Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.6: FDMA, TDMA and CDMA"
m (Text replacement - "Mobile_Kommunikation/" to "Mobile_Communications/") |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
''Notes:'' | ''Notes:'' | ||
| − | *This task refers to the chapter [[ | + | *This task refers to the chapter [[Mobile_Communications/Die_Charakteristika_von_UMTS|Die Charakteristika von UMTS]]. |
*Notes on the communication systems considered here can be found under the following links:<br> | *Notes on the communication systems considered here can be found under the following links:<br> | ||
Revision as of 10:13, 9 July 2020
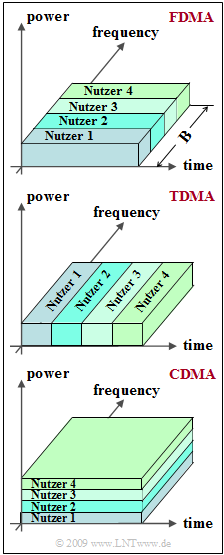
The diagram illustrates the principle of
- Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA),
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), and
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA).
The multiple access methods listed here are based on the assumption that there are several transmitter-receiver pairs that share a transmission medium independently.
On the other hand, multiplexing occurs when a multiplexer (MUX) bundles several signals at the beginning of transmission and a demultiplexer (DEMUX) splits the common signal at the end. In this case, FDM, TDM and CDM are abbreviated to Frequency (Time, Code) Division Multiplexing.
The task is to determine which of these methods (FDMA/FDM, TDMA/TDM, CDMA/CDM) is used by some of today's most important communications systems (GSM, UMTS, DSL).
Notes:
- This task refers to the chapter Die Charakteristika von UMTS.
- Notes on the communication systems considered here can be found under the following links:
- GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications),
- UMTS (Universal Mobile Communications Systems),
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line).
Questionnaire
Sample solution
(1) Correct is the solution 2:
- FDMA, TDMA and CDMA are multiple access or multiplexing techniques,
- which are then, however, abbreviated as FDM, TDM and CDM: Frequency (Time, Code) Division Multiplexing.
(2) Only the both last solutions are correct:
- FDMA/FDM can also be used in analog systems, of which classical broadcasting (since the 1930s) is an example.
(3) Correct are the solutions 1 and 2:
- At mobile radio standard GSM, FDMA and TDMA are used.
- Im so genannten D–Band (Uplink von $890$ bis $915 \ \rm MHz$, Downlink von $935$ bis $960 \ \rm MHz$) gibt es unter Berücksichtigung der Guard–Bänder von je $100 \ \rm kHz$ am oberen und unteren Bereichsende in jeder Richtung $124$ FDMA–Kanäle zu je $200 \ \rm kHz$.
- Im E–Band (Uplink: $1710 – 1785 \ \rm MHz$, Downlink: $1805 – 1880 \ \rm MHz$) sind $374$ FDMA–Kanäle nutzbar.
- Time division multiplex (TDMA) can be used to provide $8$ users additionally in each frequency band. A TDMA frame has a length of $4,615 \ \rm ms$, so that time slots of $0,577 \ \ \rm ms$ duration are available for each user in this time interval.
(4) Correct are the solutions 2 and 3:
- The UMTS variant UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access-Frequency Division Duplex (UTRA-FDD) used exclusively in Germany consists of $12$ paired uplink and downlink frequency bands of $5 \ \rm MHz$ bandwidth each.
- between $1920 \ \rm MHz$ and $1980 \ \rm MHz$ (uplink) or
- between $2110 \ \rm MHz$ and $2170 \ \rm MHz$ (downlink).
- So you could definitely speak of an FDMA system. However, the various $5 \ \rm MHz$ bands are used by other network operators.
- If, on the other hand, one considers a $5 \ \rm MHz$ band on its own, UMTS does not have an FDMA component. In each of the bands, CDMA is implemented instead, so that up to $512$ users can be active simultaneously in each frequency band. And to some extent TDMA (time slots, frames, TTI) is also used.
(5) Only solution 1 is correct:
- For fast Internet connections nowadays, it is common to use DSL (Digital Subscriber Line).
- OFDM is based on OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing), which is an FDM version.
- The individual spectrums are not separated, however, but overlap.
- There is still no mutual influence due to the orthogonality.