rm µ s}) = s_+(t = 40\;{\rm µ s})= 1.155\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\text{.....................................} $$
- $$s_+(t = 25\;{\rm µ s}) = -0.500\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
It is assumed that the corresponding physical signal has the following form:
- $$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \left(\omega_{\rm T}\cdot t\right) + {A_0}/{2}\cdot \cos\left(\left(\omega_{\rm T} + \omega_{\rm 0}\right)\cdot t \right) + {A_0}/{2}\cdot \cos\left(\left(\omega_{\rm T} - \omega_{\rm 0}\right)\cdot t \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The frequency of the carrier signal is given as $f_{\rm T} = 100\text{ kHz}$.
- The three further parameters $f_0$, $A_{\rm T}$ and $A_0$ are to be determined.
Reference will also be made to the equivalent lowpass signal $s_{\rm TP}(t)$, with the following relationship to the analytical signal:
- $$s_{\rm TP}(t) = s_+(t) \cdot {\rm e}^{-{\rm j}\hspace{0.03cm} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter General Model of Modulation.
- Particular reference is made to the page Describing the physical signal using the equivalent low-pass signal.
- You will find further information on these topics in these chapters of the book "Signal Representation":
- In our tutorial $\rm LNTwww$, the plot of the analytical signal $s_+(t)$ n the complex plane is sometimes referred to as the "pointer diagram", while the "locus curve" gives the time course of the equivalent lowpass signal $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ . We refer you to the corresponding interactive Applets
Questions
Solution
(1) Convert all cosine functions to corresponding complex exponential functions:
- $$s_+(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} + \frac{A_0}{2}\cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}(\omega_{\rm T} + \omega_{\rm 0})\hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} + \frac{A_0}{2}\cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}(\omega_{\rm T} - \omega_{\rm 0})\hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} = {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} \cdot \left[ A_{\rm T}+ \frac{A_0}{2} \cdot \left( {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} + {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}-{\rm j} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t}\right)\right]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Using the equation ${\rm e}^{{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}· \hspace{0.05cm}α} + {\rm e}^{-{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}·\hspace{0.05cm} α} = 2 · \cos(α)$ it further follows that:
- $$s_+(t) = {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.03cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} \cdot \left[ A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot t) \right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Thus, for the equivalent lowpass signal, we obtain:
- $$s_{\rm TP}(t) = s_+(t) \cdot {\rm e}^{-{\rm j}\hspace{0.03cm} \cdot \hspace{0.03cm}\omega_{\rm T}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}t} = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Therefore the last answer is correct.
- In the chapter "Envelope Demodulation" of the present book we will see that we are dealing with "DSB-AM of a cosine signal with a cosine carrier".
(2) The period of the analytical signal $s_+(t)$ is $T_0 = 50$ μs.
- The physical signal $s(t)$ has the same period duration.
- Assuming that $f_{\rm T}$ is an integer multiple of $f_0$ (which always first needs confirming, but is true for this example), this results in
- $$f_0 = 1/T_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 20 \ \rm kHz}.$$
(3) At the given times (multiples of $5$ μs), the following applies to the complex rotating pointer of the carrier:
- $${\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} 2 \pi \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} {100\,{\rm kHz}}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}(k \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} 5\,{\rm \mu s})} = {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}k \hspace{0.03cm} \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} \pi } = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} +1 \\ -1 \\ \end{array} \right. \begin{array}{*{10}c} {\rm{if}} \\ {\rm{if}} \\ \end{array}\begin{array}{*{20}c} k \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm even} , \\ k \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm odd} . \\ \end{array}$$
- Therefore, it follows from the equation calculated in Question (1):
- $$k = 0 \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} s_{\rm +}(t = 0) = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot 0) = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$k = 5 \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} s_{\rm +}(t = 25\;{\rm µ s}) = - \left[ A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm 0}\cdot {T_0}/{2}) \right] = -A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- A comparison with the first and last equation on the sheet shows:
- $$ s_{\rm +}(t = 0) = A_{\rm T}+ {A_0}=1.5 \hspace{0.05cm}, $$
- $$ s_{\rm +}(t = 25\;{\rm \mu s}) = -A_{\rm T}+ {A_0} = -0.5 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This gives $A_{\rm T} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1}$ and $A_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0.5}$.
(4) At time $t = 15$ μs $(k = 3$, odd$)$ it holds that:
- $$ s_{\rm +}(t = 15\;{\rm µ s}) = - \left[ 1+ 0.5 \cdot \cos (2 \pi \cdot 20\,{\rm kHz} \cdot 0.015\,{\rm ms}) \right] \hspace{0.05cm} = -1- 0.5 \cdot \cos (108^{\circ})\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -0.845} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In contrast, for time $t = 20$ μs $(k = 4$, even$)$:
- $$ s_{\rm +}(t = 20\;{\rm µ s}) = 1 + 0.5 \cdot \cos (144^{\circ})\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.595} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
At all these considered time points, the physical signal $s(t) = {\rm Re}[s_+(t)]$ is exactly as large.