Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.3: Sinusoidal Characteristic"
From LNTwww
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
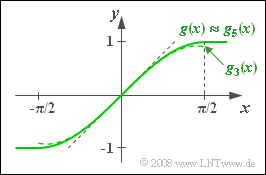
[[File:P_ID894__LZI_A_2_3.png|right|frame|Sinusoidal characteristic curve]] | [[File:P_ID894__LZI_A_2_3.png|right|frame|Sinusoidal characteristic curve]] | ||
| − | We consider a system with input $x(t)$ and output $y(t)$. For simplicity of description, the signals are considered to be dimensionless. | + | We consider a system with input $x(t)$ and output $y(t)$. For simplicity of description, the signals are considered to be dimensionless. |
| − | The relationship between the input signal $x(t)$ and the output signal $y(t)$ is given in the range between $-\pi/2$ and $+\pi/2$ | + | The relationship between the input signal $x(t)$ and the output signal $y(t)$ is given by the following characteristic curve in the range between $-\pi/2$ and $+\pi/2$: |
:$$g(x) = \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - | :$$g(x) = \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
:$$g_5(x) = x- x^3\hspace{-0.1cm}/{6}+x^5\hspace{-0.1cm}/{120}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$g_5(x) = x- x^3\hspace{-0.1cm}/{6}+x^5\hspace{-0.1cm}/{120}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | The input signal $x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 \cdot t)$ is always assumed | + | *The input signal $x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 \cdot t)$ is always assumed. |
| + | *The values $A = 0.5$, $A = 1.0$ and $A = 1.5$ are to be considered for the (dimensionless) signal amplitude. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
''Please note:'' | ''Please note:'' | ||
| − | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion|Nonlinear | + | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion|Nonlinear Distortions]]. |
*The resulting signal curves for $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ are shown graphically on the page [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion#Description_of_nonlinear_systems|Description of nonlinear systems]] . | *The resulting signal curves for $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ are shown graphically on the page [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion#Description_of_nonlinear_systems|Description of nonlinear systems]] . | ||
| − | |||
*All powers required here refer to the resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ and thus have the unit ${\rm V}^2$. | *All powers required here refer to the resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ and thus have the unit ${\rm V}^2$. | ||
*The following trigonometric relations are assumed to be known: | *The following trigonometric relations are assumed to be known: | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
| − | {Which of the following statements are true? Here, $K$ denotes the distortion factor of the sine function $g(x)$. <br>$K_{\rm g3}$ and $K_{\rm g5}$ are based on the approximations $g_3(x)$ and $g_5(x)$, respectively. | + | {Which of the following statements are true? Here, $K$ denotes the distortion factor of the sine function $g(x)$. <br>$K_{\rm g3}$ and $K_{\rm g5}$ are based on the approximations $g_3(x)$ and $g_5(x)$, respectively. |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ $K_{\rm g5}$ generally represents a better approximation for $K$ than $K_{\rm g3}$. | + $K_{\rm g5}$ generally represents a better approximation for $K$ than $K_{\rm g3}$. | ||
| − | - $K_{\rm g3} < K_{\rm g5}$ holds for $A = 1.0$ | + | - $K_{\rm g3} < K_{\rm g5}$ holds for $A = 1.0$. |
| − | + $K_{\rm g3} \approx K_{\rm g5}$ will hold for $A = 0.5$ | + | + $K_{\rm g3} \approx K_{\rm g5}$ will hold for $A = 0.5$. |
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
| − | '''(2)''' The analytical spectrum (positive frequencies only) of the input signal is: | + | '''(2)''' The analytical spectrum (positive frequencies only) of the input signal is: |
:$$X_+(f) = A \cdot {\rm \delta}(f- f_0) .$$ | :$$X_+(f) = A \cdot {\rm \delta}(f- f_0) .$$ | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
:$$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8}, \hspace{0.5cm}A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24}.$$ | :$$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8}, \hspace{0.5cm}A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24}.$$ | ||
| − | *Using $A = 0.5$ the following is obtained: $A_1 \approx 0.484$ and $A_3 \approx 0.005$. Thus, the distortion factor is: | + | *Using $A = 0.5$ the following is obtained: $A_1 \approx 0.484$ and $A_3 \approx 0.005$. Thus, the distortion factor is: |
:$$K = K_3 ={|A_3|}/{A_1}= {0.005}/{0.484} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1.08\%}.$$ | :$$K = K_3 ={|A_3|}/{A_1}= {0.005}/{0.484} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1.08\%}.$$ | ||
:Note that for the approximation $g_3(x)$ only the cubic part $K_3$ of the distortion factor is effective. | :Note that for the approximation $g_3(x)$ only the cubic part $K_3$ of the distortion factor is effective. | ||
| − | *For $A = 1.0$ and $A = 1.5$ the following numerical values | + | *For $A = 1.0$ and $A = 1.5$ the following numerical values: |
:$$A = 1.0: A_1 \approx 0.875, \hspace{0.2cm} A_3 \approx | :$$A = 1.0: A_1 \approx 0.875, \hspace{0.2cm} A_3 \approx | ||
-0.041\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{K \approx 4.76\%}\; \; \Rightarrow \; \; K_{g3},$$ | -0.041\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{K \approx 4.76\%}\; \; \Rightarrow \; \; K_{g3},$$ | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
| − | '''(3)''' Similarly as in subtask '''(2)''' | + | '''(3)''' Similarly as in subtask '''(2)''', |
:$$y(t) = A_1 \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) + A_3 \cdot {\rm | :$$y(t) = A_1 \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) + A_3 \cdot {\rm | ||
| − | cos}(3\omega_0 t )+ A_5 \cdot {\rm cos}(5\omega_0 t )$$ | + | cos}(3\omega_0 t )+ A_5 \cdot {\rm cos}(5\omega_0 t )$$ |
| − | :with the following coefficients: | + | :holds with the following coefficients: |
:$$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{192},\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{192},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{384},\hspace{0.3cm} | A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{384},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
A_5 = {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{1920}.$$ | A_5 = {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{1920}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *From this, the following numerical values arise a result with $A=1$ : |
:$$A_1 \approx 1 -0.125 +0.005 = 0.880,\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$A_1 \approx 1 -0.125 +0.005 = 0.880,\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
A_3 \approx -0.042 +0.003 = -0.039,\hspace{0.3cm} | A_3 \approx -0.042 +0.003 = -0.039,\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' <u>Approaches 1 and 3</u> are correct: |
| − | * | + | *The approach $g_5(x)$ is a better approximation for the sine function $g(x)$ than the approximation $g_3(x)$ in the entire domain. |
| − | * | + | *Thus, the value $K_{g5}$ computed in the subtask '''(3)''' is a better approximation for the actual distortion factor than $K_{g3}$. <br>Therefore, the first statement is correct. |
| − | * | + | *The second statement is false as already shown by the computation for $A=1$ : $K_{g3} \approx 4.76 \%$ is greater than $K_{g5} \approx 4.45 \%$. |
| − | * | + | *The reason for this is that $g_3(x)$ is below $g_5(x)$ and thus there is also a greater deviation from the linear curve. |
| − | * | + | *For $A=0.5$ , $K_{g5} \approx K_{g3} = 1.08 \%$ will hold. |
| − | * | + | *The characteristic curve on the information page shows that for $|x| \le 0.5$ the functions $g_3(x)$ and $g_5(x)$ are indistinguishable within the accuracy of drawing. |
| − | * | + | *This also results in (nearly) the same distortion factors. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^2.2 | + | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^2.2 Nonlinear Distortions^]] |
Latest revision as of 15:12, 29 September 2021
We consider a system with input $x(t)$ and output $y(t)$. For simplicity of description, the signals are considered to be dimensionless.
The relationship between the input signal $x(t)$ and the output signal $y(t)$ is given by the following characteristic curve in the range between $-\pi/2$ and $+\pi/2$:
- $$g(x) = \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$
The second part of this equation describes the series expansion of the sine function.
As approximations for the nonlinear characteristic curve the following is used in this task:
- $$g_1(x) = x\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ g_3(x) = x- x^{3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/6\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$g_5(x) = x- x^3\hspace{-0.1cm}/{6}+x^5\hspace{-0.1cm}/{120}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The input signal $x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 \cdot t)$ is always assumed.
- The values $A = 0.5$, $A = 1.0$ and $A = 1.5$ are to be considered for the (dimensionless) signal amplitude.
Please note:
- The task belongs to the chapter Nonlinear Distortions.
- The resulting signal curves for $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ are shown graphically on the page Description of nonlinear systems .
- All powers required here refer to the resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ and thus have the unit ${\rm V}^2$.
- The following trigonometric relations are assumed to be known:
- $$\cos^3(\alpha) = {3}/{4} \cdot \cos(\alpha) + {1}/{4} \cdot \cos(3\alpha) \hspace{0.05cm}, $$
- $$ \cos^5(\alpha) = {10}/{16} \cdot \cos(\alpha) + {5}/{16} \cdot \cos(3\alpha) + {1}/{16} \cdot \cos(5\alpha)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
(1) The very inaccurate approximation $g_1(x) = x$ is linear in $x$ and therefore does not result in nonlinear distortions. Hence, the distortion factor is $\underline{K = 0}$.
(2) The analytical spectrum (positive frequencies only) of the input signal is:
- $$X_+(f) = A \cdot {\rm \delta}(f- f_0) .$$
- Then, the following signal is applied to the output of the nonlinear characteristic curve $g_3(x)$ :
- $$y(t) = A \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) - \frac{A^3}{6} \cdot {\rm cos}^3(\omega_0 t )= A \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) - \frac{3}{4} \cdot \frac{A^3}{6} \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t )- \frac{1}{4} \cdot \frac{A^3}{6} \cdot {\rm cos}(3\omega_0 t ) = A_1 \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) + A_3 \cdot {\rm cos}(3\omega_0 t ).$$
- For the coefficients $A_1$ and $A_3$ the following is obtained by comparison of coefficients:
- $$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8}, \hspace{0.5cm}A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24}.$$
- Using $A = 0.5$ the following is obtained: $A_1 \approx 0.484$ and $A_3 \approx 0.005$. Thus, the distortion factor is:
- $$K = K_3 ={|A_3|}/{A_1}= {0.005}/{0.484} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1.08\%}.$$
- Note that for the approximation $g_3(x)$ only the cubic part $K_3$ of the distortion factor is effective.
- For $A = 1.0$ and $A = 1.5$ the following numerical values:
- $$A = 1.0: A_1 \approx 0.875, \hspace{0.2cm} A_3 \approx -0.041\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{K \approx 4.76\%}\; \; \Rightarrow \; \; K_{g3},$$
- $$A = 1.5: A_1 \approx 1.078, \hspace{0.2cm} A_3 \approx -0.140\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}{K \approx 13 \%}.$$
(3) Similarly as in subtask (2),
- $$y(t) = A_1 \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) + A_3 \cdot {\rm cos}(3\omega_0 t )+ A_5 \cdot {\rm cos}(5\omega_0 t )$$
- holds with the following coefficients:
- $$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{192},\hspace{0.3cm} A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{384},\hspace{0.3cm} A_5 = {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{1920}.$$
- From this, the following numerical values arise a result with $A=1$ :
- $$A_1 \approx 1 -0.125 +0.005 = 0.880,\hspace{0.3cm} A_3 \approx -0.042 +0.003 = -0.039,\hspace{0.3cm} A_5 \approx 0.0005$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}K_3 = {|A_3|}/{A_1}= 0.0443,\hspace{0.3cm}K_5 = {|A_5|}/{A_1}= 0.0006 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} K = \sqrt{K_3^2 + K_5^2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 4.45\%} \; \; \Rightarrow \; \; K_{g5}.$$
(4) Approaches 1 and 3 are correct:
- The approach $g_5(x)$ is a better approximation for the sine function $g(x)$ than the approximation $g_3(x)$ in the entire domain.
- Thus, the value $K_{g5}$ computed in the subtask (3) is a better approximation for the actual distortion factor than $K_{g3}$.
Therefore, the first statement is correct. - The second statement is false as already shown by the computation for $A=1$ : $K_{g3} \approx 4.76 \%$ is greater than $K_{g5} \approx 4.45 \%$.
- The reason for this is that $g_3(x)$ is below $g_5(x)$ and thus there is also a greater deviation from the linear curve.
- For $A=0.5$ , $K_{g5} \approx K_{g3} = 1.08 \%$ will hold.
- The characteristic curve on the information page shows that for $|x| \le 0.5$ the functions $g_3(x)$ and $g_5(x)$ are indistinguishable within the accuracy of drawing.
- This also results in (nearly) the same distortion factors.