Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.3Z: About the LZ77 Coding"
m (Javier moved page Exercise 2.3Z: To the LZ77 Coding to Exercise 2.3Z: About the LZ77 Coding) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
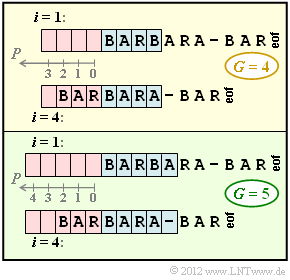
| − | [[File:P_ID2436__Inf_Z_2_3.png|right|frame|Sliding–Window | + | [[File:P_ID2436__Inf_Z_2_3.png|right|frame|Sliding–Window with $G = 4$ and $G = 5$<br>(valid for "LZ77")]] |
| − | In | + | In [[Aufgaben:2.3_Zur_LZ78-Komprimierung|task 2.3]] , you were supposed to compress <b>BARBARA–BAR</b> (string of length $11$, four different characters) using the LZ78 algorithm. |
| − | In | + | In this task we use the same text to demonstrate LZ77 compression. To note: |
| − | * | + | * While the successor "LZ78" successively builds a global dictionary, "LZ77" uses a local dictionary. |
| − | * | + | * The LZ77 method works with a <i>Sliding Window</i> that is gradually shifted over the input text. |
| − | * | + | * This "sliding window" is divided into the ''preview buffer'' (highlighted in blue in the graphic) and the ''search buffer'' (highlighted in red). Both buffers have a size of $G$ memory locations each. |
| − | * | + | * Each coding step $i$ is characterised by a number triple $(P,\ L,\ Z)$ . Here, $P$ and $L$ are integers and $Z$ is a character. The binary representations of $P$, $L$ and $Z$. |
| − | * | + | * After transmission, the <i>Sliding Window</i> is shifted one or more positions to the right and the next coding step $i + 1$ begins. |
| − | + | The upper diagram shows the initial allocation with the buffer size $G = 4$ at the times $i = 1$ as well as $i = 4$. | |
| − | * | + | *At time $i = 1$ , the search buffer is empty, so the coder output is $(0, 0,$ <b>B</b>$)$ . |
| − | * | + | *After the shift by one position, the search buffer contains a <b>B</b>, but no string that begins with <b>A</b> . The second number triple is therefore $(0, 0,$ <b>A</b>$)$. |
| − | * | + | *The output for $i = 3$ is $(0, 0,$ <b>R</b>$)$, since there is no string beginning with <b>R</b> in the search buffer even now. |
| − | + | The snapshot at time $i = 4$ is also shown in the graphic. The search is now for the character string in the search buffer that best matches the preview text <b>BARA</b> . A number triple $(P,\ L,\ Z)$, is transmitted again, but now with the following meaning: | |
| − | * $P$ | + | * $P$ indicates the position in the (red) search buffer where the match starts. The $P$& values of the individual memory locations can be seen in the graphic. |
| − | * $L$ | + | * $L$ denotes the number of characters in the search buffer that, starting at $P$ , match the current string in the preview buffer. |
| − | * $Z$ | + | * Finally $Z$ denotes the first character in the preview buffer that differs from the matching string found in the search buffer. |
| − | + | The larger the LZ77 parameter $G$ , the easier it is to find the longest possible match. In subtask '''(4)''' you will notice that the LZ77 encoding with $G = 5$ gives a better result than the one with $G = 4$. | |
| − | * | + | * However, because of the later binary representation of $P$, , one will always choose $G$ as a power of two, so that $G$ can be represented with $\log_2 \ P$ bits $(G = 8$ ⇒ three-digit binary number $P)$. |
| − | * | + | *This means that a <i>Sliding Window</i> with $G = 5$ has rather little practical relevance. |
| − | + | ''Hints:'' | |
| − | '' | + | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch|Compression according to Lempel, Ziv and Welch]]. |
| − | * | + | *In particular, reference is made to the page [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch#LZ77_-_the_basic_form_of_the_Lempel-Ziv_algorithms|LZ77 – the basic form of the Lempel-Ziv algorithms]] . |
| − | * | + | *The original literature [LZ77] on this method is: <br>Ziv, J.; Lempel, A.: ''A Universal Algorithm for Sequential Data Compression.'' In: IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, no. 3, vol. 23, 1977, p. 337–343. |
| − | * | ||
| − | * | + | * [[Aufgaben:2.3_Zur_LZ78-Komprimierung|Task 2.3]] and [[Aufgaben:Aufgabe_2.4:_Zum_LZW-Algorithmus|task 2.4]] deal with other Lempel–Ziv methods in a similar way. |
| + | |||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the LZ77 output with $G = 4$ at step $i = 4$? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- $(0, 0,$ <b>B</b>$)$, | - $(0, 0,$ <b>B</b>$)$, | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statement is true for the same buffer size $G = 4$ at step $i = 5$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The search buffer contains <b>BARA</b>. |
| − | + | + | + The preview buffer says <b>–BAR</b>. |
| − | - | + | - The output is $(0, 0,$ <b>A</b>$)$. |
| − | { | + | {After which step $i_{\rm Ende}$ is the coding with $G = 4$ finished? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$i_{\rm Ende} \ = \ $ { 9 } | $i_{\rm Ende} \ = \ $ { 9 } | ||
| − | { | + | {Now let $G = 5$. After which step $i_{\rm Ende}$ is the coding finished? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$i_{\rm Ende} \ = \ $ { 6 } | $i_{\rm Ende} \ = \ $ { 6 } | ||
| − | { | + | {What advantages does LZ78 have over LZ77 for "very large" files? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + One finds more often already stored phrases in the dictionary. |
| − | - | + | - Fewer bits have to be transferred per coding step. |
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
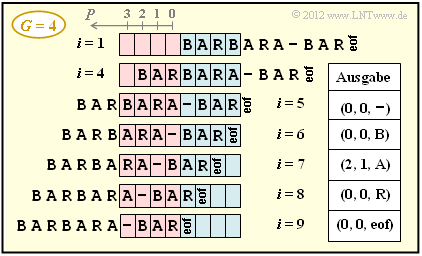
[[File:P_ID2438__Inf_Z_2_3c.png|right|frame|Beispiel zum LZ77–Algorithmus mit $G = 4$]] | [[File:P_ID2438__Inf_Z_2_3c.png|right|frame|Beispiel zum LZ77–Algorithmus mit $G = 4$]] | ||
Revision as of 16:06, 9 July 2021
In task 2.3 , you were supposed to compress BARBARA–BAR (string of length $11$, four different characters) using the LZ78 algorithm.
In this task we use the same text to demonstrate LZ77 compression. To note:
- While the successor "LZ78" successively builds a global dictionary, "LZ77" uses a local dictionary.
- The LZ77 method works with a Sliding Window that is gradually shifted over the input text.
- This "sliding window" is divided into the preview buffer (highlighted in blue in the graphic) and the search buffer (highlighted in red). Both buffers have a size of $G$ memory locations each.
- Each coding step $i$ is characterised by a number triple $(P,\ L,\ Z)$ . Here, $P$ and $L$ are integers and $Z$ is a character. The binary representations of $P$, $L$ and $Z$.
- After transmission, the Sliding Window is shifted one or more positions to the right and the next coding step $i + 1$ begins.
The upper diagram shows the initial allocation with the buffer size $G = 4$ at the times $i = 1$ as well as $i = 4$.
- At time $i = 1$ , the search buffer is empty, so the coder output is $(0, 0,$ B$)$ .
- After the shift by one position, the search buffer contains a B, but no string that begins with A . The second number triple is therefore $(0, 0,$ A$)$.
- The output for $i = 3$ is $(0, 0,$ R$)$, since there is no string beginning with R in the search buffer even now.
The snapshot at time $i = 4$ is also shown in the graphic. The search is now for the character string in the search buffer that best matches the preview text BARA . A number triple $(P,\ L,\ Z)$, is transmitted again, but now with the following meaning:
- $P$ indicates the position in the (red) search buffer where the match starts. The $P$& values of the individual memory locations can be seen in the graphic.
- $L$ denotes the number of characters in the search buffer that, starting at $P$ , match the current string in the preview buffer.
- Finally $Z$ denotes the first character in the preview buffer that differs from the matching string found in the search buffer.
The larger the LZ77 parameter $G$ , the easier it is to find the longest possible match. In subtask (4) you will notice that the LZ77 encoding with $G = 5$ gives a better result than the one with $G = 4$.
- However, because of the later binary representation of $P$, , one will always choose $G$ as a power of two, so that $G$ can be represented with $\log_2 \ P$ bits $(G = 8$ ⇒ three-digit binary number $P)$.
- This means that a Sliding Window with $G = 5$ has rather little practical relevance.
Hints:
- The task belongs to the chapter Compression according to Lempel, Ziv and Welch.
- In particular, reference is made to the page LZ77 – the basic form of the Lempel-Ziv algorithms .
- The original literature [LZ77] on this method is:
Ziv, J.; Lempel, A.: A Universal Algorithm for Sequential Data Compression. In: IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, no. 3, vol. 23, 1977, p. 337–343.
Questions
Solution
(1) Richtig ist der Lösungsvorschlag 3.
- Im Vorschaupuffer steht zum betrachteten Zeitpunkt $i = 4$ die Zeichenfolge BARA.
- Im Suchpuffer steht in den letzten drei Stellen BAR:
- $$P = 2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}L = 3\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}Z = \boldsymbol{\rm A}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Richtig sind die beiden ersten Lösungsvorschläge:
- Der Bindestrich findet sich zum Zeitpunkt $i = 5$ nicht im Suchpuffer.
- Ausgegeben wird $(0, 0,$ –$)$.
(3) Die obere Grafik zeigt das Sliding–Window und die Coderausgabe zu den Zeiten $i>5$.
- Nach $i = 9$ Codierschritten ist der Codiervorgang unter Berücksichtigung von eof beendet ⇒ $\underline{i_{\rm Ende} = 9}$.
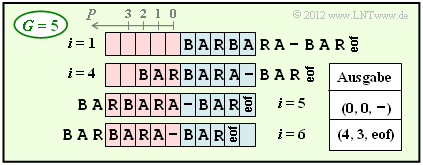
(4) Bei größerer Puffergröße $(G = 5$ anstelle von $G = 4)$ ist die Codierung schon nach dem 6. Codierschritt abgeschlossen ⇒ $\underline{i_{\rm Ende} = 6}$.
- Ein Vergleich der beiden Grafiken zeigt, dass sich für $G = 5$ gegenüber $G = 4$ bis einschließlich $i = 5$ nichts ändert.
- Aufgrund des größeren Puffers lässt sich aber nun BAR gemeinsam mit eof (end-of-file) in einem einzigen Schritt codieren, während mit $G = 4$ hierfür vier Schritte notwendig waren.
(5) Richtig ist nur die Aussage 1.
- Ein Nachteil von LZ77 ist das lokale Wörterbuch. Eigentlich schon bekannte Phrasen können nicht für die Datenkomprimierung verwendet werden, wenn sie mehr als $G$ Zeichen vorher im Text aufgetreten sind. Dagegen sind bei LZ78 alle Phrasen im globalen Wörterbuch abgelegt.
- Richtig ist zwar, dass bei LZ78 nur Pärchen $(I, \ Z)$ übertragen werden müssen, während bei LZ77 jeder Codierschritt durch ein Triple $(P, \ L, \ Z)$ gekennzeichnet ist. Das bedeutet aber noch nicht, dass pro Codierschritt auch weniger Bit übertragen werden müssen.
- Betrachten wir beispielhaft die Puffergröße $G = 8$. Bei LZ77 muss man dann $P$ mit drei Bit und $L$ mit vier Bit dargestellen. Beachten Sie bitte, dass die gefundene Übereinstimmung zwischen Vorschaupuffer und Suchpuffer auch im Vorschaupuffer enden darf.
- Das neue Zeichen $Z$ benötigt bei LZ78 genau die gleiche Bitanzahl wie bei LZ77 (nämlich zwei Bit), wenn man wie hier vom Symbolumfang $M = 4$ ausgeht.
- Die Aussage 2 wäre nur dann richtig, wenn $N_{\rm I}$ kleiner wäre als $N_{\rm P}+ N_{\rm L}$, beispielsweise $N_{\rm I} = 6$. Das würde aber bedeuten, dass man die Wörterbuchgröße auf $I = 2^6 = 64$ begrenzen müsste. Dies reicht für große Dateien nicht aus.
- Unsere Überschlagsrechnung basiert allerdings auf einer einheitlichen Bitanzahl für den Index $I$. Mit variabler Bitanzahl für den Index kann man etliche Bit einsparen, indem man $I$ nur mit so vielen Bit überträgt, wie es für den Codierschritt $i$ erforderlich ist.
- Prinzipiell ändert das aber nichts an der Beschränkung der Wörterbuchgröße, was bei großen Dateien stets zu Problemen führen wird.