Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.08Z: Basics about Interleaving"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*But other $\rm LNTwww$ books also discuss interleaving, including the book "Examples of Communication Systems" with reference to the | *But other $\rm LNTwww$ books also discuss interleaving, including the book "Examples of Communication Systems" with reference to the | ||
:* standard digital subscriber line</i> $\rm (DSL)$ ⇒ [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Methods_to_Reduce_the_Bit_Error_Rate_in_DSL#Interleaving_und_De.E2.80.93Interleaving| "Interleaving and Deinterleaving"]], | :* standard digital subscriber line</i> $\rm (DSL)$ ⇒ [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Methods_to_Reduce_the_Bit_Error_Rate_in_DSL#Interleaving_und_De.E2.80.93Interleaving| "Interleaving and Deinterleaving"]], | ||
| − | :* 2G mobile communication system $\rm GSM$ ⇒ [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Entire_GSM_Transmission_System#Komponenten_der_Sprach.E2.80.93_und_Daten.C3.BCbertragung| "Components of voice | + | :* 2G mobile communication system $\rm GSM$ ⇒ [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Entire_GSM_Transmission_System#Komponenten_der_Sprach.E2.80.93_und_Daten.C3.BCbertragung| "Components of voice and data transmission"]], |
:* 3G mobile communication system $\rm UMTS$ ⇒ [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Telecommunications_Aspects_of_UMTS#Kanalcodierung_bei_UMTS| "Channel Coding"]], | :* 3G mobile communication system $\rm UMTS$ ⇒ [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Telecommunications_Aspects_of_UMTS#Kanalcodierung_bei_UMTS| "Channel Coding"]], | ||
:* 4G mobile communication system $\rm LTE$ ⇒ [[Mobile_Communications/The_Application_of_OFDMA_and_SC-FDMA_in_LTE#Functionality_of_SC-FDMA| "Functionality of SC-FDMA"]] $($in the boo "Mobile Communications"$)$. | :* 4G mobile communication system $\rm LTE$ ⇒ [[Mobile_Communications/The_Application_of_OFDMA_and_SC-FDMA_in_LTE#Functionality_of_SC-FDMA| "Functionality of SC-FDMA"]] $($in the boo "Mobile Communications"$)$. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
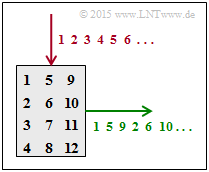
| − | [[File:P_ID3041__KC_Z_4_8b_v2.png|right|frame|4×3 | + | [[File:P_ID3041__KC_Z_4_8b_v2.png|right|frame|$4×3$ interleaver matrix]] |
| − | '''(1)''' From the regular structure of the function $I_{\rm Out}(I_{\rm In})$ one can see that it is a block interleaver ⇒ <u>Response 1</u>. | + | '''(1)''' From the regular structure of the function $I_{\rm Out}(I_{\rm In})$ one can see that it is a block interleaver ⇒ <u>Response 1</u>. |
| − | '''(2)''' The index "1" is output as the first character. Further applies: | + | '''(2)''' The index "1" is output as the first character. Further applies: |
| − | * The index 5 is output as the second character ⇒ $\underline{ | + | * The index 5 is output as the second character ⇒ $\underline{N_{\rm R} = 4}$. |
| − | |||
| + | * The index 2 is output as the fourth character ⇒ $\underline{N_{\rm C} = 3}$. | ||
| − | The upper graph shows for the 4×3 interleaver matrix: | + | |
| − | * the column by column write (red), | + | The upper graph shows for the $4×3$ interleaver matrix: |
| − | * the row by row readout (green). | + | * the column-by-column write $($red$)$, |
| + | |||
| + | * the row-by-row readout $($green$)$. | ||
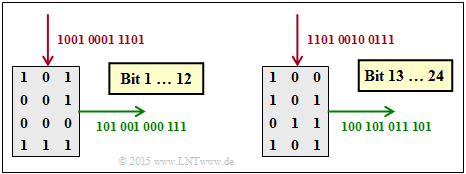
[[File:P_ID3042__KC_Z_4_8c_v3.png|right|frame|Interleaving]] | [[File:P_ID3042__KC_Z_4_8c_v3.png|right|frame|Interleaving]] | ||
| − | '''(3)''' Correct is <u>the proposed solution 2</u>: | + | '''(3)''' Correct is <u>the proposed solution 2</u>: |
| − | *The matrix is written column by column and read row by row. | + | *The matrix is written column-by-column and read row-by-row. |
| − | *After 12 bits, the matrix is cleared and the procedure starts | + | |
| − | *The graphic shows that | + | *After $12$ bits, the matrix is cleared and the procedure starts again. |
| + | |||
| + | *The graphic shows that the solution suggestion 2 is correct. | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
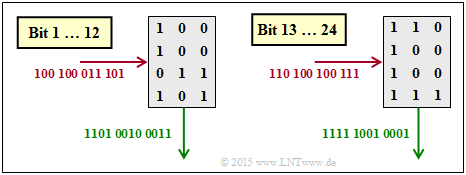
| − | [[File:P_ID3043__KC_Z_4_8d_v1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID3043__KC_Z_4_8d_v1.png|right|frame|De–interleaving]] |
| − | '''(4)''' Correct is <u>the proposed solution 1</u>: | + | '''(4)''' Correct is <u>the proposed solution 1</u>: |
| − | *In | + | *In de-interleaving, the matrix is written row-by-row and read column-by-column. |
| + | |||
*The graphic shows that here the solution suggestion 1 is correct. | *The graphic shows that here the solution suggestion 1 is correct. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:53, 14 December 2022
Interleaving is required, for example, for a channel with burst error characteristics in order to distribute the errors within the burst over a sufficiently large area so that they can subsequently be largely corrected $($or at least detected$)$.
For turbo codes based on so-called RSC encoder $($"Recursive Systematic Convolutional Encoder"$)$ – and only such make sense – interleaving is essential also with the AWGN channel, because then there are also always $($some$)$ input sequences, which deliver only "zeros" in the output sequence after quite a few "ones", and that to infinity ⇒ there are output sequences with very small Hamming weight.
If the bits of such input sequences are distributed over a wide range in the second encoder, the problem can be largely eliminated by the interaction of both component decoders in the case of iterative symbol-wise decoding.
A general distinction is made between
- block interleaver and
- random interleaver.
In block interleaving one fills a matrix with $N_{\rm C}$ columns and $N_{\rm R}$ rows column-by-column and reads the matrix row-by-row. This deterministically scrambles a block of information with $I_{\rm max} = N_{\rm C} \cdot N_{\rm R}$ bits.
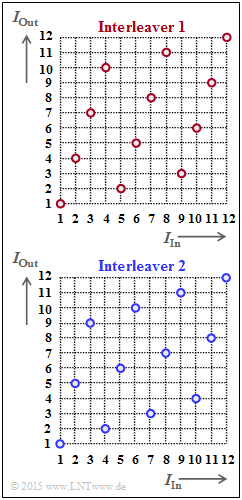
On the right, two interleavers are indicated and in graphical form by the assignment $I_{\rm Out}(I_{\rm In})$. These quantities represent the "output sequence index" and the "input sequence index", respectively. It holds:
- $$1 \le I_{\rm Out} \le I_{\rm max} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$1 \le I_{\rm In} \le I_{\rm max} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
In the subtask (1) it is asked whether this is "block interleaving" or "random interleaving". The latter are discussed in the "theory section" but only very briefly.
Hints:
- The exercise refers to the chapter "Basics of Turbo Codes".
- But other $\rm LNTwww$ books also discuss interleaving, including the book "Examples of Communication Systems" with reference to the
- standard digital subscriber line $\rm (DSL)$ ⇒ "Interleaving and Deinterleaving",
- 2G mobile communication system $\rm GSM$ ⇒ "Components of voice and data transmission",
- 3G mobile communication system $\rm UMTS$ ⇒ "Channel Coding",
- 4G mobile communication system $\rm LTE$ ⇒ "Functionality of SC-FDMA" $($in the boo "Mobile Communications"$)$.
Questions
Solution
(1) From the regular structure of the function $I_{\rm Out}(I_{\rm In})$ one can see that it is a block interleaver ⇒ Response 1.
(2) The index "1" is output as the first character. Further applies:
- The index 5 is output as the second character ⇒ $\underline{N_{\rm R} = 4}$.
- The index 2 is output as the fourth character ⇒ $\underline{N_{\rm C} = 3}$.
The upper graph shows for the $4×3$ interleaver matrix:
- the column-by-column write $($red$)$,
- the row-by-row readout $($green$)$.
(3) Correct is the proposed solution 2:
- The matrix is written column-by-column and read row-by-row.
- After $12$ bits, the matrix is cleared and the procedure starts again.
- The graphic shows that the solution suggestion 2 is correct.
(4) Correct is the proposed solution 1:
- In de-interleaving, the matrix is written row-by-row and read column-by-column.
- The graphic shows that here the solution suggestion 1 is correct.