Exercise 1.2Z: Puls Code Modulation
From LNTwww
(Redirected from Exercise 1.2Z: Puls-Code-Modulation)
All modern communication systems are digital. The principle of digital transmission of speech signals goes back to Alec Reeves, who invented the so-called "Puls Code Modulation" $\rm (PCM)$ as early as 1938.
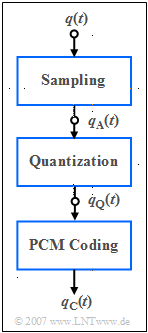
On the right you see the (simplified) block diagram of the PCM transmitter with three functional units:
- The band-limited speech signal ${q(t)}$ is sampled, where the Sampling Theorem is observed, and yields the sampled signal $q_{\rm A}(t)$.
- Each sample $q_{\rm A}(t)$ is mapped to one of $M = 2^N$ results in the quantized signal $q_{\rm Q}(t)$.
- Each individual quantized value is represented by a code sequence of $N$ binary symbols and results in the coded signal $q_{\rm C}(t)$.
In this task only the different signals of the PCM transmitter are to be classified.
Later tasks will deal with other properties of the puls code modulation.
Note: This task belongs to the chapter Signal classification.
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct are the solutions 1, 2 and 4:
- The source signal ${q(t)}$ is analog, i.e. "continuous in time and value".
- In general, it makes no sense to transmit a deterministic signal.
- For the mathematical description, a deterministic source signal – such as a periodic signal – is better suited than a random signal.
- Deterministic signals are also used for testing in order to be able to reconstruct detected errors.
(2) Correct are the solution suggestions 2 and 3:
- After sampling, the signal $q_{\rm A}(t)$ is still continuous in value, but now also discrete in time.
- The sampling frequency $f_{\rm A}$ is given by the so-called "Sampling Theorem".
- The greater the maximum frequency $f_{\rm N,\,max}$ of the source signal, the greater must $f_{\rm A} ≥ 2 \cdot f_{\rm N,\,max}$ be selected.
(3) Correct are the solution suggestions 1 and 3:
- The quantized signal $q_{\rm Q}(t)$ is discrete in time and value, where the number of levels are $M = 2^8 = 256$ .
- A binary signal, on the other hand, is a discrete-valued signal with the level number $M = 2$.
(4) Correct are the solutions 1, 3 and 5:
- The coded signal $q_{\rm C}(t)$ is binary $($level number $M = 2)$ with bit duration $T_{\rm B} = T_{\rm A}/8$.