Difference between revisions of "Mobile Communications/Non-Frequency-Selective Fading With Direct Component"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
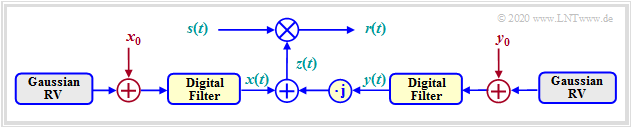
[[File:EN_Mob_T_1_4_S1.png|right|frame|Rice-Fading channel model|class=fit]] | [[File:EN_Mob_T_1_4_S1.png|right|frame|Rice-Fading channel model|class=fit]] | ||
| − | If a direct component $( | + | If a direct component $( <i>Line of Sight</i>, $\rm LoS)$ is present, it is necessary to add direct components $x_0$ and/or $y_0$ to the zero mean Gaussian processes $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ : |
::<math>x(t) \hspace{0.1cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} x(t) +x_0 \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} y(t) \hspace{0.1cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} y(t) +y_0\hspace{0.05cm},</math> | ::<math>x(t) \hspace{0.1cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} x(t) +x_0 \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} y(t) \hspace{0.1cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} y(t) +y_0\hspace{0.05cm},</math> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*The imaginary part $y(t)$ is also gaussian distributed $($mean $y_0$, equal variance $\sigma ^2)$ and independent of $x(t)$.<br> | *The imaginary part $y(t)$ is also gaussian distributed $($mean $y_0$, equal variance $\sigma ^2)$ and independent of $x(t)$.<br> | ||
| − | *For $z_0 \ne 0$ the value $|z(t)|$ is [[ | + | *For $z_0 \ne 0$ the value $|z(t)|$ is [[Stochastische Signaltheorie/Weitere Verteilungen#Riceversion| riceversified]], from which the term „<i>Rice–Fading</i>” is derived. |
*To simplify the notation we set $|z(t)| = a(t)$. For $a < 0$ it's PDF is $f_a(a) \equiv 0$, for $a \ge 0$ the following equation applies, where $\rm I_0(\cdot)$ denotes the <i>modified Bessel–function</i> of zero order: | *To simplify the notation we set $|z(t)| = a(t)$. For $a < 0$ it's PDF is $f_a(a) \equiv 0$, for $a \ge 0$ the following equation applies, where $\rm I_0(\cdot)$ denotes the <i>modified Bessel–function</i> of zero order: | ||
Revision as of 20:37, 6 July 2020
Channel model and Rice PDF
The Rayleigh distribution describes the mobile communication channel under the assumption that there is no direct path and thus the multiplicative factor $z(t) = x(t) + {\rm j} \cdot y(t)$ is solely composed of diffusely scattered components.
If a direct component $( <i>Line of Sight</i>, $\rm LoS)$ is present, it is necessary to add direct components $x_0$ and/or $y_0$ to the zero mean Gaussian processes $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ :
:\[x(t) \hspace{0.1cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} x(t) +x_0 \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} y(t) \hspace{0.1cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} y(t) +y_0\hspace{0.05cm},\]
:\[z(t) = x(t) + {\rm j} \cdot y(t) \hspace{0.1cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} z(t) +z_0 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}
z_0 = x_0 + {\rm j} \cdot y_0\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
The graphic shows this '''Rice–Fading–Channel model'''. As a special case, the Rayleigh–model results when $x_0 = y_0= 0$ .<br>
The Rice–Fading–model can be summarized as follows, see also [Hin08]'"`UNIQ--ref-00000008-QINU`"':
*The real part $x(t)$ is gaussian distributed with mean value $x_0$ and variance $\sigma ^2$.
*The imaginary part $y(t)$ is also gaussian distributed $($mean $y_0$, equal variance $\sigma ^2)$ and independent of $x(t)$.<br>
*For $z_0 \ne 0$ the value $|z(t)|$ is [[Stochastische Signaltheorie/Weitere Verteilungen#Riceversion| riceversified]], from which the term „<i>Rice–Fading</i>” is derived.
*To simplify the notation we set $|z(t)| = a(t)$. For $a < 0$ it's PDF is $f_a(a) \equiv 0$, for $a \ge 0$ the following equation applies, where $\rm I_0(\cdot)$ denotes the <i>modified Bessel–function</i> of zero order:
:\[f_a(a) = \frac{a}{\sigma^2} \cdot {\rm exp} \big [ -\frac{a^2 + |z_0|^2}{2\sigma^2}\big ] \cdot {\rm I}_0 \left [ \frac{a \cdot |z_0|}{\sigma^2} \right ]\hspace{0.5cm}\text{mit}\hspace{0.5cm}{\rm I }_0 (u) = {\rm J }_0 ({\rm j} \cdot u) =
\sum_{k = 0}^{\infty} \frac{ (u/2)^{2k}}{k! \cdot \Gamma (k+1)}
\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
*The greater the „direct path power” $(|z_0|^2)$ compared to the power of the stray components $(2\sigma^2)$ the better suited for digital signal transmission is the mobile communications channel
*If $|z_0| \gg \sigma$ $($factor $3$ or more$)$, the Rice–PDF can be approximated accurately by a Gaussian distribution with mean $|z_0|$ and variance $\sigma$ <br>
*In contrast to <i>Rayleigh fading</i> ⇒ $z_0 \equiv 0$, the phase at <i>Rice fading</i> is not equally distributed, but there is a preferred direction $\phi_0 = \arctan(y_0/x_0)$. Often one sets $y_0 = 0$ ⇒ $\phi_0 = 0$.<br>
=='"`UNIQ--h-1--QINU`"' Example of signal behaviour with Rice fading==
<br>
[[File:P ID2129 Mob T 1 4 S2 v1.png|right|frame|Comparison of Rayleigh fading (blue) and Rice fading (red)|class=fit]]
The diagram shows typical signal characteristics and density functions of two mobile communication channels:
*Rayleigh fading (blue curves) with
:'"`UNIQ-MathJax1-QINU`"'
*Rice fading (red curves) with the same $\sigma$ and
:'"`UNIQ-MathJax2-QINU`"'
For the generation of the signal sections according to the above model, the [[Mobile_Communication/Statistical_Bonds_within_the_Rayleigh_process#Doppler_frequency_and_its_distribution|maximum_Doppler_frequency]] $f_\text{D, max} = 100 \ \rm Hz$ was used as reference.
The autocorrelation function $\rm (ACF)$ and power spectral density $\rm (PSD)$ of Rayleigh and Rice differ only slightly, other than adjusted parameter values. The following applies:
:\[\varphi_z ({\rm \Delta}t)\Bigg |_{\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm Rice}} \hspace{-0.5cm} = \varphi_z ({\rm \Delta}t)\Bigg |_{\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm Rayleigh}} \hspace{-0.8cm} + |z_0|^2 \hspace{0.05cm},\]
:\[ {\it \Phi}_z(f_{\rm D})\Bigg |_{\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm Rice}} \hspace{-0.5cm} = {\it \Phi}_z(f_{\rm D})\Bigg |_{\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm Rayleigh}} \hspace{-0.8cm} + |z_0|^2 \cdot \delta (f_{\rm D}) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
It is taken into account that the spectral representation of a DC component leads to a Dirac function.<br>
<br clear="all">
It should be noted about this graphic:
*The real parts $x(t)$ of Rayleigh (blue) and Rice (red) only differ by the constant $x_0 = 0.707$. The statistical properties are otherwise the same: Gaussian PDF $f_x(x)$ with variance $\sigma = 0.707$, either zero-mean (Rayleigh) or with mean $x_0$ (Rice).<br>
*In the imaginary part $y(t)$ of the Rice distribution one can additionally recognize the direct component $y_0 = -0.707$. The (here not shown) PDF $f_y(y)$ is thus a Gaussian curve with the variance $\sigma = 0. 707$ around the mean value $ y_0 = -0.707$, thus axisymmetrical to the shown PDF $f_x(x)$.<br>
*The (logarithmic) representation of ⇒ $a(t) =|z(t)|$ shows that the red curve is usually above the blue one. This can also be read from the PDF $f_a(a)$ .
*For the Rice channel, the error probability is lower than for Rayleigh when AWGN is taken into account, since the receiver gets a lot of usable energy via the Rice direct path.
*The PDF $f_\phi(\phi)$ shows the preferred angle $\phi \approx 45^\circ$ of the given Rice–channel The complex factor $z(t)$ is located mainly in the fourth quadrant because of $x_0 > 0$ and $y_0 < 0$ , whereas in the Rayleigh channel all quadrants are equally probable.
Exercises zum Kapitel
Exercise 1.6: Autocorrelation Function and PSD with Rice Fading
Exercise 1.6Z: Comparison of Rayleigh and Rice
Exercise 1.7: PDF of Rice Fading
List of sources
- ↑ Hindelang, T.: Mobile Communications. Vorlesungsmanuskript. Lehrstuhl für Nachrichtentechnik, TU München, 2008.