Exercise 3.5Z: GSM Network Components
For the mobile phone standard Global System for Mobile Communications - abbreviated GSM - the network infrastructure includes the following subsystems:
- Base Station Subsystem ('BSS),
- Switching & Management Subsystem (SMSS),
- Operation & Maintenance Subsystem ('OMSS).
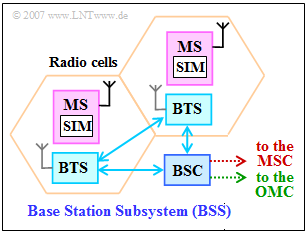
The Base Station Subsystem is mainly responsible for the GSM radio network (see diagram), while the Switching & Management Subsystem represents the switching network and the Operation & Maintenance Subsystem is responsible for operation and maintenance.
The following terms will continue to be used in the questions on these tasks:
- Authentication Center (AUC)
- Base Station Controller (BSC),
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS),
- Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC),
- Home Location Register (HLR),
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC),
- Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC),
- Visitor Location Register ('VLR’).
Notes:
- This task belongs to the chapter Charakteristika von GSM.
Fragebogen
Sample Solution
(1) Jede Mobilstation (MS) steht mit einer Base Transceiver Station (BTS) in Funkverbindung. Diese ist Teil des Base Station Subsystems (BSS) ⇒ Lösungsvorschlag 1.
(2) Richtig sind die Aussagen 1 und 3. Dagegen ist die Base Transceiver Station nicht für Vermittlungsaufgaben zuständig, sondern dies ist die Aufgabe eines Mobile Switching Centers (MSC), das einen Teil des Switching and Management Subsystems (SMSS) darstellt.
(3) Wenn wie meist bei GSM die einzelnen Antennen $120^\circ$–Sektoren abdecken, so kann eine BTS bis zu drei Verbindungswege bereitstellen ⇒ $N_{\rm max} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 3}$.
(4) Nur das Operation and Management Center (OMC) gehört zum OMSS ⇒ Vorschlag 3 .
- Dagegen sind MSC und GMSC Komponenten des Mobilvermittlungsnetzes (SMSS).
- Bezüglich des OMC unterscheidet man schließlich noch zwischen OMC–B (zur BSS–Überwachung) und OMC–S (zur SMSS–Überwachung).
(5) Lösungsvorschläge 1, 3 und 4:
- Das Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC) ist eine Hardware-Einheit, die für die Vermittlung zwischen dem Festnetz und dem Mobilnetz zuständig ist.
- Die drei anderen angegebenen Begriffe beschreiben tatsächlich Datenbanken des Switching & Management Subsystem (SMSS).
- Das Authentication Center (AUC) ist für die Speicherung von vertraulichen Daten und Schlüsseln verantwortlich.
- Das Home Location Register (HLR) ist ein Zentralregister für das gesamte Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) zur Verwaltung unverschlüsselter Telnehmerdaten, der abonnierten Dienste und zur Wegesuche für Rufe der eigenen Teilnehmer eines Mobilfunkbetreibers.
- Dagegen sind im Besucherregister (VLR) die Informationen über die momentanen Besucher anderer Betreiber abgelegt, die sich im aktuellen PLMN befinden.