Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.6Z: Magnitude and Phase"
From LNTwww
m (Text replacement - "analyse" to "analyze") |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
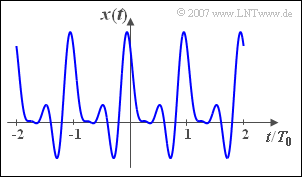
| − | [[File:P_ID348__Sig_Z_2_6.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID348__Sig_Z_2_6.png|right|frame|Signal $x(t)$ to be analyzed]] |
| − | The | + | The aim is to show the connection between |
| − | + | * the real Fourier coefficients $A_n$ und $B_n$, | |
| − | + | * the complex coefficients $D_n$, and | |
| − | + | * the magnitude or phase coefficients $(C_n$, $\varphi_n)$. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 17: | Line 14: | ||
:$$x(t)=1{\rm V+2V}\cdot\cos(\omega_0 t) +{\rm 2V}\cdot\cos(2\omega_0 t)- \ {\rm 1V}\cdot\sin(2\omega_0 t)-{\rm 1V}\cdot\sin(3\omega_0 t).$$ | :$$x(t)=1{\rm V+2V}\cdot\cos(\omega_0 t) +{\rm 2V}\cdot\cos(2\omega_0 t)- \ {\rm 1V}\cdot\sin(2\omega_0 t)-{\rm 1V}\cdot\sin(3\omega_0 t).$$ | ||
| − | This signal is shown in the graph in the range from $–2T_0$ | + | This signal is shown in the graph in the range from $–2T_0$ to $+2T_0$. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 26: | Line 21: | ||
''Hints:'' | ''Hints:'' | ||
| − | *This exercise belongs | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Signal_Representation/Fourier_Series|Fourier Series]]. |
| − | *You can find a compact summary of the topic in the two learning videos | + | *You can find a compact summary of the topic in the two learning videos |
| − | + | :[[Zur_Berechnung_der_Fourierkoeffizienten_(Lernvideo)|Zur Berechnung der Fourierkoeffizienten]] ⇒ "To calculate the Fourier coefficients", | |
| − | + | : [[Eigenschaften_der_Fourierreihendarstellung_(Lernvideo)|Eigenschaften der Fourierreihendarstellung]] ⇒ "Properties of the Fourier series representation". | |
| Line 36: | Line 31: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {What are the | + | {What are the coefficients $A_0$, $D_0$, $C_0$ and $\varphi_0$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$A_0\ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\text{V}$ | $A_0\ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\text{V}$ | ||
| Line 54: | Line 49: | ||
| − | {What are | + | {What are the coefficients $\varphi_1$, $C_1$ and $D_1$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\varphi_1\ = \ $ { 0. } $\text{deg}$ | $\varphi_1\ = \ $ { 0. } $\text{deg}$ | ||
| Line 62: | Line 57: | ||
| − | {What are | + | {What are the coefficients $\varphi_2$, $C_2$ and $D_2$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\varphi_2\ = \ $ { -26.6--26.5 } $\text{deg | + | $\varphi_2\ = \ $ { -26.6--26.5 } $\text{deg}$ |
$\text{Re}[D_2]\ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\text{V}$ | $\text{Re}[D_2]\ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\text{V}$ | ||
$\text{Im}[D_2]\ = \ $ { 0.5 3% } $\text{V}$ | $\text{Im}[D_2]\ = \ $ { 0.5 3% } $\text{V}$ | ||
| Line 70: | Line 65: | ||
| − | {What are | + | {What are the coefficients $\varphi_3$ and $C_3$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\varphi_3\ = \ $ { -91--89 } $\text{deg}$ | $\varphi_3\ = \ $ { -91--89 } $\text{deg}$ | ||
| Line 76: | Line 71: | ||
| − | {What is | + | {What is the complex Fourier coefficient $D_\text{–3}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\text{Re}[D_{-3}]\ = \ $ { 0. } $\text{V}$ | $\text{Re}[D_{-3}]\ = \ $ { 0. } $\text{V}$ | ||
| Line 86: | Line 81: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The DC signal coefficient is $A_0 = 1\,{\rm V}$. |
| − | * | + | *At the same time, $C_0 = D_0 = A_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} C_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 1\,{\rm V}}, \varphi_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 0}$. |
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' <u>The correct answers are 1, 3, 4 and 6</u>: | ||
| + | *There are no components with $\sin(\omega_0t)$ and $\cos(3\omega_0t)$. | ||
| + | *It follows directly that $B_1 = A_3 = 0$. | ||
| + | *All other coefficients listed here are non-zero. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''(3)''' In general: | ||
| − | |||
:$$\varphi_n=\arctan\left({B_n}/{A_n}\right),\hspace{0.5cm}C_n=\sqrt{A_n^2+B_n^2},\hspace{0.5cm}D_n={1}/{2} \cdot (A_n-{\rm j}\cdot B_n).$$ | :$$\varphi_n=\arctan\left({B_n}/{A_n}\right),\hspace{0.5cm}C_n=\sqrt{A_n^2+B_n^2},\hspace{0.5cm}D_n={1}/{2} \cdot (A_n-{\rm j}\cdot B_n).$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Because $B_1 = 0$ we get $\varphi_1 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 0}, \ C_1 = A_1 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 2 \,{\rm V}}$ and $D_1 = A_1/2 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 1 \,{\rm V}}$. |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' With $A_2 = 2\,{\rm V}$ and $B_2 = -1\,{\rm V}$ one obtains: |
:$$\varphi_2=\arctan(-0.5)\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-26.56^{\circ}},\hspace{0.5cm}C_2=\sqrt{A_2^2+B_2^2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=2.236 \; \rm V},$$ | :$$\varphi_2=\arctan(-0.5)\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-26.56^{\circ}},\hspace{0.5cm}C_2=\sqrt{A_2^2+B_2^2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=2.236 \; \rm V},$$ | ||
:$$D_2={1}/{2} \cdot (A_2-{\rm j}\cdot B_2)=1\;\rm V+{\rm j}\cdot 0.5\, {\rm V} | :$$D_2={1}/{2} \cdot (A_2-{\rm j}\cdot B_2)=1\;\rm V+{\rm j}\cdot 0.5\, {\rm V} | ||
| Line 113: | Line 109: | ||
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' It is $\varphi_3 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\hspace{0.1cm}-90^{\circ}}$ and $C_3 = |B_3| \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1 \,{\rm V}}$. |
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' It is $D_3 = -{\rm j} · B_3/2 ={\rm j}· 0.5 \,{\rm V}$ and $D_\text{–3} = D_3^{\star} ={\rm j}· B_3/2 = {- {\rm j} · 0.5 \,{\rm V}}$ |
:$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \text{Re}[D_{-3}]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=0}, \hspace{0.5cm}\text{Im}[D_{-3}]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\hspace{0.1cm}- 0.5 \,{\rm V}}.$$ | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \text{Re}[D_{-3}]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=0}, \hspace{0.5cm}\text{Im}[D_{-3}]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\hspace{0.1cm}- 0.5 \,{\rm V}}.$$ | ||
| Line 124: | Line 120: | ||
__NOEDITSECTION__ | __NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Signal Representation: Exercises|^2.4 Fourier Series^]] |
Latest revision as of 12:47, 22 September 2021
The aim is to show the connection between
- the real Fourier coefficients $A_n$ und $B_n$,
- the complex coefficients $D_n$, and
- the magnitude or phase coefficients $(C_n$, $\varphi_n)$.
For this we consider the periodic signal
- $$x(t)=1{\rm V+2V}\cdot\cos(\omega_0 t) +{\rm 2V}\cdot\cos(2\omega_0 t)- \ {\rm 1V}\cdot\sin(2\omega_0 t)-{\rm 1V}\cdot\sin(3\omega_0 t).$$
This signal is shown in the graph in the range from $–2T_0$ to $+2T_0$.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Fourier Series.
- You can find a compact summary of the topic in the two learning videos
- Zur Berechnung der Fourierkoeffizienten ⇒ "To calculate the Fourier coefficients",
- Eigenschaften der Fourierreihendarstellung ⇒ "Properties of the Fourier series representation".
Questions
Solution
(1) The DC signal coefficient is $A_0 = 1\,{\rm V}$.
- At the same time, $C_0 = D_0 = A_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm} C_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 1\,{\rm V}}, \varphi_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 0}$.
(2) The correct answers are 1, 3, 4 and 6:
- There are no components with $\sin(\omega_0t)$ and $\cos(3\omega_0t)$.
- It follows directly that $B_1 = A_3 = 0$.
- All other coefficients listed here are non-zero.
(3) In general:
- $$\varphi_n=\arctan\left({B_n}/{A_n}\right),\hspace{0.5cm}C_n=\sqrt{A_n^2+B_n^2},\hspace{0.5cm}D_n={1}/{2} \cdot (A_n-{\rm j}\cdot B_n).$$
- Because $B_1 = 0$ we get $\varphi_1 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 0}, \ C_1 = A_1 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 2 \,{\rm V}}$ and $D_1 = A_1/2 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 1 \,{\rm V}}$.
(4) With $A_2 = 2\,{\rm V}$ and $B_2 = -1\,{\rm V}$ one obtains:
- $$\varphi_2=\arctan(-0.5)\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-26.56^{\circ}},\hspace{0.5cm}C_2=\sqrt{A_2^2+B_2^2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=2.236 \; \rm V},$$
- $$D_2={1}/{2} \cdot (A_2-{\rm j}\cdot B_2)=1\;\rm V+{\rm j}\cdot 0.5\, {\rm V} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Re}[D_2]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1 \,{\rm V}}, \hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Im}[D_2]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0.5\, {\rm V}} .$$
(5) It is $\varphi_3 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\hspace{0.1cm}-90^{\circ}}$ and $C_3 = |B_3| \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1 \,{\rm V}}$.
(6) It is $D_3 = -{\rm j} · B_3/2 ={\rm j}· 0.5 \,{\rm V}$ and $D_\text{–3} = D_3^{\star} ={\rm j}· B_3/2 = {- {\rm j} · 0.5 \,{\rm V}}$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \text{Re}[D_{-3}]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=0}, \hspace{0.5cm}\text{Im}[D_{-3}]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\hspace{0.1cm}- 0.5 \,{\rm V}}.$$