Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.3: Rayleigh Fading"
From LNTwww
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Mobile Kommunikation/Wahrscheinlichkeitsdichte des Rayleigh–Fadings}} Datei:P_ID2106__Mob_A_1_3.png|right|frame|Zeitverlauf von Ra…“) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Mobile Kommunikation/Wahrscheinlichkeitsdichte des Rayleigh–Fadings}} | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Mobile Kommunikation/Wahrscheinlichkeitsdichte des Rayleigh–Fadings}} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2106__Mob_A_1_3.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2106__Mob_A_1_3.png|right|frame|Time evolution of Rayleigh fading]] |
| − | Rayleigh–Fading | + | Rayleigh–Fading should be used when |
| − | * | + | * there is no direct connection between sender and receiver, and |
| − | * | + | * the signal reaches the receiver in many ways, but their transit times are approximately the same. |
| − | + | An example of such a Rayleigh–channel occurs in urban mobile communications when narrowband signals are used with ranges between $50$ and $100$ meters. | |
| − | + | Looking at the radio signals $s(t)$ and $r(t)$ in the equivalent low-pass range $($that is, around the frequency $f = 0)$, the signal transmission is given by the equation | |
| − | :$$r(t)= | + | :$$r(t)= z(t) \cdot s(t)$ |
| − | + | described completely. The multiplicative falsification | |
| − | :$$z(t)= | + | :$$z(t)= x(t) + {\rm j} \cdot y(t)$$ |
| − | + | is always complex and has the following characteristics: | |
| − | * | + | * The real part $x(t)$ and the imaginary part $y(t)$ are Gaussian mean-free random variables, both with equal variance $\sigma^2$. Within the components $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ there may be statistical bindings, but this is not relevant for the solution of the present task. There are no bonds between $x(t)$ and $y(t)$; their cross-correlation function is identical to zero. |
| − | * | + | * The amount $a(t) = |z(t)|$ has a Rayleigh–WDF, from which the name „<i>Rayleigh–Fading</i>” is derived: |
:$$f_a(a) = | :$$f_a(a) = | ||
| − | \left\{ \begin{array}{c} a/\sigma^2 \cdot {\rm e}^ { -a^2/(2\sigma^2)} \\ | + | \left\{ \begin{array}{c} a/\sigma^2 \cdot {\rm e}^ { -a^2/(2\sigma^2)} \\\ |
| − | 0 | + | 0 \end{array} \right.\quad |
| − | \begin{array}{*{1}c} {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} a \ge 0 | + | \begin{array}{*{*{1}c} {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} a \ge 0 |
| − | \\ | + | \\ {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} a < 0 \\\ \\ \end{array} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * The absolute square $p(t) = a(t)^2 = |z(t)|^2$ is exponentially distributed according to the equation |
| − | + | $$f_p(p) = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} 1/(2\sigma^2) \cdot {\rm e}^ { -p/(2\sigma^2)} \\ | |
| − | 0 | + | 0 \end{array} \right.\quad |
| − | \begin{array}{*{1}c} {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} p \ge 0 | + | \begin{array}{*{*{1}c} {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} p \ge 0 |
| − | \\ | + | \\ {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} p < 0 \\\ \\ \end{array} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
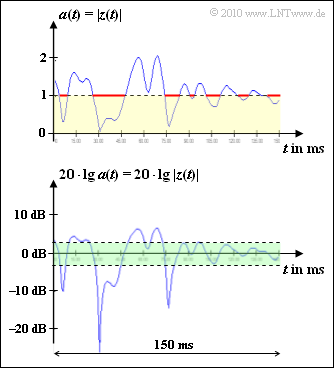
| − | + | Measurements have shown that the time intervals with $a(t) ≤ 1$ (highlighted in yellow in the graphic) add up to $\text{59 ms}$ (areas highlighted in red). With the total measurement time of $\text{150 ms}$ the probability that the amount of the <i>Rayleigh–fading</i> is less than or equal to $1$ results in | |
| − | + | $${\rm Pr}(a(t) \le 1) = \frac{59\,\,{\,{\rm ms}}}{150\,\,{\rm ms}} = 39.4 \% | |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | In | + | In the lower graphic the value range between $\text{-3 dB}$ and $\text{+3 dB}$ regarding the logarithmic Rayleigh–Size $20 \cdot {\rm lg} is highlighted in green. \ a(t)$. The subtask '''(4)'' refers to this. |
| − | '' | + | ''Notes:'' |
| − | * | + | * The task belongs to chapter [[Mobile_Communications/Probability Density_of_Rayleigh%E2%80%93Fadings|Probability Density of Rayleigh–Fadings]] of this book. |
| − | * | + | * A similar topic is treated with a different approach in chapter [[Stochastic_Signal Theory/Weitere_Verteilungen|Weitere Verteilungen]] of the book „Stochastic Signal Theory”. |
| − | * | + | * To check your results you can use the interactive applet [[Applets:WDF_VTF|WDF, VTF and Moments]] of the book „Stochastic Signal Theory”. |
| − | === | + | ===Questionnaire=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {For the entire range, the amount function $a(t) ≤ 2$ applies. What is the maximum value for the logarithmic quantity in this range? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | ${\rm Max}\big[20 \cdot {\rm lg} \ {a(t)}\big] \ = \ | + | ${\rm Max}\big [20 \cdot {\rm lg} \ {a(t)}\big] \ = \ $ { 6 3% } $\ \rm dB$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the maximum value for $p(t) = |z(t)|^2$ both in linear and logarithmic representation? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | ${\rm Max}\big[p(t)\big] \ = \ | + | ${\rm Max}\big[p(t)\big] \ = \ $ {\ $ 4 3% } |
| − | ${\rm Max}\big[10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ p(t)\big] \ = \ | + | ${\rm Max}\big [10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ p(t)\big] \ = \ $ { 6 3% } $ \ \rm dB$ |
| − | { | + | {Let ${\rm Pr}\big[a(t) ≤ 1\big] = $0.394 Determine the Rayleigh–parameter $\sigma$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\sigma \ = \ | + | $\sigma \ = \ $ { 1 3% } |
| − | { | + | {What is the probability of the logarithmic Rayleigh–size ⇒ $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ p(t)$ in the range between between $\text{-3 dB}$ and $\text{+3 dB}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | ${\rm Pr}(|10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ p(t)| < 3 \ \rm dB) \ = \ | + | ${\rm Pr}(|10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ p(t)| < 3 \ \rm dB) \ = \ $ { 0.411 3% } |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Sample solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1) | + | '''(1)'' From ${\rm Max}[a(t)] = 2$ follows directly: |
| − | + | $${\rm Max} \left [ 20 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}a(t) \right ] = 20 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}(2) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 6\,\,{\rm dB}} | |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' The maximum value of the square $p(t) = a(t)^2$ is |
| − | + | $$${\rm Max} \left [ p(t) \right ] = {\rm Max} \left [ a(t)^2 \right ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\4} | |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The logarithmic representation of the square of the amount $p(t)$ is identical to the logarithmic representation of the amount $a(t)$. Since $p(t)$ is a power quantity |
| − | + | $$10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm} p(t) = 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}a(t)^2 = 20 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm} a(t) | |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The maximum value is thus also $\underline{\approx 6\,\,{\rm dB}}$. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' The condition $a(t) ≤ 1$ is equivalent to the requirement $p(t) = a(t)^2 ≤ 1$. |
| − | * | + | *The absolute square is known to be exponentially distributed, and for $p ≥ 0$ applies accordingly: |
| − | + | $$f_p(p) = \frac{1}{2\sigma^2} \cdot {\rm exp} [ -\frac{p}{2\sigma^2}] | |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2112__Mob_A_1_3c.png|right|frame|WDF | + | [[File:P_ID2112__Mob_A_1_3c.png|right|frame|WDF and probability regions ]] |
| − | * | + | *It follows: |
| − | + | $${\rm Pr}(p(t) \le 1) = \frac{1}{2\sigma^2} \cdot \int_{0}^{1}{\rm exp} [ -\frac{p}{2\sigma^2}] \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm d}p = | |
1 - {\rm exp} [ -\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}] = 0.394$$ | 1 - {\rm exp} [ -\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}] = 0.394$$ | ||
| − | + | $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm exp} [ -\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}] = 0.606 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | |
| − | \sigma^2 = \frac{1}{2 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(0.606)} | + | \sigma^2 = \frac{1}{2 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(0.606)} = 1 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} |
\underline{\sigma = 1} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \underline{\sigma = 1} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The graphic shows | |
| − | * | + | * left the probability ${\rm Pr}(p(t) ≤ 1)$, |
| − | * | + | * right the probability ${\rm Pr}(0.5 \le p(t) ≤ 2)$. |
| − | '''(4) | + | '''(4)'' From $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ p_1 = \ –3 \ \ \rm dB$ follows $p_1 = 0.5$ and the upper limit of the integration range results from the condition $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ p_2 = +3 \ \ \rm dB$ to $p_2 = 2$. |
| − | * | + | *This gives you, according to the above graphic: |
| − | + | $${\rm Pr}(-3\,\,{\rm dB}\le 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}p(t) \le +3\,\,{\rm dB}) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \int_{0.5}^{2}f_p(p)\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm d}p = | |
\left [ - {\rm e}^{ -{p}/(2\sigma^2)}\hspace{0.15cm} \right ]_{0.5}^{2} ={\rm e}^{-0.25}- {\rm e}^{-1} \approx 0.779 - 0.368 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ = 0.411} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \left [ - {\rm e}^{ -{p}/(2\sigma^2)}\hspace{0.15cm} \right ]_{0.5}^{2} ={\rm e}^{-0.25}- {\rm e}^{-1} \approx 0.779 - 0.368 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ = 0.411} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
Revision as of 17:09, 25 March 2020
Rayleigh–Fading should be used when
- there is no direct connection between sender and receiver, and
- the signal reaches the receiver in many ways, but their transit times are approximately the same.
An example of such a Rayleigh–channel occurs in urban mobile communications when narrowband signals are used with ranges between $50$ and $100$ meters.
Looking at the radio signals $s(t)$ and $r(t)$ in the equivalent low-pass range $($that is, around the frequency $f = 0)$, the signal transmission is given by the equation
- $$r(t)= z(t) \cdot s(t)$ described completely. The multiplicative falsification :$$z(t)= x(t) + {\rm j} \cdot y(t)$$ is always complex and has the following characteristics: * The real part $x(t)$ and the imaginary part $y(t)$ are Gaussian mean-free random variables, both with equal variance $\sigma^2$. Within the components $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ there may be statistical bindings, but this is not relevant for the solution of the present task. There are no bonds between $x(t)$ and $y(t)$; their cross-correlation function is identical to zero. * The amount $a(t) = |z(t)|$ has a Rayleigh–WDF, from which the name „<i>Rayleigh–Fading</i>” is derived: :$$f_a(a) =
\left\{ \begin{array}{c} a/\sigma^2 \cdot {\rm e}^ { -a^2/(2\sigma^2)} \\\ 0 \end{array} \right.\quad \begin{array}{*{*{1}c} {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} a \ge 0 \\ {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} a < 0 \\\ \\ \end{array}
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
* The absolute square $p(t) = a(t)^2 = |z(t)|^2$ is exponentially distributed according to the equation
$$f_p(p) = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} 1/(2\sigma^2) \cdot {\rm e}^ { -p/(2\sigma^2)} \\
0 \end{array} \right.\quad
\begin{array}{*{*{1}c} {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} p \ge 0 \\ {\rm f\ddot{u}r}\hspace{0.15cm} p < 0 \\\ \\ \end{array}
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Measurements have shown that the time intervals with $a(t) ≤ 1$ (highlighted in yellow in the graphic) add up to $\text{59 ms}$ (areas highlighted in red). With the total measurement time of $\text{150 ms}$ the probability that the amount of the <i>Rayleigh–fading</i> is less than or equal to $1$ results in
$${\rm Pr}(a(t) \le 1) = \frac{59\,\,{\,{\rm ms}}}{150\,\,{\rm ms}} = 39.4 \%
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In the lower graphic the value range between $\text{-3 dB}$ and $\text{+3 dB}$ regarding the logarithmic Rayleigh–Size $20 \cdot {\rm lg} is highlighted in green. \ a(t)$. The subtask '''(4)'' refers to this.
''Notes:''
* The task belongs to chapter [[Mobile_Communications/Probability Density_of_Rayleigh%E2%80%93Fadings|Probability Density of Rayleigh–Fadings]] of this book.
* A similar topic is treated with a different approach in chapter [[Stochastic_Signal Theory/Weitere_Verteilungen|Weitere Verteilungen]] of the book „Stochastic Signal Theory”.
* To check your results you can use the interactive applet [[Applets:WDF_VTF|WDF, VTF and Moments]] of the book „Stochastic Signal Theory”.
==='"`UNIQ--h-0--QINU`"'Questionnaire===
'"`UNIQ--quiz-00000002-QINU`"'
==='"`UNIQ--h-1--QINU`"'Sample solution===
'"`UNIQ--html-00000003-QINU`"'
'''(1)'' From ${\rm Max}[a(t)] = 2$ follows directly:
$${\rm Max} \left [ 20 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}a(t) \right ] = 20 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}(2) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 6\,\,{\rm dB}}
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
'''(2)''' The maximum value of the square $p(t) = a(t)^2$ is
$$${\rm Max} \left [ p(t) \right ] = {\rm Max} \left [ a(t)^2 \right ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\4}
\hspace{0.05cm}.'"`UNIQ-MathJax21-QINU`"'10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm} p(t) = 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}a(t)^2 = 20 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm} a(t)
\hspace{0.05cm}.'"`UNIQ-MathJax22-QINU`"'f_p(p) = \frac{1}{2\sigma^2} \cdot {\rm exp} [ -\frac{p}{2\sigma^2}]
\hspace{0.05cm}.'"`UNIQ-MathJax23-QINU`"'{\rm Pr}(p(t) \le 1) = \frac{1}{2\sigma^2} \cdot \int_{0}^{1}{\rm exp} [ -\frac{p}{2\sigma^2}] \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm d}p =
1 - {\rm exp} [ -\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}] = 0.394'"`UNIQ-MathJax24-QINU`"'\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm exp} [ -\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}] = 0.606 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}
\sigma^2 = \frac{1}{2 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(0.606)} = 1 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}
\underline{\sigma = 1} \hspace{0.05cm}.'"`UNIQ-MathJax25-QINU`"'{\rm Pr}(-3\,\,{\rm dB}\le 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}p(t) \le +3\,\,{\rm dB}) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \int_{0.5}^{2}f_p(p)\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm d}p =
\left [ - {\rm e}^{ -{p}/(2\sigma^2)}\hspace{0.15cm} \right ]_{0.5}^{2} ={\rm e}^{-0.25}- {\rm e}^{-1} \approx 0.779 - 0.368 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ = 0.411} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$