Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.3: Sinusoidal Characteristic"
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What distortion factor $K$ is obtained with the approximation $\underline{g_1(x)}$ of the characteristic curve independent of the amplitude $A$ of the input signal? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$K \ = \ $ { 0. } $\ \%$ | $K \ = \ $ { 0. } $\ \%$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Compute the distortion factor $K$ for the input signal $x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 \cdot t)$ and the approximation $\underline{g_3(x)}$. <br>What values arise as a result for $A = 0.5$ and $A = 1.0$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$A = 0.5\hspace{-0.08cm}:\ \ K \ = \ $ { 1.08 3% } $\ \%$ | $A = 0.5\hspace{-0.08cm}:\ \ K \ = \ $ { 1.08 3% } $\ \%$ | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the distortion factor for $\underline{A = 1.0}$ considering the approximation $\underline{g_5(x)}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$K \ = \ $ { 4.45 3% } $\ \%$ | $K \ = \ $ { 4.45 3% } $\ \%$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements are true? Here, $K$ denotes the distortion factor of the sine function $g(x)$. <br>$K_{\rm g3}$ and $K_{\rm g5}$ are based on the approximations $g_3(x)$ and $g_5(x)$, respectively. |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + $K_{\rm g5}$ | + | + $K_{\rm g5}$ generally represents a better approximation for $K$ than $K_{\rm g3}$. |
| − | - | + | - For $A = 1.0$ gilt $K_{\rm g3} < K_{\rm g5}$. |
| − | + | + | + For $A = 0.5$ wird $K_{\rm g3} \approx K_{\rm g5}$ gelten. |
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The very inaccurate approximation $g_1(x) = x$ is linear in $x$ and therefore does not result in nonlinear distortions. Hence, the distortion factor is $\underline{K = 0}$. |
Revision as of 21:50, 14 September 2021
We consider a system with input $x(t)$ and output $y(t)$. For simplicity of description, the signals are considered to be dimensionless.
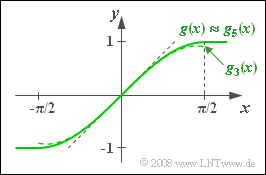
The relationship between the input signal $x(t)$ and the output signal $y(t)$ is given in the range between $-\pi/2$ and $+\pi/2$ by the following characteristic curve.
- $$g(x) = \sin(x) = x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$
The second part of this equation describes the series expansion of the sine function.
As approximations for the nonlinear characteristic curve the following is used in this task:
- $$g_1(x) = x\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ g_3(x) = x- x^{3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/6\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$g_5(x) = x- x^3\hspace{-0.1cm}/{6}+x^5\hspace{-0.1cm}/{120}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The input signal $x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 \cdot t)$ is always assumed wherat the values $A = 0.5$, $A = 1.0$ and $A = 1.5$ are to be considered for the (dimensionless) signal amplitude.
Please note:
- The task belongs to the chapter Nonlinear Distortion.
- The resulting signal curves for $x(t)$ and $y(t)$ are shown graphically on the page Description of nonlinear systems .
- All powers required here refer to the resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ and thus have the unit ${\rm V}^2$.
- The following trigonometric relations are assumed to be known:
- $$\cos^3(\alpha) = {3}/{4} \cdot \cos(\alpha) + {1}/{4} \cdot \cos(3\alpha) \hspace{0.05cm}, $$
- $$ \cos^5(\alpha) = {10}/{16} \cdot \cos(\alpha) + {5}/{16} \cdot \cos(3\alpha) + {1}/{16} \cdot \cos(5\alpha)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
(2) Das analytische Spektrum (nur positive Frequenzen) des Eingangssignals lautet:
- $$X_+(f) = A \cdot {\rm \delta}(f- f_0) .$$
- Am Ausgang der nichtlinearen Kennlinie $g_3(x)$ liegt dann folgendes Signal an:
- $$y(t) = A \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) - \frac{A^3}{6} \cdot {\rm cos}^3(\omega_0 t )= A \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) - \frac{3}{4} \cdot \frac{A^3}{6} \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t )- \frac{1}{4} \cdot \frac{A^3}{6} \cdot {\rm cos}(3\omega_0 t ) = A_1 \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) + A_3 \cdot {\rm cos}(3\omega_0 t ).$$
- Für die Koeffizienten $A_1$ und $A_3$ erhält man durch Koeffizientenvergleich:
- $$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8}, \hspace{0.5cm}A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24}.$$
- Mit $A = 0.5$ ergibt sich $A_1 \approx 0.484$ und $A_3 \approx 0.005$. Somit lautet der Klirrfaktor:
- $$K = K_3 ={|A_3|}/{A_1}= {0.005}/{0.484} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1.08\%}.$$
- Anzumerken ist, dass bei der Näherung $g_3(x)$ nur der kubische Anteil $K_3$ des Klirrfaktors wirksam ist.
- Für $A = 1.0$ und $A = 1.5$ ergeben sich folgende Zahlenwerte:
- $$A = 1.0: A_1 \approx 0.875, \hspace{0.2cm} A_3 \approx -0.041\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{K \approx 4.76\%}\; \; \Rightarrow \; \; K_{g3},$$
- $$A = 1.5: A_1 \approx 1.078, \hspace{0.2cm} A_3 \approx -0.140\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}{K \approx 13 \%}.$$
(3) In ähnlicher Weise wie beim Unterpunkt (2) gilt nun
- $$y(t) = A_1 \cdot {\rm cos}(\omega_0 t ) + A_3 \cdot {\rm cos}(3\omega_0 t )+ A_5 \cdot {\rm cos}(5\omega_0 t )$$
- mit folgenden Koeffizienten:
- $$A_1 = A - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{8} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{192},\hspace{0.3cm} A_3 = - {A^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{24} + {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{384},\hspace{0.3cm} A_5 = {A^5}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{1920}.$$
- Daraus ergeben sich mit $A=1$ die Zahlenwerte:
- $$A_1 \approx 1 -0.125 +0.005 = 0.880,\hspace{0.3cm} A_3 \approx -0.042 +0.003 = -0.039,\hspace{0.3cm} A_5 \approx 0.0005$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}K_3 = {|A_3|}/{A_1}= 0.0443,\hspace{0.3cm}K_5 = {|A_5|}/{A_1}= 0.0006 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} K = \sqrt{K_3^2 + K_5^2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 4.45\%} \; \; \Rightarrow \; \; K_{g5}.$$
(4) Richtig sind die Lösungsvorschläge 1 und 3:
- Der Ansatz $g_5(x)$ ist im gesamten Bereich eine bessere Näherung für die Sinusfunktion $g(x)$ als die Näherung $g_3(x)$.
- Deshalb ist der in der Teilaufgabe (3) berechnete Wert $K_{g5}$ eine bessere Näherung für den tatsächlichen Klirrfaktor als $K_{g3}$.
die erste Aussage ist somit richtig. - Die zweite Aussage ist falsch, wie schon die Berechnung für $A=1$ gezeigt hat: $K_{g3} \approx 4.76 \%$ ist größer als $K_{g5} \approx 4.45 \%$.
- Der Grund hierfür ist, dass $g_3(x)$ unterhalb von $g_5(x)$ liegt und damit auch eine größere Abweichung vom linearen Verlauf vorliegt.
- Für $A=0.5$ wird $K_{g5} \approx K_{g3} = 1.08 \%$ gelten.
- Die Kennlinie auf der Angabenseite zeigt, dass für $|x| \le 0.5$ die Funktionen $g_3(x)$ und $g_5(x)$ innerhalb der Zeichengenauigkeit nicht zu unterscheiden sind.
- Damit ergeben sich auch gleiche Klirrfaktoren.