Difference between revisions of "Information Theory/Different Entropy Measures of Two-Dimensional Random Variables"
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
[[File:P_ID2765__Inf_T_3_2_S3_neu.png|frame|Diagram of all entropies of the „dice experiment” ]] | [[File:P_ID2765__Inf_T_3_2_S3_neu.png|frame|Diagram of all entropies of the „dice experiment” ]] | ||
| − | + | These quantities are compiled in the graph, with the random quantity $R$ marked by the basic colour „red” and the sum $S$ marked by the basic colour „green” . Conditional entropies are shaded. | |
| − | + | One can see from this representation: | |
| − | * | + | *The entropy $H(R) = \log_2 (6) = 2.585\ \rm bit$ is exactly half as large as the compound entropy $H(RS)$. Because: If one knows $R$, $S$ provides exactly the same information as the random quantity $B$, namely $H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R) = H(B) = \log_2 (6) = 2.585\ \rm bit$. ''Note'': $H(R)$ = $H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R)$ only applies in this example, not in general. |
| − | * | + | *As expected, the entropy $H(S) = 3.274 \ \rm bit$ is greater than $H(R)= 2.585\ \rm bit$ in this example. Because of $H(S) + H(R \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} S) = H(R) + H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R)$ , $H(R \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} S)$ must therefore be smaller than $H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R)$ by $I(R;\ S) = 0.689 \ \rm bit$ . $H(R)$ is also smaller than $H(S)$ by $I(R;\ S) = 0.689 \ \rm bit$ . |
| − | + | *The mutual information between the random variables $R$ and $S$ also results from the equation | |
:$$I(R;\ S) = H(R) + H(S) - H(RS) = 2.585\ {\rm bit} + 3.274\ {\rm bit} - 5.170\ {\rm bit} = 0.689\ {\rm bit} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$}} | :$$I(R;\ S) = H(R) + H(S) - H(RS) = 2.585\ {\rm bit} + 3.274\ {\rm bit} - 5.170\ {\rm bit} = 0.689\ {\rm bit} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$}} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Conditional Mutual Information == |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | We now consider three random variables $X$, $Y$ and $Z$, that are (can be) related to each other. | |
| − | |||
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{Definition:}$ | + | $\text{Definition:}$ The '''conditional mutual information''' between the random variables $X$ and $Y$ for a given $Z = z$ is as follows: |
:$$I(X;Y \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) - H(X\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Y ,\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$I(X;Y \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) - H(X\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Y ,\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | One denotes as the conditional '''conditional mutual information''' between the random variables $X$ and $Y$ for the random variable $Z$ in general after averaging over all $z \in Z$: | |
:$$I(X;Y \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) - H(X\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Y Z )= \hspace{-0.3cm} | :$$I(X;Y \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) - H(X\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Y Z )= \hspace{-0.3cm} | ||
| Line 199: | Line 198: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | $P_Z(Z)$ | + | $P_Z(Z)$ is the probability function (PMF) of the random variable $Z$ and $P_Z(z)$ dis the probability for the realisation $Z = z$.}} |
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | $\text{Please note:}$ |
| − | * | + | *For conditional entropy, as is well known, the relation $H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Z) ≤ H(X)$ holds. |
| − | * | + | *For the mutual information, this relation does not necessarily hold: |
| − | *$I(X; Y\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Z)$ | + | *$I(X; Y\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Z)$ can be '''smaller, equal, but also larger than''' als $I(X; Y)$.}} |
[[File:P_ID2824__Inf_T_3_2_S4a.png|right|frame|2D–PMF $P_{XZ}$ ]] | [[File:P_ID2824__Inf_T_3_2_S4a.png|right|frame|2D–PMF $P_{XZ}$ ]] | ||
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | $\text{Example 4:}$ |
| − | + | We consider the binary random variables $X$, $Y$ and $Z$ with the following properties: | |
| − | * $X$ | + | * $X$ and $Y$ be statistically independent. Let the following be true for their probability functions: |
:$$P_X(X) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big], \hspace{0.2cm} P_Y(Y) = \big[1– p, \ p \big] \ ⇒ \ H(X) = 1\ {\rm bit}, \hspace{0.2cm} H(Y) = H_{\rm bin}(p).$$ | :$$P_X(X) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big], \hspace{0.2cm} P_Y(Y) = \big[1– p, \ p \big] \ ⇒ \ H(X) = 1\ {\rm bit}, \hspace{0.2cm} H(Y) = H_{\rm bin}(p).$$ | ||
| − | * $Z$ | + | * $Z$ is the modulo-2 sum of $X$ and $Y$: $Z = X ⊕ Y$. |
| − | + | From the joint probability function $P_{XZ}$ according to the upper graph, it follows: | |
| − | * | + | *Summing the column probabilities gives $P_Z(Z) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big ]$ ⇒ $H(Z) = 1\ {\rm bit}$. |
| − | * $X$ | + | * $X$ and $Z$ are also statistically independent, since for the 2D-PMF $P_{XZ}(X, Z) = P_X(X) · P_Z(Z)$ holds. |
| − | * | + | *It follows that: $H(Z\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} X) = H(Z)$ and $H(X \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z) = H(X)$ sowie $I(X; Z) = 0$. |
| − | [[File:P_ID2826__Inf_T_3_2_S4b.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2826__Inf_T_3_2_S4b.png|right|frame|Conditional 2D–PMF $P_{X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm}YZ}$]] |
| − | <br><br> | + | <br><br>From the conditional probability function $P_{X\vert YZ}$ according to the graph below, we can calculate: |
| − | * $H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ) = 0$, | + | * $H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ) = 0$, since all $P_{X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ}$ entries entweder $0$ or $1$ sind ⇒ ''conditional entropy'', |
| − | * $I(X; YZ) = H(X) - H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ) = H(X)= 1 \ {\rm bit}$ ⇒ '' | + | * $I(X; YZ) = H(X) - H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ) = H(X)= 1 \ {\rm bit}$ ⇒ ''mutual information'', |
| − | * $I(X; Y\vert Z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z) =H(X)=1 \ {\rm bit} $ ⇒ '' | + | * $I(X; Y\vert Z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z) =H(X)=1 \ {\rm bit} $ ⇒ ''conditional mutual information''. |
| − | + | In the present example | |
| − | * | + | *the conditional mutual information $I(X; Y\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z) = 1$ |
| − | * | + | *is greater than the conventional mutual information $I(X; Y) = 0$. }} |
| − | == | + | ==Chain rule of mutual information == |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | So far we have only considered the transinformation between two one-dimensional random variables. Now we extend the definition to a total of $n + 1$ random variables, which, for reasons of representation, we denote with $X_1$, ... , $X_n$ and $Z$ . Then applies: | |
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | $\text{Chain rule of mutual information:}$ |
| − | + | The mutual information between the $n$–dimensional random variable $X_1 X_2 \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} X_n$ and the random variable $Z$ can be represented and calculated as follows: | |
:$$I(X_1\hspace{0.05cm}X_2\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}X_n;Z) = | :$$I(X_1\hspace{0.05cm}X_2\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}X_n;Z) = | ||
| Line 252: | Line 251: | ||
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | $\text{Proof:}$ |
| − | + | We restrict ourselves here to the case $n = 2$, i.e. to a total of three random variables, and replace $X_1$ by $X$ and $X_2$ by $Y$. Then we obtain: | |
:$$\begin{align*}I(X\hspace{0.05cm}Y;Z) & = H(XY) - H(XY\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm}Z) = \\ | :$$\begin{align*}I(X\hspace{0.05cm}Y;Z) & = H(XY) - H(XY\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm}Z) = \\ | ||
| Line 261: | Line 260: | ||
| − | + | From this equation one can see that the size relation $I(X Y; Z) ≥ I(X; Z)$ is always given. | |
| − | * | + | *Equality results for the conditional mutual information $I(Y; Z \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} X) = 0$, |
| − | * | + | * i.e. when the random variables $Y$ and $Z$ for a given $X$ are statistically independent. |
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | $\text{Example 5:}$ We consider the [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Markovketten|Markov chain]] $X → Y → Z$. For such a constellation, the ''Data Processing Theorem'' always holds with the following consequence, which can be derived from the chain rule of mutual information: |
:$$I(X;Z) \hspace{-0.05cm} \le \hspace{-0.05cm}I(X;Y ) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$I(X;Z) \hspace{-0.05cm} \le \hspace{-0.05cm}I(X;Y ) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
:$$I(X;Z) \hspace{-0.05cm} \le \hspace{-0.05cm} I(Y;Z ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$I(X;Z) \hspace{-0.05cm} \le \hspace{-0.05cm} I(Y;Z ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The theorem thus states: | |
| − | * | + | *One cannot gain any additional information about input $X$  by manipulating $($''processing'' $Z)$ data $Y$ . |
| − | * | + | *Data processing $Y → Z$ $($by a second processor$)$ only serves the purpose of making the information about $X$ more visible. |
| − | + | For more information on the ''Data Processing Theorem'' see [[Aufgaben:Aufgabe_3.15:_Data_Processing_Theorem|task 3.15]].}} | |
| − | == | + | ==Relevant tasks== |
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Aufgaben:3.7 Einige Entropieberechnungen|Aufgabe 3.7: Einige Entropieberechnungen]] | [[Aufgaben:3.7 Einige Entropieberechnungen|Aufgabe 3.7: Einige Entropieberechnungen]] | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 4 April 2021
Contents
Definition of entropy using supp(PXY)
We briefly summarise the results of the last chapter again, assuming the two-dimensional random variable $XY$ with the probability function $P_{XY}(X,\ Y)$ . At the same time we use the notation
- $${\rm supp} (P_{XY}) = \big \{ \hspace{0.05cm}(x,\ y) \in XY \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm where} \hspace{0.15cm} P_{XY}(X,\ Y) \ne 0 \hspace{0.05cm} \big \} \hspace{0.05cm};$$
$\text{Summarising the last chapter:}$
With this subset $\text{supp}(P_{XY}) ⊂ P_{XY}$ , the following holds for
- the joint entropy :
- $$H(XY) = {\rm E}\hspace{-0.1cm} \left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{XY}(X, Y)}\right ] =\hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{(x, y) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{XY}\hspace{-0.05cm})} \hspace{-0.6cm} P_{XY}(x, y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{XY}(x, y)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- the entropies of the 1D random variables $X$ and $Y$:
- $$H(X) = {\rm E}\hspace{-0.1cm} \left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{X}(X)}\right ] =\hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{x \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{X})} \hspace{-0.2cm} P_{X}(x) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{X}(x)} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$H(Y) = {\rm E}\hspace{-0.1cm} \left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{Y}(Y)}\right ] =\hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{y \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{Y})} \hspace{-0.2cm} P_{Y}(y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{Y}(y)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\text{Example 1:}$ We refer again to the examples on the joint probability and joint entropy in the last chapter. For the 2D probability function $P_{RB}(R, B)$ in $\text{example 5}$ there with the parameters
- $R$ ⇒ numbers of the red die and
- $B$ ⇒ number of the blue die
the sets $P_{RB}$ and $\text{supp}(P_{RB})$ are identical. Here, all $6^2 = 36$ squares are occupied by non-zero values.
For the 2D probability function $P_{RS}(R, S)$ in $\text{example 6}$ mit den Parametern
- $R$ ⇒ numbers of the red die
- $S = R + B$ ⇒ sum of both dice
there are $6 · 11 = 66$ squares, many of which, however, are empty, i.e. stand for the probability „0” .
- The subset $\text{supp}(P_{RS})$ , on the other hand, contains only the $36$ shaded squares with non-zero probabilities.
- The entropy remains the same no matter whether one averages over all elements of $P_{RS}$ or only over the elements of $\text{supp}(P_{RS})$ since for $x → 0$ the limit is $x · \log_2 ({1}/{x}) = 0$ ist.
Conditional probability and conditional entropy
In the book „Theory of Stochastic Signals” the following conditional probabilities were given for the case of two events $X$ and $Y$ ⇒ Bayes' theorem:
- $${\rm Pr} (X \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} Y) = \frac{{\rm Pr} (X \cap Y)}{{\rm Pr} (Y)} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr} (Y \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} X) = \frac{{\rm Pr} (X \cap Y)}{{\rm Pr} (X)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Applied to probability functions, one thus obtains:
- $$P_{\hspace{0.03cm}X \mid \hspace{0.03cm} Y} (X \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} Y) = \frac{P_{XY}(X, Y)}{P_{Y}(Y)} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} P_{\hspace{0.03cm}Y \mid \hspace{0.03cm} X} (Y \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} X) = \frac{P_{XY}(X, Y)}{P_{X}(X)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Analogous to the joint entropy $H(XY)$ , the following entropy functions can be derived here:
$\text{Definitions:}$
- The conditional entropy of the random variable $X$ under condition $Y$ is:
- $$H(X \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} Y) = {\rm E} \hspace{-0.1cm}\left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{P_{\hspace{0.03cm}X \mid \hspace{0.03cm} Y} (X \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} Y)}\right ] = \hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{(x, y) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{XY}\hspace{-0.08cm})} \hspace{-0.6cm} P_{XY}(x, y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{\hspace{0.03cm}X \mid \hspace{0.03cm} Y} (x \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} y)}=\hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{(x, y) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{XY}\hspace{-0.08cm})} \hspace{-0.6cm} P_{XY}(x, y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{P_{Y}(y)}{P_{XY}(x, y)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Similarly, for the second conditional entropy we obtain:
- $$H(Y \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} X) = {\rm E} \hspace{-0.1cm}\left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{P_{\hspace{0.03cm}Y\hspace{0.03cm} \mid \hspace{0.01cm} X} (Y \hspace{-0.08cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm}X)}\right ] =\hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{(x, y) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{XY}\hspace{-0.08cm})} \hspace{-0.6cm} P_{XY}(x, y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{\hspace{0.03cm}Y\hspace{-0.03cm} \mid \hspace{-0.01cm} X} (y \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} x)}=\hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{(x, y) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{XY}\hspace{-0.08cm})} \hspace{-0.6cm} P_{XY}(x, y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{P_{X}(x)}{P_{XY}(x, y)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In the argument of the logarithm function there is always a conditional probability function ⇒ $P_{X\hspace{0.03cm}| \hspace{0.03cm}Y}(·)$ bzw. $P_{Y\hspace{0.03cm}|\hspace{0.03cm}X}(·)$, while the joint probability ⇒ $P_{XY}(·)$ is needed for the expectation value formation.
For the conditional entropies, there are the following limitations:
- Both $H(X|Y)$ and $H(Y|X)$ are always greater than or equal to zero. From $H(X|Y) = 0$ it follows directly also $H(Y|X) = 0$. Both are only possible for disoint sets $X$ and $Y$ .
- $H(X|Y) ≤ H(X)$ and $H(Y|X) ≤ H(Y)$ always apply. These statements are plausible if one realises that one can also use „uncertainty” synonymously for „entropy” . For: the uncertainty with respect to the quantity $X$ cannot be increased by knowing $Y$ .
- Except in the case of statistical independence ⇒ $H(X|Y) = H(X)$ , $H(X|Y) < H(X)$ always holds. Because of $H(X) ≤ H(XY)$ and $H(Y) ≤ H(XY)$ , $H(X|Y) ≤ H(XY)$ and $H(Y|X) ≤ H(XY)$ therefore also hold. Thus, a conditional entropy can never become larger than the joint entropy.
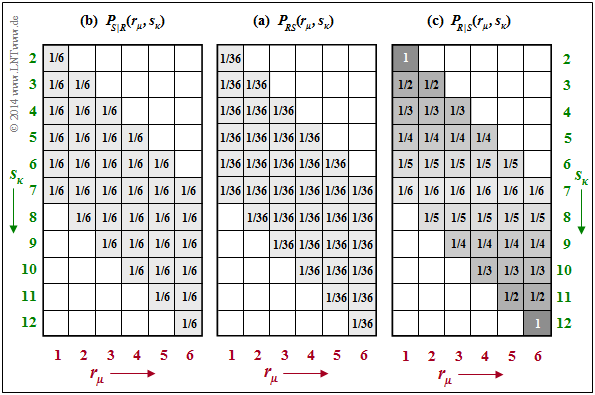
$\text{Example 2:}$ We consider the joint probabilities $P_{RS}(·)$ of our dice experiment, which were determined in the last chapter als $\text{example 6}$ . $P_{RS}(·)$ is given again in the middle of the following graph.
The two conditional probability functions are drawn on the outside:
- Given on the left is the conditional probability function $P_{S \vert R}(⋅) = P_{SR}(⋅)/P_R(⋅)$. Because of $P_R(R) = \big [1/6, \ 1/6, \ 1/6, \ 1/6, \ 1/6, \ 1/6 \big ]$ the same probability value $1/6$ is here in all shaded fields ⇒ $\text{supp}(P_{S\vert R}) = \text{supp}(P_{R\vert S})$ . From this follows for the conditional entropy:
- $$H(S \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.13cm} R) = \hspace{-0.2cm} \sum_{(r, s) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{RS})} \hspace{-0.6cm} P_{RS}(r, s) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{P_{\hspace{0.03cm}S \hspace{0.03cm} \mid \hspace{0.03cm} R} (s \hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} r)} = 36 \cdot \frac{1}{36} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} (6) = 2.585\ {\rm bits} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- On the right, the conditional probability function $P_{R\vert S}(⋅) = P_{RS}(⋅)/P_S(⋅)$ is given with $P_S(⋅)$ according to $\text{example 6}$ . The same non-zero fields result ⇒ $\text{supp}(P_{R\vert S}) = \text{supp}(P_{S\vert R})$. However, the probability values now increase continuously from the centre $(1/6)$ towards the edges up to probability $1$ in the corners. It follows that:
- $$H(R \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.13cm} S) = \frac{1}{36} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} (6) + \frac{2}{36} \cdot \sum_{i=1}^5 \big [ i \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} (i) \big ]= 1.896\ {\rm bit} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
On the other hand, for the conditional probabilities of the 2D random variable $RB$ according to $\text{example 5}$ , one obtains because of $P_{RB}(⋅) = P_R(⋅) · P_B(⋅)$:
- $$\begin{align*}H(B \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.13cm} R) \hspace{-0.15cm} & = \hspace{-0.15cm} H(B) = {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} (6) = 2.585\ {\rm bit} \hspace{0.05cm},\\ H(R \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.13cm} B) \hspace{-0.15cm} & = \hspace{-0.15cm} H(R) = {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} (6) = 2.585\ {\rm bit} \hspace{0.05cm}.\end{align*}$$
Mutual information between two random variables
We consider the random variable $XY$ with the 2D probability function $P_{XY}(X, Y)$. Let the 1D functionsn $P_X(X)$ and $P_Y(Y)$ also be known.
Now the following questions arise:
- How does knowledge of the random variable $Y$ reduce the uncertainty with respect to $X$?
- How does knowledge of the random variable $X$ reduce the uncertainty with respect to $Y$?
To answer this question, we need a definition that is substantial for information theory:
$\text{Definition:}$ The mutual information between the random variables $X$ and $Y$ – both over the same alphabet – is given as follows:
- $$I(X;\ Y) = {\rm E} \hspace{-0.1cm}\left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.08cm} \frac{P_{XY}(X, Y)} {P_{X}(X) \cdot P_{Y}(Y) }\right ] =\hspace{-0.25cm} \sum_{(x, y) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{XY})} \hspace{-0.8cm} P_{XY}(x, y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.08cm} \frac{P_{XY}(x, y)} {P_{X}(x) \cdot P_{Y}(y) } \hspace{0.01cm}.$$
A comparison with the last chapter shows that the transinformation can also be written as a Kullback–Leibler distance between the 2D-PMF $P_{XY}$ and the product $P_X · P_Y$ :
- $$I(X;Y) = D(P_{XY} \hspace{0.05cm}\vert \vert \hspace{0.05cm} P_X \cdot P_Y) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
It is thus obvious that $I(X;\ Y) ≥ 0$ always holds. Because of the symmetry, $I(Y;\ X)$ = $I(X;\ Y)$ is also true.
- By splitting the $\log_2$ argument according to
- $$I(X;Y) = {\rm E} \hspace{-0.1cm}\left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1} {P_{X}(X) }\right ] - {\rm E} \hspace{-0.1cm}\left [ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac {P_{Y}(Y) }{P_{XY}(X, Y)} \right ] $$
- is obtained using $P_{X|Y}(\cdot) = P_{XY}(\cdot)/P_Y(Y)$:
- $$I(X;Y) = H(X) - H(X \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm} Y) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This means: The uncertainty regarding the random quantity $X$ ⇒ entropy $H(X)$ decreases by the amount $H(X|Y)$ when $Y$ is known. The remainder is the mutual information $I(X; Y)$.
- With a different splitting, one arrives at the result
- $$I(X;Y) = H(Y) - H(Y \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm} X) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Ergo: The mutual information $I(X; Y)$ is symmetrical ⇒ $X$ says just as much about $Y$ as $Y$ says about $X$ ⇒ mutual information. The semicolon indicates equality.
$\text{Conclusion:}$ Often the equations mentioned here are clarified by a diagram, as in the following examples. From this you can see that the following equations also apply:
- $$I(X;\ Y) = H(X) + H(Y) - H(XY) \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$I(X;\ Y) = H(XY) - H(X \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm} Y) - H(Y \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm} X) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\text{Example 3:}$ We return (for the last time) to the dice experiment with the red $(R)$ and blue $(B)$ dice. The random variable $S$ gives the sum of the two dice: $S = R + B$. Here we consider the 2D random variable $RS$. In earlier examples we calculated
- the entropies $H(R) = 2.585 \ \rm bit$ and $H(S) = 3.274 \ \rm bit$ ⇒ example 6 in the last chapter,
- the join entropies $H(RS) = 5.170 \ \rm bit$ ⇒ example 6 in the last chapter,
- die conditional entropies $H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R) = 2.585 \ \rm bit$ and $H(R \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} S) = 1.896 \ \rm bit$ ⇒ example 2 in the previous section.
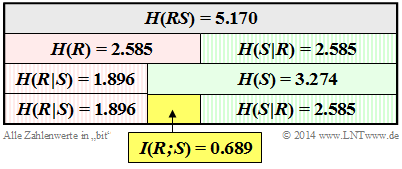
These quantities are compiled in the graph, with the random quantity $R$ marked by the basic colour „red” and the sum $S$ marked by the basic colour „green” . Conditional entropies are shaded. One can see from this representation:
- The entropy $H(R) = \log_2 (6) = 2.585\ \rm bit$ is exactly half as large as the compound entropy $H(RS)$. Because: If one knows $R$, $S$ provides exactly the same information as the random quantity $B$, namely $H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R) = H(B) = \log_2 (6) = 2.585\ \rm bit$. Note: $H(R)$ = $H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R)$ only applies in this example, not in general.
- As expected, the entropy $H(S) = 3.274 \ \rm bit$ is greater than $H(R)= 2.585\ \rm bit$ in this example. Because of $H(S) + H(R \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} S) = H(R) + H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R)$ , $H(R \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} S)$ must therefore be smaller than $H(S \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} R)$ by $I(R;\ S) = 0.689 \ \rm bit$ . $H(R)$ is also smaller than $H(S)$ by $I(R;\ S) = 0.689 \ \rm bit$ .
- The mutual information between the random variables $R$ and $S$ also results from the equation
- $$I(R;\ S) = H(R) + H(S) - H(RS) = 2.585\ {\rm bit} + 3.274\ {\rm bit} - 5.170\ {\rm bit} = 0.689\ {\rm bit} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
Conditional Mutual Information
We now consider three random variables $X$, $Y$ and $Z$, that are (can be) related to each other.
$\text{Definition:}$ The conditional mutual information between the random variables $X$ and $Y$ for a given $Z = z$ is as follows:
- $$I(X;Y \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) - H(X\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Y ,\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
One denotes as the conditional conditional mutual information between the random variables $X$ and $Y$ for the random variable $Z$ in general after averaging over all $z \in Z$:
- $$I(X;Y \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) - H(X\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Y Z )= \hspace{-0.3cm} \sum_{z \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{Z})} \hspace{-0.25cm} P_{Z}(z) \cdot I(X;Y \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$P_Z(Z)$ is the probability function (PMF) of the random variable $Z$ and $P_Z(z)$ dis the probability for the realisation $Z = z$.
$\text{Please note:}$
- For conditional entropy, as is well known, the relation $H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Z) ≤ H(X)$ holds.
- For the mutual information, this relation does not necessarily hold:
- $I(X; Y\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm}Z)$ can be smaller, equal, but also larger than als $I(X; Y)$.
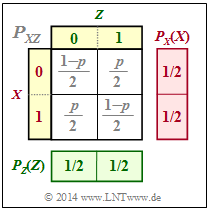
$\text{Example 4:}$ We consider the binary random variables $X$, $Y$ and $Z$ with the following properties:
- $X$ and $Y$ be statistically independent. Let the following be true for their probability functions:
- $$P_X(X) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big], \hspace{0.2cm} P_Y(Y) = \big[1– p, \ p \big] \ ⇒ \ H(X) = 1\ {\rm bit}, \hspace{0.2cm} H(Y) = H_{\rm bin}(p).$$
- $Z$ is the modulo-2 sum of $X$ and $Y$: $Z = X ⊕ Y$.
From the joint probability function $P_{XZ}$ according to the upper graph, it follows:
- Summing the column probabilities gives $P_Z(Z) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big ]$ ⇒ $H(Z) = 1\ {\rm bit}$.
- $X$ and $Z$ are also statistically independent, since for the 2D-PMF $P_{XZ}(X, Z) = P_X(X) · P_Z(Z)$ holds.
- It follows that: $H(Z\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} X) = H(Z)$ and $H(X \hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z) = H(X)$ sowie $I(X; Z) = 0$.
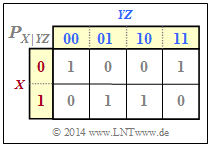
From the conditional probability function $P_{X\vert YZ}$ according to the graph below, we can calculate:
- $H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ) = 0$, since all $P_{X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ}$ entries entweder $0$ or $1$ sind ⇒ conditional entropy,
- $I(X; YZ) = H(X) - H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} YZ) = H(X)= 1 \ {\rm bit}$ ⇒ mutual information,
- $I(X; Y\vert Z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z) =H(X)=1 \ {\rm bit} $ ⇒ conditional mutual information.
In the present example
- the conditional mutual information $I(X; Y\hspace{0.05cm}\vert\hspace{0.05cm} Z) = 1$
- is greater than the conventional mutual information $I(X; Y) = 0$.
Chain rule of mutual information
So far we have only considered the transinformation between two one-dimensional random variables. Now we extend the definition to a total of $n + 1$ random variables, which, for reasons of representation, we denote with $X_1$, ... , $X_n$ and $Z$ . Then applies:
$\text{Chain rule of mutual information:}$
The mutual information between the $n$–dimensional random variable $X_1 X_2 \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} X_n$ and the random variable $Z$ can be represented and calculated as follows:
- $$I(X_1\hspace{0.05cm}X_2\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}X_n;Z) = I(X_1;Z) + I(X_2;Z \vert X_1) + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}+ I(X_n;Z\vert X_1\hspace{0.05cm}X_2\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}X_{n-1}) = \sum_{i = 1}^{n} I(X_i;Z \vert X_1\hspace{0.05cm}X_2\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}X_{i-1}) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\text{Proof:}$ We restrict ourselves here to the case $n = 2$, i.e. to a total of three random variables, and replace $X_1$ by $X$ and $X_2$ by $Y$. Then we obtain:
- $$\begin{align*}I(X\hspace{0.05cm}Y;Z) & = H(XY) - H(XY\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm}Z) = \\ & = \big [ H(X)+ H(Y\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} X)\big ] - \big [ H(X\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} Z) + H(Y\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} XZ)\big ] =\\ & = \big [ H(X)- H(X\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} Z)\big ] - \big [ H(Y\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} X) + H(Y\hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm}XZ)\big ]=\\ & = I(X;Z) + I(Y;Z \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} X) \hspace{0.05cm}.\end{align*}$$
From this equation one can see that the size relation $I(X Y; Z) ≥ I(X; Z)$ is always given.
- Equality results for the conditional mutual information $I(Y; Z \hspace{0.05cm} \vert \hspace{0.05cm} X) = 0$,
- i.e. when the random variables $Y$ and $Z$ for a given $X$ are statistically independent.
$\text{Example 5:}$ We consider the Markov chain $X → Y → Z$. For such a constellation, the Data Processing Theorem always holds with the following consequence, which can be derived from the chain rule of mutual information:
- $$I(X;Z) \hspace{-0.05cm} \le \hspace{-0.05cm}I(X;Y ) \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$I(X;Z) \hspace{-0.05cm} \le \hspace{-0.05cm} I(Y;Z ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The theorem thus states:
- One cannot gain any additional information about input $X$  by manipulating $($processing $Z)$ data $Y$ .
- Data processing $Y → Z$ $($by a second processor$)$ only serves the purpose of making the information about $X$ more visible.
For more information on the Data Processing Theorem see task 3.15.
Relevant tasks
Aufgabe 3.7: Einige Entropieberechnungen
Aufgabe 3.8: Nochmals Transinformation
Aufgabe 3.8Z: Tupel aus ternären Zufallsgrößen
Aufgabe 3.9: Bedingte Transinformation