Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.8: OVSF Codes"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The spreading codes for UMTS should | The spreading codes for UMTS should | ||
*be orthogonal, in order to avoid mutual influence of the participants, | *be orthogonal, in order to avoid mutual influence of the participants, | ||
| − | *at the same time also allow a flexible realization of different spreading factors $J$ | + | *at the same time also allow a flexible realization of different spreading factors $J$. |
| − | An example are the "Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor Codes" $\rm (OVSF)$, which provide the spreading codes of lengths from $J = 4$ to $J = 512$ | + | An example are the "Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor Codes" $\rm (OVSF)$, which provide the spreading codes of lengths from $J = 4$ to $J = 512$. |
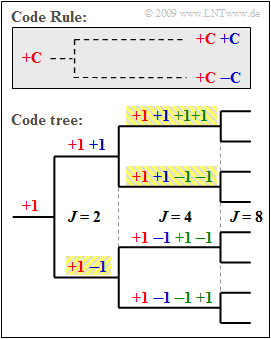
| − | As shown in the graphic, these can be created with the help of a code tree. In doing so, each branching from a code $\mathcal{C}$ results in two new codes $(+\mathcal{C}\ +\mathcal{C})$ and $(+\mathcal{C} \ –\mathcal{C})$. | + | As shown in the graphic, these can be created with the help of a code tree. In doing so, each branching from a code $\mathcal{C}$ results in two new codes $(+\mathcal{C}\ +\mathcal{C})$ and $(+\mathcal{C} \ –\mathcal{C})$. |
The diagram illustrates the principle given here using the following example $J = 4$. If you number the spreading sequences from $0$ to $J -1$, the spreading sequences result | The diagram illustrates the principle given here using the following example $J = 4$. If you number the spreading sequences from $0$ to $J -1$, the spreading sequences result | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
It should be noted that no predecessor or successor of a code may be used by other participants. | It should be noted that no predecessor or successor of a code may be used by other participants. | ||
| − | *In the example, four spreading codes with spreading factor | + | *In the example, four spreading codes with spreading factor $J = 4$ could be used, or |
| − | *the three codes highlighted in yellow – once with | + | *the three codes highlighted in yellow – once with $J = 2$ and twice with $J = 4$. |
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
$K \ = \ $ { 5 } | $K \ = \ $ { 5 } | ||
| − | {The tree structure applies to $J = 32$. Is the following assignment feasible: | + | {The tree structure applies to $J = 32$. Is the following assignment feasible: Twice $J = 4$, once $J = 8$, once $J = 164$ and eight times $J = 32$? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
+ Yes. | + Yes. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
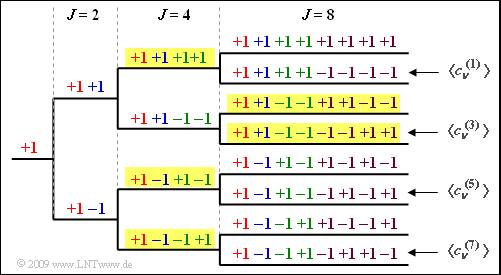
| − | [[File:P_ID2263__Bei_A_4_6a.png|right|frame|OVSF tree structure for | + | [[File:P_ID2263__Bei_A_4_6a.png|right|frame|OVSF tree structure for $J = 8$]] |
'''(1)''' The following graphic shows the OVSF tree structure for $J = $8 users. | '''(1)''' The following graphic shows the OVSF tree structure for $J = $8 users. | ||
Revision as of 11:59, 25 February 2021
The spreading codes for UMTS should
- be orthogonal, in order to avoid mutual influence of the participants,
- at the same time also allow a flexible realization of different spreading factors $J$.
An example are the "Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor Codes" $\rm (OVSF)$, which provide the spreading codes of lengths from $J = 4$ to $J = 512$.
As shown in the graphic, these can be created with the help of a code tree. In doing so, each branching from a code $\mathcal{C}$ results in two new codes $(+\mathcal{C}\ +\mathcal{C})$ and $(+\mathcal{C} \ –\mathcal{C})$.
The diagram illustrates the principle given here using the following example $J = 4$. If you number the spreading sequences from $0$ to $J -1$, the spreading sequences result
- $$\langle c_\nu^{(0)}\rangle = \ {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ \langle c_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\langle c_\nu^{(2)}\rangle = \ {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ \langle c_\nu^{(3)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
According to this nomenclature, there are the spreading sequences $\langle c_\nu^{(0)}\rangle, \text{...} ,\langle c_\nu^{(7)}\rangle$ for the spreading factor $J = 8$.
It should be noted that no predecessor or successor of a code may be used by other participants.
- In the example, four spreading codes with spreading factor $J = 4$ could be used, or
- the three codes highlighted in yellow – once with $J = 2$ and twice with $J = 4$.
Notes:
- This task belongs to the chapter Spreading sequences for CDMA.
- Particular reference is made to the page Codes with variable spreading factor.
Questionnaire
Solution
(1) The following graphic shows the OVSF tree structure for $J = $8 users.
- From this it can be seen that the solutions 1, 3 and 4 apply, but not the second.
(2) If each user is assigned a spreading code with the spreading degree $J = 8$, $K_{\rm max} \ \underline{= 8}$ users can be supplied.
(3) If three users are supplied with $J = 4$, only two users can be served by a spreading sequence with $J = 8$ (see example yellow background in the graphic) $\ \Rightarrow \ \ \underline{K = 5}$.
(4) We denote
- $K_{4} = 2$ as the number of spreading sequences with $J = 4$,
- $K_{8} = 1$ as the number of spreading sequences with $J = 8$,
- $K_{16} = 2$ as the number of spreading sequences with $J = 16$,
- $K_{32} = 8$ as the number of spreading sequences with $J = 32$,
Then the following condition must be fulfilled:
- $$K_4 \cdot \frac{32}{4} + K_8 \cdot \frac{32}{8} +K_{16} \cdot \frac{32}{16} +K_{32} \cdot \frac{32}{32} \le 32\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} K_4 \cdot8 + K_8 \cdot 4 +K_{16} \cdot 2 +K_{32} \cdot1 \le 32 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Because $2 \cdot 8 + 1 \cdot 4 + 2 \cdot 2 + 8 = 32$ the desired assignment is just allowed ⇒ The answer is YES.
- For example, providing the $J = 4$ twice blocks the upper half of the tree, after providing a $J = 8$ spreading code, $3$ of the $8$ branches remain to be occupied at the $J = 8$ level, and so on and so forth.