Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.7: Comparison of Two Convolutional Encoders"
From LNTwww
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Code_Description_with_State_and_Trellis_Diagram}} |
| − | [[File:P_ID2672__KC_A_3_7.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2672__KC_A_3_7.png|right|frame|Two convolutional encoders with parameters $n = 2, \ k = 1, \ m = 2$]] |
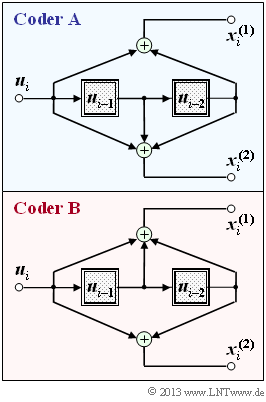
| − | + | The graph shows two rate $1/2$ convolutional encoders, each with memory $m = 2$: | |
| − | * | + | * The coder $\rm A$ has the transfer function matrix $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1 + D^2, \ 1 + D + D^2)$. |
| − | * | + | * In the coder $\rm B$ the two filters (top and bottom) are interchanged, and it holds : $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1 + D + D^2, \ 1 + D^2)$. |
| − | + | The lower encoder $\rm B$ has already been treated in detail in the theory part. | |
| − | In | + | In the present exercise, you are to first determine the state transition diagram for coder $\rm A$ and then work out the differences and the similarities between the two state diagrams. |
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Code_Description_with_State_and_Trellis_Diagram| "Code description with state– and trellis diagram"]]. |
| − | * | + | *Reference is made in particular to the sections. |
| − | ** [[Channel_Coding/ | + | ** [[Channel_Coding/Code_Description_with_State_and_Trellis_Diagram#State_definition_for_a_memory_register|"State definition for a memory register"]] and. |
| − | ** [[Channel_Coding/ | + | ** [[Channel_Coding/Code_Description_with_State_and_Trellis_Diagram#Representation_in_the_state_transition_diagram|"Representation in the state transition diagram"]]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | { $\underline{u} = (0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})$ holds. Which sequences does Coder $\rm A$ generate? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ $\underline{x}^{(1)} = (0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1, \, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})$, | + $\underline{x}^{(1)} = (0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1, \, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})$, | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
+ $\underline{x}^{(2)} = (0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})$. | + $\underline{x}^{(2)} = (0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})$. | ||
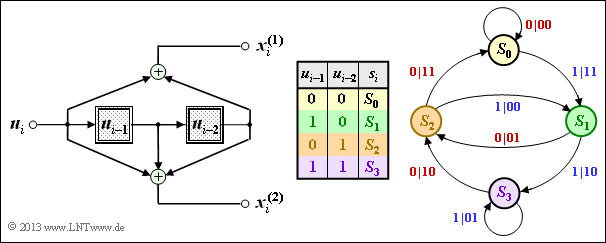
| − | { | + | {Which of the above state transitions exist in encoder $\rm A$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ $s_i = S_0, \ u_i = 0 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_0; \hspace{1cm} s_i = S_0, \ u_i = 1 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_1$. | + $s_i = S_0, \ u_i = 0 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_0; \hspace{1cm} s_i = S_0, \ u_i = 1 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_1$. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
+ $s_i = S_3, \ u_i = 0 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_2; \hspace{1cm} s_i = S_3, \ u_i = 1 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_3$. | + $s_i = S_3, \ u_i = 0 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_2; \hspace{1cm} s_i = S_3, \ u_i = 1 \ ⇒ \ s_{i+1} = S_3$. | ||
| − | { | + | {How do the two state transition diagrams differ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - Other state transitions are possible. |
| − | - | + | - All eight transitions have different code sequences. |
| − | + | + | + Differences exist only for the code sequences $(01)$ and $(10)$. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2673__KC_A_3_7a_neu.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2673__KC_A_3_7a_neu.png|right|frame|Calculation of the code sequence]] |
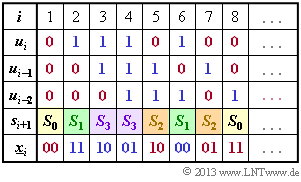
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The calculation is based on the equations. |
:$$x_i^{(1)} = u_i + u_{i–2},$$ | :$$x_i^{(1)} = u_i + u_{i–2},$$ | ||
:$$x_i^{(2)} = u_i + u_{i–1} + u_{i–2}.$$ | :$$x_i^{(2)} = u_i + u_{i–1} + u_{i–2}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Initially, the two memories ($u_{i–1}$ and $u_{i–2}$) are preallocated with zeros ⇒ $s_1 = S_0$. |
| − | * | + | *With $u_1 = 0$, we get $\underline{x}_1 = (00)$ and $s_2 = S_0$. |
| − | * | + | *With $u_2 = 1$ one obtains the output $\underline{x}_2 = (11)$ and the new state $s_3 = S_3$. |
| − | + | From the adjacent calculation scheme one recognizes the correctness of the <u>proposed solutions 1 and 4</u>. | |
| − | + | [[File:P_ID2674__KC_A_3_7b.png|right|frame|State transition diagram of encoder $\rm A$]] | |
| − | [[File:P_ID2674__KC_A_3_7b.png|right|frame| | + | '''(2)''' <u>All proposed solutions</u> are correct: |
| − | '''(2)''' <u> | + | *This can be seen by evaluating the table at '''(1)'''. |
| − | * | + | *The results are shown in the adjacent graph. |
| − | * | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2675__KC_A_3_7c.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2675__KC_A_3_7c.png|right|frame|State transition diagram of encoder $\rm B$]] |
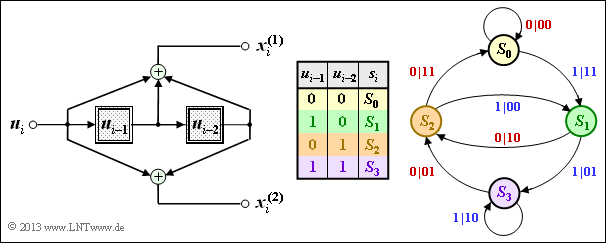
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' Correct is only <u>statement 3</u>: |
| − | * | + | *The state transition diagram of Coder $\rm B$ is sketched on the right. For derivation and interpretation, see section [[Channel_Coding/Code_Description_with_State_and_Trellis_Diagram#Representation_in_the_state_transition_diagram|"Representation in the state transition diagram"]]. |
| − | * | + | *If we swap the two output bits $x_i^{(1)}$ and $x_i^{(2)}$, we get from the convolutional encoder $\rm A$ to the convolutional encoder $\rm B$ (and vice versa). |
Revision as of 16:00, 3 October 2022
The graph shows two rate $1/2$ convolutional encoders, each with memory $m = 2$:
- The coder $\rm A$ has the transfer function matrix $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1 + D^2, \ 1 + D + D^2)$.
- In the coder $\rm B$ the two filters (top and bottom) are interchanged, and it holds : $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1 + D + D^2, \ 1 + D^2)$.
The lower encoder $\rm B$ has already been treated in detail in the theory part.
In the present exercise, you are to first determine the state transition diagram for coder $\rm A$ and then work out the differences and the similarities between the two state diagrams.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Code description with state– and trellis diagram".
- Reference is made in particular to the sections.
Questions
Solution
(1) The calculation is based on the equations.
- $$x_i^{(1)} = u_i + u_{i–2},$$
- $$x_i^{(2)} = u_i + u_{i–1} + u_{i–2}.$$
- Initially, the two memories ($u_{i–1}$ and $u_{i–2}$) are preallocated with zeros ⇒ $s_1 = S_0$.
- With $u_1 = 0$, we get $\underline{x}_1 = (00)$ and $s_2 = S_0$.
- With $u_2 = 1$ one obtains the output $\underline{x}_2 = (11)$ and the new state $s_3 = S_3$.
From the adjacent calculation scheme one recognizes the correctness of the proposed solutions 1 and 4.
(2) All proposed solutions are correct:
- This can be seen by evaluating the table at (1).
- The results are shown in the adjacent graph.
(3) Correct is only statement 3:
- The state transition diagram of Coder $\rm B$ is sketched on the right. For derivation and interpretation, see section "Representation in the state transition diagram".
- If we swap the two output bits $x_i^{(1)}$ and $x_i^{(2)}$, we get from the convolutional encoder $\rm A$ to the convolutional encoder $\rm B$ (and vice versa).