Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.11Z: Extremely Asymmetrical Channel"
From LNTwww
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
:and corresponding post-differentialisation one obtains: | :and corresponding post-differentialisation one obtains: | ||
:$${1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{(1-p_0)/2}{1- (1-p_0)/2} +1 \stackrel{!}{=} 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{(1-p_0)/2}{(1+p_0)/2} +1 \stackrel{!}{=} 0$$ | :$${1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{(1-p_0)/2}{1- (1-p_0)/2} +1 \stackrel{!}{=} 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{(1-p_0)/2}{(1+p_0)/2} +1 \stackrel{!}{=} 0$$ | ||
| − | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1+p_0}{1-p_0} \stackrel{!}{=} 2 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{1+p_0}{1-p_0} \stackrel{!}{=} 4 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} p_0 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.6}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | + | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1+p_0}{1-p_0} \stackrel{!}{=} 2 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{1+p_0}{1-p_0} \stackrel{!}{=} 4 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} p_0 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.6}=p_0^{(*)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
Revision as of 13:14, 22 September 2021
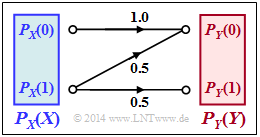
The channel shown opposite with the following properties is considered:
- The symbol $X = 0$ is always transmitted correctly and leads always to the result $Y = 0$.
- The symbol $X = 1$ is distorted to the maximum.
From the point of view of information theory, this means:
- $${\rm Pr}(Y \hspace{-0.05cm} = 0\hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} X \hspace{-0.05cm}= 1) ={\rm Pr}(Y \hspace{-0.05cm} = 1\hspace{-0.05cm}\mid \hspace{-0.05cm} X \hspace{-0.05cm}= 1) = 0.5 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
To be determined in this task are:
- the mutual information $I(X; Y)$ for $P_X(0) = p_0 = 0.4$ and $P_X(1) = p_1 = 0.6$.
The general rule is:
- $$ I(X;Y) = H(X) - H(X \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm} Y)\hspace{0.05cm}=H(Y) - H(Y \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm} X)\hspace{0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.15cm} H(X) + H(Y)- H(XY)\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- the channel capacity:
- $$ C = \max_{P_X(X)} \hspace{0.15cm} I(X;Y) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Application to digital signal transmission.
- Reference is made in particular to the page Channel capacity of a binary channel.
- In Exercise 3.14 the results found here are to be interpreted in comparison to the BSC channel.
Questions
Solution
(1) The source entropy results according to the binary entropy function:
- $$H(X) = H_{\rm bin}(p_0)= H_{\rm bin}(0.4) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.971\,{\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) The probabilities of the sink symbols are:
- $$P_Y(1) = p_1/2 = (1 - p_0)/2 = 0.3\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} P_Y(0) = 1-P_Y(1) = p_1/2 = (1 - p_0)/2 = 0.7$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H(Y) = H_{\rm bin}(\frac{1+p_0}{2})= H_{\rm bin}(0.7) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.881\,{\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) The joint probabilities $p_{μκ} = {\rm Pr}\big[(X = μ) ∩ (Y = κ)\big] $ are obtained as:
- $$ p_{00} = p_0 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} p_{01} = 0 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} p_{10} = (1 - p_0)/2 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} p_{11} = (1 - p_0)/2$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H(XY) =p_0 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{ p_0} + 2 \cdot \frac{1-p_0}{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{2}{ 1- p_0} = p_0 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{ p_0} + (1-p_0) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{ 1- p_0} + (1-p_0) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} (2)$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H(XY) =H_{\rm bin}(p_0) + 1 - p_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The numerical result for $p_0 = 0.4$ is thus:
- $$H(XY) = H_{\rm bin}(0.4) + 0.6 = 0.971 + 0.6 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=1.571\,{\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) A (possible) equation to calculate the mutual information is:
- $$ I(X;Y) = H(X) + H(Y)- H(XY)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- From this, using the results of the first three subtasks, one obtains:
- $$I(X;Y) = H_{\rm bin}(p_0) + H_{\rm bin}(\frac{1+p_0}{2}) - H_{\rm bin}(p_0) -1 + p_0 = H_{\rm bin}(\frac{1+p_0}{2}) -1 + p_0.$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} p_0 = 0.4 {\rm :}\hspace{0.5cm} I(X;Y) = H_{\rm bin}(0.7) - 0.6 = 0.881 - 0.6 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.281\,{\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) The channel capacity $C$ is the mutual information $I(X; Y)$ at best possible probabilities $p_0$ and $p_1$ of the source symbols.
- After differentiation, the determination equation is obtained:
- $$\frac{\rm d}{{\rm d}p_0} \hspace{0.1cm} I(X;Y) = \frac{\rm d}{{\rm d}p_0} \hspace{0.1cm} H_{\rm bin}(\frac{1+p_0}{2}) +1 \stackrel{!}{=} 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- With the differential quotient of the binary entropy function
- $$ \frac{\rm d}{{\rm d}p} \hspace{0.1cm} H_{\rm bin}(p) = {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1-p}{ p} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- and corresponding post-differentialisation one obtains:
- $${1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{(1-p_0)/2}{1- (1-p_0)/2} +1 \stackrel{!}{=} 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{(1-p_0)/2}{(1+p_0)/2} +1 \stackrel{!}{=} 0$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1+p_0}{1-p_0} \stackrel{!}{=} 2 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{1+p_0}{1-p_0} \stackrel{!}{=} 4 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} p_0 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.6}=p_0^{(*)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) Accordingly, for the channel capacity:
- $$C = I(X;Y) \big |_{p_0 \hspace{0.05cm}=\hspace{0.05cm} 0.6} = H_{\rm bin}(0.8) - 0.4 = 0.722 -0.4 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.322\,{\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Exercise 3.14 interprets this result in comparison to the BSC channel model.
(7) For the equivocation holds:
- $$ H(X \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm}Y) = H(X) - I(X;Y) = 0.971 -0.322 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.649\,{\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Because of $H_{\rm bin}(0.4) = H_{\rm bin}(0.6)$ the source entropy $H(X)$ is the same as in subtask (1).
- The sink entropy must be recalculated. With $p_0 = 0.6$ we get $H(Y) = H_{\rm bin}(0.8) = 0.722\ \rm bit$.
- This gives the irrelevance:
- $$H(Y \hspace{-0.1cm}\mid \hspace{-0.1cm} X) = H(Y) - I(X;Y) = 0.722 -0.322 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.400\,{\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$