Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.2: Mismatched Line"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Some_Results_from_Line_Transmission_Theory |
}} | }} | ||
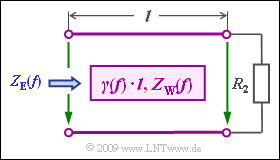
| − | [[File:P_ID1799__LZI_A_4_2.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1799__LZI_A_4_2.png|right|frame|Message line with wiring]] |
| − | + | A transmission system occupies the range from $f_{\rm U} = 10 \ \rm MHz$ to $f_{\rm O} = 40 \ \rm MHz$. | |
| − | + | The transmission line used also has a constant wave impedance $Z_{\rm W} = 100 \ \rm \Omega$ (real), which does not quite correspond to reality, since the wave impedance usually decreases slightly with frequency and often an imaginary part (usually smaller) must also be taken into account. | |
| − | + | The line is supplied by a voltage source with internal resistance $R_{\rm 1} = 100 \ \rm \Omega$ and is terminated by resistor $R_{\rm 2}$ . The input impedance of the line is given by | |
:$$Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm W}\cdot \frac {R_2 + Z_{\rm W} \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} | :$$Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm W}\cdot \frac {R_2 + Z_{\rm W} \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} | ||
{Z_{\rm W}+ R_2 \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} | {Z_{\rm W}+ R_2 \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The complex propagation function should – again very simplified – approximated by a real function: | |
:$$\frac {\gamma(f)}{1\,{\rm Np/km}} = \frac {\alpha(f)}{1\,{\rm Np/km}} = \sqrt{f/f_{\rm O}} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}f_{\rm O} = 40\,{\rm MHz}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\frac {\gamma(f)}{1\,{\rm Np/km}} = \frac {\alpha(f)}{1\,{\rm Np/km}} = \sqrt{f/f_{\rm O}} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}f_{\rm O} = 40\,{\rm MHz}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Notes:'' |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Some_Results_from_Line_Transmission_Theory|Some Results from Line Transmission Theory]]. |
| − | * | + | * In particular, it should be examined whether there are reflections. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are valid for the wave impedance $Z_{\rm W}$ of a line in general? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $Z_{\rm W}$ | + | - $Z_{\rm W}$ depends on the line length. |
| − | + $Z_{\rm W}$ | + | + $Z_{\rm W}$ can be frequency dependent. |
| − | + $Z_{\rm W}$ | + | + $Z_{\rm W}$ can take on complex values at certain frequencies. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are valid for the wiring with $R_1 = R_2 = Z_{\rm W}$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The input impedance $Z_{\rm E}(f)$ is equal to the wave impedance. |
| − | + | + | + The input impedance $Z_{\rm E}(f)$ is frequency independent. |
| − | - | + | - The input impedance $Z_{\rm E}(f)$ depends on the line length. |
| − | + $R_1 = R_2 =Z_{\rm W}$ | + | + $R_1 = R_2 =Z_{\rm W}$ indicates the best possible wiring. |
| − | { | + | {At which line length $l = l_\text{min}$ do $Z_{\rm E}$ and $Z_{\rm W}$ differ by less than $1\%$ in the '''short-circuit case''' $(R_{\rm 2} = 0)$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$f_{\rm U} = 10\ {\rm MHz}\hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm} l_\text{min}\ = \ $ { 5.3 3% } $\ \rm km$ | $f_{\rm U} = 10\ {\rm MHz}\hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm} l_\text{min}\ = \ $ { 5.3 3% } $\ \rm km$ | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
| − | { | + | {At what line length $l = l_\text{min}$ do $Z_{\rm E}$ differ from $Z_{\rm W}$ in '''idle''' $(R_2 → ∞)$ by less than $1\%$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$f_{\rm U} = 10\ {\rm MHz}\hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm} l_\text{min}\ = \ $ { 5.3 3% } $\ \rm km$ | $f_{\rm U} = 10\ {\rm MHz}\hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm} l_\text{min}\ = \ $ { 5.3 3% } $\ \rm km$ | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' <u>Solutions 2 and 3</u> are correct: |
| − | * | + | *The wave impedance $Z_{\rm W}$ is defined as the quotient of voltage and current of the wave propagating along the line. |
| − | * | + | *The wave impedance $Z_{\rm W}$ is independent of the location. |
| − | * | + | *Therefore, $Z_{\rm W}$ is also independent of the line length $l$ and is determined solely by the primary line parameters $R\hspace{0.05cm}'$, $L\hspace{0.05cm}'$, $G\hspace{0.08cm}'$ and $C\hspace{0.08cm}'$. |
| − | * | + | *The following equation given in the theory section |
:$$Z_{\rm W}(f) = \sqrt{\frac {R\hspace{0.05cm}' + {\rm j} \cdot \omega L\hspace{0.05cm}'}{G\hspace{0.08cm}' + {\rm j} \cdot \omega C\hspace{0.08cm}'}} | :$$Z_{\rm W}(f) = \sqrt{\frac {R\hspace{0.05cm}' + {\rm j} \cdot \omega L\hspace{0.05cm}'}{G\hspace{0.08cm}' + {\rm j} \cdot \omega C\hspace{0.08cm}'}} | ||
\hspace{0.1cm}\bigg |_{\hspace{0.05cm} \omega \hspace{0.05cm}= \hspace{0.05cm}2\pi f}$$ | \hspace{0.1cm}\bigg |_{\hspace{0.05cm} \omega \hspace{0.05cm}= \hspace{0.05cm}2\pi f}$$ | ||
| − | + | makes it clear that the wave impedance does depend on the frequency and is generally also complex-valued. | |
| − | + | It should be noted that wave impedance is not a resistor in the sense of a user: | |
| − | * | + | *The wave impedance does not characterize the line as a lossy element. |
| − | * | + | *Even a lossless line has a wave impedance. |
| − | * | + | *Similarly, a wave impedance is always defined in the propagation of an electromagnetic wave. |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' With the terminating resistor $Z_{\rm 2}(f) = Z_{\rm W}(f)$ the resistance value transformed to the beginning of the line is also equal to the characteristic impedance, independent of the line length: |
:$$Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm W}(f)\cdot \frac {Z_{\rm 2}(f) + Z_{\rm W}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} | :$$Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm W}(f)\cdot \frac {Z_{\rm 2}(f) + Z_{\rm W}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} | ||
{Z_{\rm W}(f)+ Z_{\rm 2}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)}= | {Z_{\rm W}(f)+ Z_{\rm 2}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)}= | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
{Z_{\rm W}(f)+ Z_{\rm W}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)}= | {Z_{\rm W}(f)+ Z_{\rm W}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)}= | ||
Z_{\rm W}(f) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | Z_{\rm W}(f) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | <u>Solutions 1, 2 and 4</u> are correct: | |
| − | * | + | *Since $Z_{\rm W}(f) = Z_{\rm W}$ was assumed to be frequency-independent in the exercise, the input impedance $Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm E}$ is also frequency-independent. |
| − | * | + | *In contrast, with frequency-dependent wave impedance with real termination, reflections cannot be avoided for all frequencies. |
| − | *Die Beschaltung $R_1 = R_2 =Z_{\rm W}$ ⇒ $R_1 =Z_{\rm E}$ | + | *Die Beschaltung $R_1 = R_2 =Z_{\rm W}$ ⇒ $R_1 =Z_{\rm E}$ is to be aimed at, since then the maximum power is delivered by the source. |
Revision as of 16:02, 5 November 2021
A transmission system occupies the range from $f_{\rm U} = 10 \ \rm MHz$ to $f_{\rm O} = 40 \ \rm MHz$.
The transmission line used also has a constant wave impedance $Z_{\rm W} = 100 \ \rm \Omega$ (real), which does not quite correspond to reality, since the wave impedance usually decreases slightly with frequency and often an imaginary part (usually smaller) must also be taken into account.
The line is supplied by a voltage source with internal resistance $R_{\rm 1} = 100 \ \rm \Omega$ and is terminated by resistor $R_{\rm 2}$ . The input impedance of the line is given by
- $$Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm W}\cdot \frac {R_2 + Z_{\rm W} \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} {Z_{\rm W}+ R_2 \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm tanh}(x) = \frac {{\rm e}^{x}-{\rm e}^{-x}}{{\rm e}^{x}+{\rm e}^{-x}}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}x \in {\cal C} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The complex propagation function should – again very simplified – approximated by a real function:
- $$\frac {\gamma(f)}{1\,{\rm Np/km}} = \frac {\alpha(f)}{1\,{\rm Np/km}} = \sqrt{f/f_{\rm O}} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}f_{\rm O} = 40\,{\rm MHz}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Some Results from Line Transmission Theory.
- In particular, it should be examined whether there are reflections.
Questions
Solution
- The wave impedance $Z_{\rm W}$ is defined as the quotient of voltage and current of the wave propagating along the line.
- The wave impedance $Z_{\rm W}$ is independent of the location.
- Therefore, $Z_{\rm W}$ is also independent of the line length $l$ and is determined solely by the primary line parameters $R\hspace{0.05cm}'$, $L\hspace{0.05cm}'$, $G\hspace{0.08cm}'$ and $C\hspace{0.08cm}'$.
- The following equation given in the theory section
- $$Z_{\rm W}(f) = \sqrt{\frac {R\hspace{0.05cm}' + {\rm j} \cdot \omega L\hspace{0.05cm}'}{G\hspace{0.08cm}' + {\rm j} \cdot \omega C\hspace{0.08cm}'}} \hspace{0.1cm}\bigg |_{\hspace{0.05cm} \omega \hspace{0.05cm}= \hspace{0.05cm}2\pi f}$$
makes it clear that the wave impedance does depend on the frequency and is generally also complex-valued.
It should be noted that wave impedance is not a resistor in the sense of a user:
- The wave impedance does not characterize the line as a lossy element.
- Even a lossless line has a wave impedance.
- Similarly, a wave impedance is always defined in the propagation of an electromagnetic wave.
(2) With the terminating resistor $Z_{\rm 2}(f) = Z_{\rm W}(f)$ the resistance value transformed to the beginning of the line is also equal to the characteristic impedance, independent of the line length:
- $$Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm W}(f)\cdot \frac {Z_{\rm 2}(f) + Z_{\rm W}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} {Z_{\rm W}(f)+ Z_{\rm 2}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)}= Z_{\rm W}(f)\cdot \frac {Z_{\rm W}(f) + Z_{\rm W}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)} {Z_{\rm W}(f)+ Z_{\rm W}(f) \cdot {\rm tanh}(\gamma(f) \cdot l)}= Z_{\rm W}(f) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Solutions 1, 2 and 4 are correct:
- Since $Z_{\rm W}(f) = Z_{\rm W}$ was assumed to be frequency-independent in the exercise, the input impedance $Z_{\rm E}(f) = Z_{\rm E}$ is also frequency-independent.
- In contrast, with frequency-dependent wave impedance with real termination, reflections cannot be avoided for all frequencies.
- Die Beschaltung $R_1 = R_2 =Z_{\rm W}$ ⇒ $R_1 =Z_{\rm E}$ is to be aimed at, since then the maximum power is delivered by the source.
(3) Mit dem Abschlusswiderstand $R_{\rm 2} = 0$ ⇒ Kurzschluss folgt aus der angegebenen Gleichung mit reellem $x = \gamma (f) \cdot l$:
- $$\frac{Z_{\rm E}(f)}{Z_{\rm W}} = {\rm tanh}(x) = \frac {{\rm e}^{x}-{\rm e}^{-x}}{{\rm e}^{x}+{\rm e}^{-x}}= \frac {{\rm e}^{2x}-1}{{\rm e}^{2x}+1}.$$
Insbesondere gilt:
- $${Z_{\rm E}(f)}/{Z_{\rm W}} = 0.99 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm e}^{2x} = 199\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} x ={1}/{2}\cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(199) \approx 2.65\,{\rm Np}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- $$f_{\rm U} = 10\,\text {MHz:}\hspace{0.2cm}\alpha(f_{\rm U})= 0.5\,{\rm Np/km}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}l_{\rm min}= \frac{2.65\,{\rm Np}}{0.5\,{\rm Np/km}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 5.3\,{\rm km}} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ f_{\rm O} = 40\,\text {MHz:}\hspace{0.2cm}\alpha(f_{\rm U})= 1.0\,{\rm Np/km}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}l_{\rm min}= \frac{2.65\,{\rm Np}}{1.0\,{\rm Np/km}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2.65\,{\rm km}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Das heißt:
- Bei der Frequenz $f_{\rm O} = 40\ {\rm MHz}$ genügt bereits die Leitungslänge $l= 2.65 \ \rm km$, um Reflexionen weitgehend zu unterdrücken.
- Bei niedrigerer Frequenz $f_{\rm U} = 10\ {\rm MHz}$ ist wegen des geringeren Dämpfungsmaßes eine größere Kabellänge erforderlich.
- Diese Aussagen beziehen sich natürlich nur auf das Vermeiden von Reflexionen.
- Insgesamt ist natürlich die niedrigere Signalfrequenz günstiger als die höhere.
(4) In gleicher Weise erhält man für $R_2 → ∞$ ⇒ Leerlauf die Gleichung
- $$\frac{Z_{\rm E}(f)}{Z_{\rm W}} = \frac{1}{{\rm tanh}(x)} = \frac {{\rm e}^{2x}+1}{{\rm e}^{2x}-1}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Im Gegensatz zum Kurzschluss–Fall ergibt sich nun für den Quotienten $Z_{\rm E}/Z_{\rm W} > 1$:
- $${Z_{\rm E}(f)}/{Z_{\rm W}} = 1.01 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm e}^{2x} = 201\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} x ={1}/{2}\cdot{\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(201) \approx 2.65\,{\rm Np}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Näherungsweise erhält man hier das gleiche Ergebnis wie bei Teilaufgabe (3):
- Bei der Frequenz $f_{\rm O} = 40\ {\rm MHz}$ genügt bereits die Leitungslänge $l= 2.65 \ \rm km$, um Reflexionen weitgehend zu unterdrücken.
- Bei der niedrigeren Frequenz $f_{\rm U} = 10\ {\rm MHz}$ ist wegen des geringeren Dämpfungsmaßes eine größere Kabellänge erforderlich.