Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.6Z: Again on the Huffman Code"
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
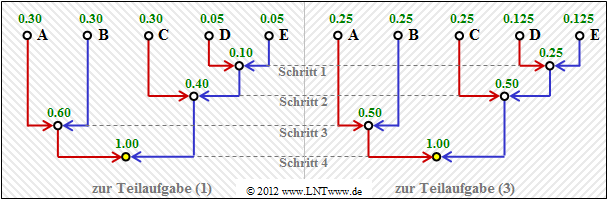
| − | [[File:Inf_Z_2_6a_version2.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:Inf_Z_2_6a_version2.png|right|frame|Huffman tree diagrams for subtasks '''(1)''' and '''(3)''']] |
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' <u>Solution suggestion 1</u> is correct. |
| − | * | + | *The diagram shows the construction of the Huffman code by means of a tree diagram. |
| − | * | + | *With the assignment red → <b>1</b> and blue → <b>0</b> one obtains: <br>$\rm A$ → <b>11</b>, $\rm B$ → <b>10</b>, $\rm C$ → <b>01</b>, $\rm D$ → <b>001</b>, $\rm E$ → <b>000</b>. |
| − | * | + | *The left diagram applies to the probabilities according to subtask '''(1)'''. |
| − | * | + | *The diagram on the right belongs to subtask '''(3)''' with slightly different probabilities. |
| − | * | + | *However, it provides exactly the same code. |
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' <u>Proposed solution 3</u> is correct, as the following calculation also shows: |
| − | :$$L_{\rm M} \hspace{0.2cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} (0.3 + 0.3 + 0.3) \cdot 2 + (0.05 + 0.05) \cdot 3 = 2.1\,{\rm bit/ | + | :$$L_{\rm M} \hspace{0.2cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} (0.3 + 0.3 + 0.3) \cdot 2 + (0.05 + 0.05) \cdot 3 = 2.1\,{\rm bit/source symbol}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ |
:$$H \hspace{0.2cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} 3 \cdot 0.3 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}(1/0.3) + 2 \cdot 0.05 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}(1/0.05) | :$$H \hspace{0.2cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} 3 \cdot 0.3 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}(1/0.3) + 2 \cdot 0.05 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}(1/0.05) | ||
| − | \approx 2.0\,{\rm bit/ | + | \approx 2.0\,{\rm bit/source symbol}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | * | + | *According to the source coding theorem, $L_{\rm M} \ge H$ always holds. |
| − | * | + | *However, a prerequisite for $L_{\rm M} = H$ is that all symbol probabilities can be represented in the form $2^{-k} \ (k = 1, \ 2, \ 3,\ \text{ ...})$ . |
| − | * | + | *This does not apply here. |
| − | '''(3)''' $\rm A$, $\rm B$ | + | '''(3)''' $\rm A$, $\rm B$ and $\rm C$ are represented by two bits in $\text{code 1}$ , $\rm E$ and $\rm F$ by three bits. Thus one obtains for |
| − | * | + | * the average codeword length |
:$$L_{\rm M} = p_{\rm A}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm B}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm C}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm D}\cdot 3 + p_{\rm E}\cdot 3 | :$$L_{\rm M} = p_{\rm A}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm B}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm C}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm D}\cdot 3 + p_{\rm E}\cdot 3 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * for the source entropy: |
:$$H = p_{\rm A}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm A}} + p_{\rm B}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm B}} + p_{\rm C}\cdot | :$$H = p_{\rm A}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm A}} + p_{\rm B}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm B}} + p_{\rm C}\cdot | ||
{\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm C}} + p_{\rm D}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm D}} + p_{\rm E}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm E}} | {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm C}} + p_{\rm D}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm D}} + p_{\rm E}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm E}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | By comparing all the terms, we arrive at the result: | |
:$$p_{\rm A}= p_{\rm B}= p_{\rm C}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.25} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm D}= p_{\rm E}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.125}\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$p_{\rm A}= p_{\rm B}= p_{\rm C}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.25} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm D}= p_{\rm E}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.125}\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| − | \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm M} = H = 2.25\,{\rm bit/ | + | \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm M} = H = 2.25\,{\rm bit/source symbol} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | It can be seen: | |
| − | * | + | *With these "more favourable" probabilities, there is even a larger mean codeword length than with the "less favourable" ones. |
| − | * | + | *The equality $(L_{\rm M} = H)$ is therefore solely due to the now larger source entropy. |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' For example, one (of many) simulations with the probabilities according to subtask '''(3)''' yields the sequence with $N = 40$ character: |
:$$\rm EBDCCBDABEBABCCCCCBCAABECAACCBAABBBCDCAB.$$ | :$$\rm EBDCCBDABEBABCCCCCBCAABECAACCBAABBBCDCAB.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *This results in $L_{\rm M}\hspace{0.01cm}' = ( 34 \cdot 2 + 6 \cdot 3)/50 = 2.15$ bit/source symbol, i.e. a smaller value than for the unlimited sequence $(L_{\rm M} = 2.25$ bit/source symbol$)$. |
| − | * | + | *However, with a different starting value of the random generator, $(L_{\rm M}\hspace{0.03cm}' \ge L_{\rm M})$ is also possible. |
| − | * | + | *This means: <u>All statements</u> are correct. |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' Only <u>solution suggestion 1</u>: |
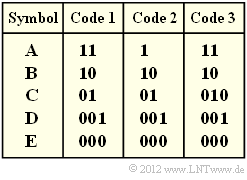
| − | * | + | * $\text{Code 1}$ is a Huffman code, as has already been shown in the previous subtasks. <br>This is not true for all symbol probabilities, but at least for the parameter sets according to subtasks '''(1)''' and '''(3)'''. |
| − | * | + | * $\text{Code 2}$ is not a Huffman code, since such a code would always have to be prefix-free. <br>However, the prefix freedom is not given here, since <b>0</b> is the beginning of the code word <b>01</b> . |
| − | * | + | * $\text{Code 3}$ is also not a Huffman code, since it has an average codeword length that is $p_{\rm C}$ longer than required $($see $\text{code 1})$. It is not optimal <br>There are no symbol probabilities $p_{\rm A}$, ... , $p_{\rm E}$, that would justify coding the symbol $\rm C$ with <b>010</b> instead of <b>01</b> . |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Revision as of 22:25, 2 August 2021
David Albert Huffman's algorithm implements entropy coding with the following properties:
- The resulting binary code is prefix-free and thus easily (and immediately) decodable.
- With a memoryless source, the code leads to the smallest possible mean codeword length $L_{\rm M}$.
- However, $L_{\rm M}$ is never smaller than the source entropy $H$.
- These two quantities can be calculated from the $M$ symbol probabilities alone.
For this exercise, we assume a memoryless source with the symbol range $M = 5$ and the alphabet
- $$\{ {\rm A},\ {\rm B},\ {\rm C},\ {\rm D},\ {\rm E} \}.$$
In the above diagram, three codes are given.nbsp; You are to decide which of these codes were (or could be) created by applying the Huffman algorithm.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Entropy Coding according to Huffman.
- Further information on the Huffman algorithm can also be found in the information sheet for exercise 2.6.
- To check your results, please refer to the interaction module Shannon–Fano– and Huffman–coding.
Questions
Solution
(1) Solution suggestion 1 is correct.
- The diagram shows the construction of the Huffman code by means of a tree diagram.
- With the assignment red → 1 and blue → 0 one obtains:
$\rm A$ → 11, $\rm B$ → 10, $\rm C$ → 01, $\rm D$ → 001, $\rm E$ → 000. - The left diagram applies to the probabilities according to subtask (1).
- The diagram on the right belongs to subtask (3) with slightly different probabilities.
- However, it provides exactly the same code.
(2) Proposed solution 3 is correct, as the following calculation also shows:
- $$L_{\rm M} \hspace{0.2cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} (0.3 + 0.3 + 0.3) \cdot 2 + (0.05 + 0.05) \cdot 3 = 2.1\,{\rm bit/source symbol}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$H \hspace{0.2cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} 3 \cdot 0.3 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}(1/0.3) + 2 \cdot 0.05 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}(1/0.05) \approx 2.0\,{\rm bit/source symbol}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- According to the source coding theorem, $L_{\rm M} \ge H$ always holds.
- However, a prerequisite for $L_{\rm M} = H$ is that all symbol probabilities can be represented in the form $2^{-k} \ (k = 1, \ 2, \ 3,\ \text{ ...})$ .
- This does not apply here.
(3) $\rm A$, $\rm B$ and $\rm C$ are represented by two bits in $\text{code 1}$ , $\rm E$ and $\rm F$ by three bits. Thus one obtains for
- the average codeword length
- $$L_{\rm M} = p_{\rm A}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm B}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm C}\cdot 2 + p_{\rm D}\cdot 3 + p_{\rm E}\cdot 3 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- for the source entropy:
- $$H = p_{\rm A}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm A}} + p_{\rm B}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm B}} + p_{\rm C}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm C}} + p_{\rm D}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm D}} + p_{\rm E}\cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1}{p_{\rm E}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
By comparing all the terms, we arrive at the result:
- $$p_{\rm A}= p_{\rm B}= p_{\rm C}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.25} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm D}= p_{\rm E}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.125}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm M} = H = 2.25\,{\rm bit/source symbol} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
It can be seen:
- With these "more favourable" probabilities, there is even a larger mean codeword length than with the "less favourable" ones.
- The equality $(L_{\rm M} = H)$ is therefore solely due to the now larger source entropy.
(4) For example, one (of many) simulations with the probabilities according to subtask (3) yields the sequence with $N = 40$ character:
- $$\rm EBDCCBDABEBABCCCCCBCAABECAACCBAABBBCDCAB.$$
- This results in $L_{\rm M}\hspace{0.01cm}' = ( 34 \cdot 2 + 6 \cdot 3)/50 = 2.15$ bit/source symbol, i.e. a smaller value than for the unlimited sequence $(L_{\rm M} = 2.25$ bit/source symbol$)$.
- However, with a different starting value of the random generator, $(L_{\rm M}\hspace{0.03cm}' \ge L_{\rm M})$ is also possible.
- This means: All statements are correct.
(5) Only solution suggestion 1:
- $\text{Code 1}$ is a Huffman code, as has already been shown in the previous subtasks.
This is not true for all symbol probabilities, but at least for the parameter sets according to subtasks (1) and (3).
- $\text{Code 2}$ is not a Huffman code, since such a code would always have to be prefix-free.
However, the prefix freedom is not given here, since 0 is the beginning of the code word 01 .
- $\text{Code 3}$ is also not a Huffman code, since it has an average codeword length that is $p_{\rm C}$ longer than required $($see $\text{code 1})$. It is not optimal
There are no symbol probabilities $p_{\rm A}$, ... , $p_{\rm E}$, that would justify coding the symbol $\rm C$ with 010 instead of 01 .