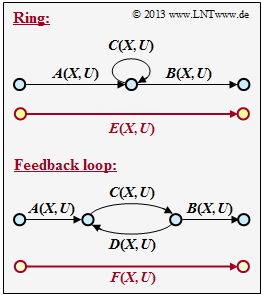
Exercise 3.12Z: Ring and Feedback
From LNTwww
(Redirected from Aufgabe 3.12Z: Ring und Rückkopplung)
In order to determine the path weighting enumerator function $T(X)$ of a convolutional code from the state transition diagram, it is necessary to reduce the diagram until it can be represented by a single connection from the initial state to the final state.
In the course of this diagram reduction can occur:
- serial and parallel transitions,
- a ring according to the sketch above,
- a feedback according to the sketch below.
For these two graphs, find the correspondences $E(X, \, U)$ and $F(X, \, U)$ depending on the given functions $A(X, \, U), \ B(X, \ U), \ C(X, \, U), \ D(X, \, U)$ .
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Distance Characteristics and Error Probability Bounds".
- This exercise is intended to prove some of the statements on the "Rules for manipulating the state transition diagram" section.
- Applied these rules in $\text{Exercise 3.12}$ and $\text{Exercise 3.13}$.
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct are the solutions 1 and 2:
- In general terms, one first goes from $S_1$ to $S_2$, remains $j$–times in the state $S_2 \ (j = 0, \ 1, \, 2, \ \text{ ...})$, and finally continues from $S_2$ to $S_3$.
(2) Correct is the solution suggestion 2:
- In accordance with the explanations for subtask (1), one obtains for the substitution of the ring:
- $$E \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} A \cdot B + A \cdot C \cdot B + A \cdot C^2 \cdot B + A \cdot C^3 \cdot B + \text{ ...} \hspace{0.1cm}=A \cdot B \cdot [1 + C + C^2+ C^3 +\text{ ...}\hspace{0.1cm}] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The parenthesis expression gives $1/(1 \, –C)$.
- $$E(X, U) = \frac{A(X, U) \cdot B(X, U)}{1- C(X, U)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) Correct are the solutions 1, 3 and 4:
- One goes first from $S_1$ to $S_2 \ \Rightarrow \ A(X, \, U)$,
- then from $S_2$ to $S_3 \ \Rightarrow \ C(X, \, U)$,
- then $j$–times back to $S_2$ and again to $S_3 \ (j = 0, \ 1, \ 2, \ \text{ ...} \ ) \ \Rightarrow \ E(X, \, U)$,
- finally from $S_3$ to $S_4 \ \Rightarrow \ B(X, \, U)$,
(4) Thus, the correct solution is the suggested solution 1:
- According to the sample solution to subtask (3) applies:
- $$F(X, U) = A(X, U) \cdot C(X, U) \cdot E(X, U) \cdot B(X, U)\hspace{0.05cm}$$
- Here $E(X, \, U)$ describes the path "$j$–times" back to $S_2$ and again to $S_3 \ (j =0, \ 1, \ 2, \ \text{ ...})$:
- $$E(X, U) = 1 + D \cdot C + (1 + D)^2 + (1 + D)^3 + \text{ ...} \hspace{0.1cm}= \frac{1}{1-C \hspace{0.05cm} D} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} F(X, U) = \frac{A(X, U) \cdot B(X, U)\cdot C(X, U)}{1- C(X, U) \cdot D(X, U)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$