Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.9: Higher-Level Modulation"
From LNTwww
| (29 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Information_Theory/AWGN_Channel_Capacity_for_Discrete_Input |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_Inf_A_4_9.png|right|frame|Some channel capacity curves]] |
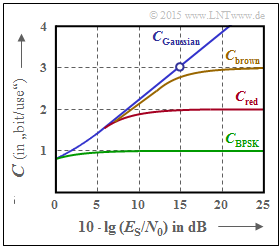
| − | + | The graph shows AWGN channel capacity curves over the $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0})$: | |
| − | + | * $C_\text{Gaussian}$: Shannon's boundary curve, | |
| − | + | * $C_\text{BPSK}$: valid for "Binary Phase Shift Keying". | |
| − | |||
| + | The two other curves $C_\text{red}$ and $C_\text{brown}$ should be analyzed and assigned to possible modulation schemes in subtasks '''(3)''' and '''(4)'''. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | [[ | + | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/AWGN–Kanalkapazität_bei_wertdiskretem_Eingang|AWGN channel capacity with discrete value input]]. |
| − | + | *Reference is made in particular to the page [[Information_Theory/AWGN–Kanalkapazität_bei_wertdiskretem_Eingang#The_channel_capacity_.7F.27.22.60UNIQ-MathJax81-QINU.60.22.27.7F_as_a_function_of_.7F.27.22.60UNIQ-MathJax82-QINU.60.22.27.7F|Channel capacity $C$ as a function of $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$]]. | |
| − | + | *Since the results are to be given in "bit" ⇒ "log" ⇒ "log<sub>2</sub>" is used in the equations. | |
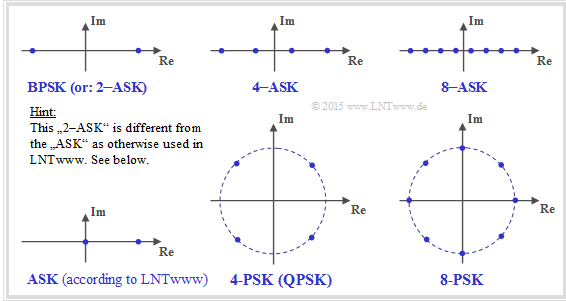
| + | *The modulation methods mentioned in the questions are described in terms of their signal space constellation <br>(see lower graph). | ||
| − | === | + | [[File:EN_Inf_A_4_9_Zusatz.png|right|frame|Proposed signal space constellations]] |
| + | |||
| + | '''Notes on nomenclature:''' | ||
| + | *In the literature, "BPSK" is sometimes also referred to as "2–ASK": | ||
| + | :$$x ∈ X = \{+1,\ -1\}.$$ | ||
| + | *In contrast, in our learning tutorial we understand as "ASK" the unipolar case: | ||
| + | :$$x ∈ X = \{0,\ 1 \}.$$ | ||
| + | *Therefore, according to our nomenclature: | ||
| + | :$$C_\text{ASK} < C_\text{BPSK}$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | But: This fact is irrelevant for the solution of the present problem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What equation underlies Shannon's boundary curve $C_{\rm Gaussian}$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - $C_{\rm Gaussian} = C_1= {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 1 + E_{\rm S}/{N_0})$ , |
| − | + | + | + $C_{\rm Gaussian} = C_2= {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 1 + 2 \cdot E_{\rm S}/{N_0})$ , |
| − | - | + | - $C_{\rm Gaussian} = C_3= {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 1 + E_{\rm S}/{N_0})$ . |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the green curve $(C_{\rm BPSK})$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + $C_{\rm BPSK}$ cannot be given in closed form. |
| − | + | + | + $C_{\rm BPSK}$ is greater than zero if $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} > 0$ is assumed. |
| − | - | + | - For $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} < \ln (2)$ ⇒ $C_{\rm BPSK} ≡ 0$. |
| − | + | + | + In the whole range $C_{\rm BPSK} < C_{\rm Gaussian} $ is valid. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the red curve $(C_{\rm red})$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - For the associated random variable $X$ holds $M_X = |X| = 2$. |
| − | + | + | + For the associated random variable $X$ holds $M_X = |X| = 4$. |
| − | + | + | + $C_{\rm red}$ is simultaneously the channel capacity of the "4–ASK". |
| − | - | + | - $C_{\rm red}$ is simultaneously the channel capacity of the "4–QAM". |
| − | + | + | + For all $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} > 0$ $C_{\rm red}$ is between "green" and "brown". |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the brown curve $(C_{\rm brown})$? <br>Note: $p_{\rm B}$ denotes the bit error probability here. |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + For the associated random variable $X$ ⇒ $M_X = |X| = 8$. |
| − | + | + | + $C_{\rm brown}$ is simultaneously the channel capacity of the "8–ASK". |
| − | - | + | - $C_{\rm brown}$ is simultaneously the channel capacity of the "8–PSK". |
| − | - | + | - $p_{\rm B} ≡ 0$ is possible with "8–ASK", $R = 2.5$ and $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 10 \ \rm dB$. |
| − | + | + | + $p_{\rm B} ≡ 0$ is possible with "8–ASK", $R = 2.0$ and $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 10 \ \rm dB$ . |
| Line 60: | Line 72: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''1 | + | '''(1)''' <u>Proposition 2</u> is correct, as shown by the calculation for $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 15 \ \rm dB$ ⇒ $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} = 31.62$: |
| − | '''2 | + | :$$C_2(15\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm dB}) = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 1 + 2 \cdot 31.62 ) = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 64.25 ) \approx 3\,{\rm bit/use}\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ |
| − | '''3 | + | *The other two proposed solutions provide the following numerical values: |
| − | ' | + | :$$C_3(15\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm dB}) \ = \ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 1 + 31.62 ) \approx 5.03\,{\rm bit/use}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ |
| − | '' | + | :$$ C_1(15\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm dB}) \ = \ C_3/2 \approx 2.51\,{\rm bit/use}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | ''' | + | *The proposed solution 3 corresponds to the case of "two independent Gaussian channels" with half transmission power per channel. |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' <u>Proposed solutions 1, 2 and 4</u> are correct: | ||
| + | *If one would replace $E_{\rm S}$ by $E_{\rm B}$, then the statement 3 would be also correct. | ||
| + | *For $E_{\rm B}/{N_0} < \ln (2)$ ⇒ $C_{\rm Gaussian} ≡ 0$ is valid, and therefore also $C_{\rm BPSK} ≡ 0$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' <u>Statements 2, 3 and 5</u> are correct: | ||
| + | *The red curve $(C_{\rm red})$ is always above $C_{\rm BPSK}$, but below $C_{\rm brown}$ and Shannon's boundary curve $(C_{\rm Gaussian})$. | ||
| + | *The statements also hold if (for certain $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$ values) curves are indistinguishable within the drawing precision. | ||
| + | *From the limit $C_{\rm red}= 2 \ \rm bit/use$ for $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} → ∞$, the symbol set size $M_X = |X| = 4$. | ||
| + | *Thus, the red curve describes "4–ASK". $M_X = |X| = 2$ would apply to the "BPSK". | ||
| + | *The "4–QAM" leads exactly to the same final value "2 bit/use". For small $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$ values, however, the channel capacity $C_{\rm 4–QAM}$ is above the red curve, since $C_{\rm red}$ is bounded by the Gaussian boundary curve $(C_2)$, but $C_{\rm 4–QAM}$ is bounded by $C_3$. The designations $C_2$ and $C_3$ here refer to subtask '''(1)'' | ||
| + | |||
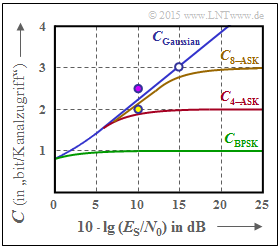
| + | [[File:EN_Inf_A_4_9e_v2.png|right|frame|Channel capacity limits for <br>BPSK, 4–ASK and 8–ASK]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | '''(4)''' <u>Proposed solutions 1, 2 and 5</u> are correct: | ||
| + | *From the brown curve, one can see the correctness of the first two statements. | ||
| + | *The "8–PSK" with I– and Q–components – i.e. with $K = 2$ dimensions – lies slightly above the brown curve for small $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$ values ⇒ the answer 3 is incorrect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In the graph, the two "8–ASK"nbsp; systems are also drawn as dots according to propositions 4 and 5. | ||
| + | * The purple dot is above the $C_{\rm 8–ASK}$ curve ⇒ $R = 2.5$ and $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 10 \ \rm dB$ are not enough to decode the "8–ASK" without errors ⇒ $R > C_{\rm 8–ASK}$ ⇒ channel coding theorem is not satisfied ⇒ answer 4 is wrong. | ||
| + | * However, if we reduce the code rate to $R = 2 < C_{\rm 8–ASK}$ for the same $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 10 \ \rm dB$ according to the yellow dot, the channel coding theorem is satisfied ⇒ answer 5 is correct. | ||
| + | |||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Information Theory: Exercises|^4.3 AWGN and Value-Discrete Input^]] |
Latest revision as of 15:28, 4 November 2021
The graph shows AWGN channel capacity curves over the $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0})$:
- $C_\text{Gaussian}$: Shannon's boundary curve,
- $C_\text{BPSK}$: valid for "Binary Phase Shift Keying".
The two other curves $C_\text{red}$ and $C_\text{brown}$ should be analyzed and assigned to possible modulation schemes in subtasks (3) and (4).
Hints:
- The task belongs to the chapter AWGN channel capacity with discrete value input.
- Reference is made in particular to the page Channel capacity $C$ as a function of $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$.
- Since the results are to be given in "bit" ⇒ "log" ⇒ "log2" is used in the equations.
- The modulation methods mentioned in the questions are described in terms of their signal space constellation
(see lower graph).
Notes on nomenclature:
- In the literature, "BPSK" is sometimes also referred to as "2–ASK":
- $$x ∈ X = \{+1,\ -1\}.$$
- In contrast, in our learning tutorial we understand as "ASK" the unipolar case:
- $$x ∈ X = \{0,\ 1 \}.$$
- Therefore, according to our nomenclature:
- $$C_\text{ASK} < C_\text{BPSK}$$
But: This fact is irrelevant for the solution of the present problem.
Questions
Solution
(1) Proposition 2 is correct, as shown by the calculation for $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 15 \ \rm dB$ ⇒ $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} = 31.62$:
- $$C_2(15\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm dB}) = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 1 + 2 \cdot 31.62 ) = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 64.25 ) \approx 3\,{\rm bit/use}\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
- The other two proposed solutions provide the following numerical values:
- $$C_3(15\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm dB}) \ = \ {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} ( 1 + 31.62 ) \approx 5.03\,{\rm bit/use}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ C_1(15\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm dB}) \ = \ C_3/2 \approx 2.51\,{\rm bit/use}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The proposed solution 3 corresponds to the case of "two independent Gaussian channels" with half transmission power per channel.
(2) Proposed solutions 1, 2 and 4 are correct:
- If one would replace $E_{\rm S}$ by $E_{\rm B}$, then the statement 3 would be also correct.
- For $E_{\rm B}/{N_0} < \ln (2)$ ⇒ $C_{\rm Gaussian} ≡ 0$ is valid, and therefore also $C_{\rm BPSK} ≡ 0$.
(3) Statements 2, 3 and 5 are correct:
- The red curve $(C_{\rm red})$ is always above $C_{\rm BPSK}$, but below $C_{\rm brown}$ and Shannon's boundary curve $(C_{\rm Gaussian})$.
- The statements also hold if (for certain $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$ values) curves are indistinguishable within the drawing precision.
- From the limit $C_{\rm red}= 2 \ \rm bit/use$ for $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} → ∞$, the symbol set size $M_X = |X| = 4$.
- Thus, the red curve describes "4–ASK". $M_X = |X| = 2$ would apply to the "BPSK".
- The "4–QAM" leads exactly to the same final value "2 bit/use". For small $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$ values, however, the channel capacity $C_{\rm 4–QAM}$ is above the red curve, since $C_{\rm red}$ is bounded by the Gaussian boundary curve $(C_2)$, but $C_{\rm 4–QAM}$ is bounded by $C_3$. The designations $C_2$ and $C_3$ here refer to subtask '(1)
(4) Proposed solutions 1, 2 and 5 are correct:
- From the brown curve, one can see the correctness of the first two statements.
- The "8–PSK" with I– and Q–components – i.e. with $K = 2$ dimensions – lies slightly above the brown curve for small $E_{\rm S}/{N_0}$ values ⇒ the answer 3 is incorrect.
In the graph, the two "8–ASK"nbsp; systems are also drawn as dots according to propositions 4 and 5.
- The purple dot is above the $C_{\rm 8–ASK}$ curve ⇒ $R = 2.5$ and $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 10 \ \rm dB$ are not enough to decode the "8–ASK" without errors ⇒ $R > C_{\rm 8–ASK}$ ⇒ channel coding theorem is not satisfied ⇒ answer 4 is wrong.
- However, if we reduce the code rate to $R = 2 < C_{\rm 8–ASK}$ for the same $10 \cdot \lg (E_{\rm S}/{N_0}) = 10 \ \rm dB$ according to the yellow dot, the channel coding theorem is satisfied ⇒ answer 5 is correct.