Exercise 3.09Z: Viterbi Algorithm again
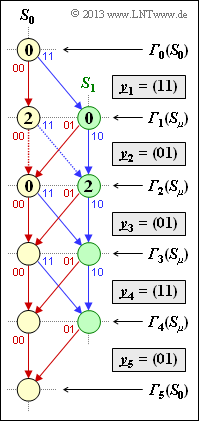
The diagram shows the trellis of the convolutional code according to $\text{Exercise 3.6}$, characterized by the following quantities:
- Rate 1/2 ⇒ $k = 1, \ n = 2$,
- memory $m = 1$,
- transfer function matrix $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1, \ 1 + D)$,
- length of the information sequence: $L = 4$,
- sequence length including termination: $L\hspace{0.05cm}' = L + m = 5$.
On the basis of this representation, the Viterbi decoding is to be understood step-by-step, starting from the following received sequence:
- $$\underline{y} = (11, \, 01, \, 01, \, 11, \, 01).$$
Into the trellis are drawn:
- The initial value ${\it \Gamma}_0(S_0)$ for the Viterbi algorithm, which is always chosen to $0$.
- The two error values for the first decoding step $(i = 1)$ are obtained with $\underline{y}_1 = (11)$ as follows:
- $${\it \Gamma}_1(S_0) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\it \Gamma}_0(S_0) + d_{\rm H} \big ((00)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} (11) \big ) = 2 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\it \Gamma}_1(S_1) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\it \Gamma}_0(S_0) + d_{\rm H} \big ((11)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} (11) \big ) = 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The error values for step $i = 2$ ⇒ $\underline{y}_2 = (01)$ are obtained by the following comparisons:
- $${\it \Gamma}_2(S_0) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}{\rm min} \left [{\it \Gamma}_{1}(S_0) + d_{\rm H} \big ((00)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} (01) \big )\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}{\it \Gamma}_{1}(S_1) + d_{\rm H} \big ((01)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} (01) \big ) \right ] $$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} {\it \Gamma}_2(S_0) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm min} \big [ 2+1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0+0 \big ] = 0\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\it \Gamma}_2(S_1) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}{\rm min} \left [{\it \Gamma}_{1}(S_0) + d_{\rm H} \big ((11)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} (01) \big )\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}{\it \Gamma}_{1}(S_1) + d_{\rm H} \big ((10)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} (01) \big ) \right ]$$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} {\it \Gamma}_2(S_1) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm min} \big [ 2+1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0+2 \big ] = 2\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In the same way you are
- to compute the error values at time points $i = 3, \ i = 4$ and $i = 5$ $($termination$)$, and
- to eliminate the less favorable paths to a node ${\it \Gamma}_i(S_{\mu})$ in each case; in the graph this is indicated by dotted lines for $i = 2$ .
⇒ Then the continuous path from ${\it \Gamma}_0(S_0)$ to ${\it \Gamma}_5(S_0)$ is to be found, where the backward direction is recommended.
⇒ If one follows the found path in forward direction, one recognizes:
- the most likely decoded sequence $\underline{z}$ $($ideally equal $\underline{x})$ by the labels,
- the most probable information sequence $\underline{v}$ $($ideally equal $\underline{u})$ at the colors.
Hints: This exercise belongs to the chapter "Decoding of Convolutional Codes".
Questions
Solution
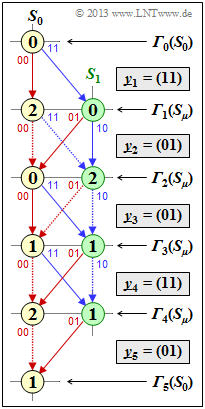
(1) Starting from ${\it \Gamma}_2(S_0) = 0, \ \ {\it \Gamma}_2(S_1) = 2$ we get $\underline{y}_3 = (01)$:
- $${\it \Gamma}_3(S_0) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm min} \left [0 + d_{\rm H} \big ((00), (01) \big ), \hspace{0.05cm}2 + d_{\rm H} \big ((01), (01) \big ) \right ] = {\rm min} \left [ 0+1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 2+0 \right ] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\it \Gamma}_3(S_1) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}{\rm min} \left [0 + d_{\rm H} \big ((11), (01) \big ), \hspace{0.05cm}2 + d_{\rm H} \big ((10), (01) \big ) \right ] {\rm min} \left [ 0+1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 2+2 \right ] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
⇒ Eliminated are the two (dotted) subpaths that start from state $S_1$ at time $i = 2$ $($i.e., at the third decoding step$)$.
(2) Analogous to subtask (1), we obtain with $y_4 = (11)$:
- $${\it \Gamma}_4(S_0) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}{\rm min} \left [1 + d_{\rm H} \big ((00), (11) \big ), \hspace{0.05cm}1 + d_{\rm H} \big ((01), (11) \big ) \right ] = {\rm min} \left [ 1+2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 1+1 \right ] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\it \Gamma}_4(S_1) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}{\rm min} \left [1 + d_{\rm H} \big ((11), (11) \big ), \hspace{0.05cm}1 + d_{\rm H} \big ((10), (11) \big ) \right ] ={\rm min} \left [ 1+0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 1+1 \right ] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}\hspace{0.05cm}$$
⇒ Elimination in the fourth decoding step of the two subpaths "$S_0 → S_0$" and "$S_1 → S_1$".
(3) For $i = 5$ ⇒ the "termination" is obtained with $\underline{y}_5 = (01)$:
- $${\it \Gamma}_5(S_0) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}{\rm min} \left [2 + d_{\rm H} \big ((00), (01) \big ), \hspace{0.05cm}1 + d_{\rm H} \big ((01), (01) \big ) \right ] {\rm min} \left [ 2+1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 1+0 \right ] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
⇒ To be eliminated is the subpath "$S_0 → S_0$".
(4) The backward search of the continuous path from ${\it \Gamma}_5(S_0)$ to ${\it \Gamma}_0(S_0)$ yields
- $$S_0 ← S_1 ← S_0 ← S_0 ← S_1 ← S_0.$$
In the forward direction, this yields the path "$S_0 → S_1 → S_0 → S_0 → S_1 → S_0$" and thus the
- the most likely code sequence $\underline{z} = (11, \, 01, \, 00, \, 11, \, 01)$,
- the most likely information sequence $\underline{v} = (1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0)$.
Thus, the proposed solutions 1 and 3 are correct:
- Comparison with the received vector $\underline{y} = (11, \, 01, \, 01, \, 11, \, 01)$ shows that the sixth bit was falsified during transmission.
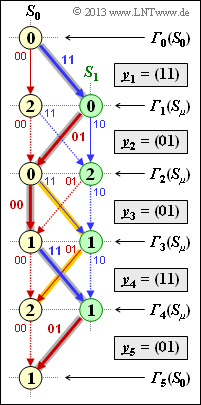
(5) Without termination ⇒ final decision at $i = 4$, there would have been two continuous paths:
- from "$S_0 → S_1 → S_0 → S_1 → S_0$" $($shown in yellow$)$,
- from "$S_0 → S_1 → S_0 → S_0 → S_1$" $($the ultimately correct path$)$.
The constraint decision at time $i = 4$ would have led here to the second path and thus to the result $\underline{v} = (1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1)$ because of ${\it \Gamma}_4(S_1) < {\it \Gamma}_4(S_0)$.
- In the considered example, therefore, to the same decision as in subtask (4) with termination bit.
- However, there are many constellations where only the termination bit enables the correct and safe decision.