Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.4Z: Entropy of the AMI Code"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* The binary symbol $\rm L$ ⇒ <i>Low</i> is always represented by the ternary symbol $\rm N$ ⇒ <i>Null</i> . | * The binary symbol $\rm L$ ⇒ <i>Low</i> is always represented by the ternary symbol $\rm N$ ⇒ <i>Null</i> . | ||
| − | * The binary symbol $\rm H$ ⇒ <i>High</i> is also coded deterministically but alternately (hence the name „AMI”) by the symbols $\rm P$ ⇒ <i>Plus</i> and $\rm M$ ⇒ <i>Minus</i> | + | * The binary symbol $\rm H$ ⇒ <i>High</i> is also coded deterministically but alternately (hence the name „AMI”) by the symbols $\rm P$ ⇒ <i>Plus</i> and $\rm M$ ⇒ <i>Minus</i> . |
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' Since each $\rm L$ is mapped to $\rm N$ and $\rm H$ is mapped alternately to $\rm M$ and $\rm P$, it holds that |
:$$p_{\rm N} = p_{\rm L} = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm P} = p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm H}/2 = 3/8\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$p_{\rm N} = p_{\rm L} = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm P} = p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm H}/2 = 3/8\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} H_1 = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4) + | \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} H_1 = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4) + | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' Now the probabilities of occurrence of the ternary symbols are $p_{\rm N} = 3/4$ sowie $p_{\rm P} = p_{\rm M} =1/8$. Thus: |
:$$H_1 = {3}/{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4/3) + | :$$H_1 = {3}/{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4/3) + | ||
2 \cdot {1}/{8} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(8) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.06 \,{\rm bit/Tern\ddot{a}rsymbol}} | 2 \cdot {1}/{8} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(8) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.06 \,{\rm bit/Tern\ddot{a}rsymbol}} | ||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
''Interpretation:'' | ''Interpretation:'' | ||
| − | * | + | *For $p_{\rm L} = 1/4, \ p_{\rm H} = 3/4$ gives $H_1 = 1.56 \; \rm bit/symbol$. |
| − | * | + | *For $p_{\rm L} = 3/4, \ p_{\rm H} = 1/4$ , on the other hand, $H_1 = 1.06 \; \rm bit/symbol$ results in a significantly smaller value. |
| − | * | + | *For both parameter combinations, however, the same applies: |
| − | :$$H_0 = 1.585 \,{\rm bit/ | + | :$$H_0 = 1.585 \,{\rm bit/symbol}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}H_{\rm C} = |
\lim_{k \rightarrow \infty } H_k = 0.811 \,{\rm bit/Symbol} | \lim_{k \rightarrow \infty } H_k = 0.811 \,{\rm bit/Symbol} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | It follows from this: <br> | |
| − | * | + | *If one considers two message sources $\rm Q1$ and $\rm Q2$ with the same symbol range $M$ ⇒ decision content $H_0 = \rm const.$, whereby the first-order entropy approximation $\rm Q1$ is clearly greater for source $(H_1)$ than for source $\rm Q2$, one cannot conclude from this by any means that the entropy of $\rm Q1$ is actually greater than the entropy of $\rm Q2$. |
| − | * | + | *Rather, one must |
| − | :* | + | :* calculate enough entropy approximations $H_1$, $H_2$, $H_3$, ... for both sources and |
| − | :* | + | :* determine from them (graphically or analytically) the limit value of $H_k$ für $k \to \infty$ . |
| − | * | + | *Only then is a final statement about the entropy ratios possible. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Revision as of 18:24, 22 May 2021
We assume similar prerequisites as in task 1.4 :
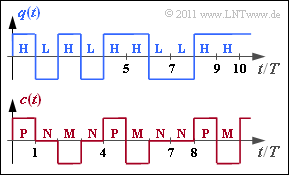
A binary source provides the source symbol sequence $\langle q_\nu \rangle$ with $q_\nu \in \{ {\rm L}, {\rm H} \}$, where there are no statistical ties between the individual sequence elements.
For the symbol probabilities, let:
- $p_{\rm L} =p_{\rm H} = 1/2$ (in subtasks 1 und 2),
- $p_{\rm L} = 1/4, \, p_{\rm H} = 3/4$ (subtasks 3, 4 and 5),
- $p_{\rm L} = 3/4, \, p_{\rm H} = 1/4$ (subtask 6).
The presented code signal $c(t)$ and the corresponding symbol sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle$ with $c_\nu \in \{{\rm P}, {\rm N}, {\rm M} \}$ results from the AMI coding (Alternate Mark Inversion) according to the following rule:
- The binary symbol $\rm L$ ⇒ Low is always represented by the ternary symbol $\rm N$ ⇒ Null .
- The binary symbol $\rm H$ ⇒ High is also coded deterministically but alternately (hence the name „AMI”) by the symbols $\rm P$ ⇒ Plus and $\rm M$ ⇒ Minus .
In this task, the decision content $H_0$ and the resulting entropy $H_{\rm C}$ the code symbol sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle$ are to be determined for the three parameter sets mentioned above. The relative redundancy of the code sequence results from this according to the equation
- $$r_{\rm C} = \frac{H_{\rm 0}-H_{\rm C}}{H_{\rm C}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- The task belongs to the chapter Sources with Memory.
- Reference is made in particular to the page Die Entropie des AMI–Codes.
- In general, the following relations exist between the decision content $H_0$, the entropy $H$ $($here equal to $H_{\rm C})$ und den Entropienäherungen:
- $$H \le \ \text{...} \ \le H_3 \le H_2 \le H_1 \le H_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In task 1.4 for equally probable symbols $\rm L$ and $\rm H$ the entropy approximations were calculated as follows (each in „bit/symbol”):
- $$H_1 = 1.500\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} H_2 = 1.375\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}H_3 = 1.292 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
- Therefore, for equally probable and statistically independent source symbols, the following holds:
- $$H_{\rm Q} {= 1 \,{\rm bit/Bin\ddot{a}rsymbol}} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} H_{\rm C} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1 \,{\rm bit/Tern\ddot{a}rsymbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) The decision content of a ternary source is $H_0 = \log_2 \; (3) = 1.585\; \rm bit/symbol$.
- This gives the following for the relative redundancy
- $$r_{\rm C} =1 -{H_{\rm C}/H_{\rm 0}}=1-1/{\rm log}_2\hspace{0.05cm}(3) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 36.9 \,\%} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) $H_{\rm C} = H_{\rm Q}$ is still valid. However, because of the unequal symbol probabilities, $H_{\rm Q}$ is now smaller:
- $$H_{\rm Q} = \frac{1}{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.05cm} (4) + \frac{3}{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4/3) {= 0.811 \,{\rm bit/binary symbol}} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} H_{\rm C} = H_{\rm Q} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 0.811 \,{\rm bit/Tern\ddot{a}rsymbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) By analogy with sub-task (2) $r_{\rm C} = 1 - 0.811/1.585 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 48.8 \,\%} \hspace{0.05cm} now holds.$
- One can generalise this result. Namely, it holds:
- $$(1-0.488) = (1- 0.189) \cdot (1- 0.369)\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} (1-r_{\rm Codefolge}) = (1-r_{\rm Quelle}) \cdot (1- r_{\rm AMI-Code}) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) Since each $\rm L$ is mapped to $\rm N$ and $\rm H$ is mapped alternately to $\rm M$ and $\rm P$, it holds that
- $$p_{\rm N} = p_{\rm L} = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm P} = p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm H}/2 = 3/8\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} H_1 = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4) + 2 \cdot {3}/{8} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(8/3) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.56 \,{\rm bit/ternary symbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) Now the probabilities of occurrence of the ternary symbols are $p_{\rm N} = 3/4$ sowie $p_{\rm P} = p_{\rm M} =1/8$. Thus:
- $$H_1 = {3}/{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4/3) + 2 \cdot {1}/{8} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(8) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.06 \,{\rm bit/Tern\ddot{a}rsymbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Interpretation:
- For $p_{\rm L} = 1/4, \ p_{\rm H} = 3/4$ gives $H_1 = 1.56 \; \rm bit/symbol$.
- For $p_{\rm L} = 3/4, \ p_{\rm H} = 1/4$ , on the other hand, $H_1 = 1.06 \; \rm bit/symbol$ results in a significantly smaller value.
- For both parameter combinations, however, the same applies:
- $$H_0 = 1.585 \,{\rm bit/symbol}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}H_{\rm C} = \lim_{k \rightarrow \infty } H_k = 0.811 \,{\rm bit/Symbol} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
It follows from this:
- If one considers two message sources $\rm Q1$ and $\rm Q2$ with the same symbol range $M$ ⇒ decision content $H_0 = \rm const.$, whereby the first-order entropy approximation $\rm Q1$ is clearly greater for source $(H_1)$ than for source $\rm Q2$, one cannot conclude from this by any means that the entropy of $\rm Q1$ is actually greater than the entropy of $\rm Q2$.
- Rather, one must
- calculate enough entropy approximations $H_1$, $H_2$, $H_3$, ... for both sources and
- determine from them (graphically or analytically) the limit value of $H_k$ für $k \to \infty$ .
- Only then is a final statement about the entropy ratios possible.