Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 5.6Z: Single-Carrier and Multi-Carrier System"
From LNTwww
| (21 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/General_Description_of_OFDM |
}} | }} | ||
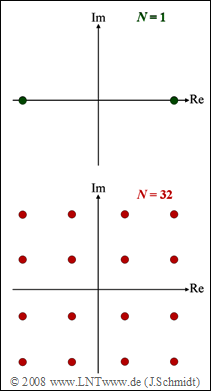
| − | [[File:P_ID1660__Z_5_6.png|right|]] | + | [[File:P_ID1660__Z_5_6.png|right|frame|Signal space assignments for $\rm SC$ (above), $\rm MC$ (bottom)]] |
| − | In | + | In this exercise, a comparison is to be made between |
| + | *a single-carrier $\rm (SC)$ system $(N = 1)$, and | ||
| + | *a multi-carrier $\rm (MC)$ system with $N = 32$ carriers. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | For both transmission systems (see diagram), a data bit rate of $R_{\rm B} = 1 \ \rm Mbit/s$ is required in each case. | |
| − | === | + | Notes: |
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Allgemeine_Beschreibung_von_OFDM|General Description of OFDM]]. | ||
| + | *Reference is also made to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Quadratur%E2%80%93Amplitudenmodulation|Quadrature Amplitude Modulation]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which mapping does the single-carrier system use? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
- ASK, | - ASK, | ||
+ BPSK, | + BPSK, | ||
- 4-QAM | - 4-QAM | ||
| − | - | + | - 16-QAM |
| − | { | + | {Which mapping does the multi-carrier system use? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
- ASK, | - ASK, | ||
- BPSK, | - BPSK, | ||
| Line 30: | Line 37: | ||
+ 16-QAM | + 16-QAM | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the symbol duration $T_{\rm SC}$ of the single-carrier system. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $T_{ | + | $T_{\rm SC} \ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\ \rm µ s$ |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the symbol duration $T_{\rm MC}$ of the multi-carrier system. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $T_{MC}$ | + | $T_{\rm MC} \ = \ $ { 128 3% } $\ \rm µ s$ |
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements is true? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
| − | - | + | - The intersymbol interferences are independent of the symbol duration $T$. |
| − | + | + | + The intersymbol interferences decrease with increasing symbol duration $T$. |
| − | - | + | - The intersymbol interferences increase with increasing symbol duration $T$. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''1.''' | + | '''(1)''' From the diagram on the front page, it is immediately apparent that the single-carrier system is based on "binary phase modulation" $\rm (BPSK)$ ⇒ <u>solution 2</u>. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' In contrast, the multi-carrier system is based on $\rm 16–QAM$ ⇒ <u>solution 4</u>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' In general, for an OFDM system with $N$ carriers and $M$ signal space points, the symbol duration is: | ||
| + | :$$T = N \cdot {\rm{log}_2}\hspace{0.04cm}(M) \cdot T_{\rm{B}}.$$ | ||
| + | *Because of $R_{\rm{B}} = 1 \ \rm Mbit/s$, the bit duration for BPSK is equal to $T_{\rm{B}} = 1 \ \rm µ s$. | ||
| + | *From this, the symbol duration of the single-carrier system with $N = 1$ and $M = 2$ is: | ||
| + | :$$ T_{\rm{SC}} = 1 \cdot {\rm{log}_2}\hspace{0.04cm}(2) \cdot T_{\rm{B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1\,\,{\rm µ s}}.$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''(4)''' Similarly, for the multi-carrier system with $N = 32$ and $M = 16$, we obtain: |
| − | + | :$$T_{\rm{MC}} = 32 \cdot {\rm{log}_2}\hspace{0.04cm}(16) \cdot T_{\rm{B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 128\,\,{\rm µ s}}.$$ | |
| − | |||
| − | $$ T_{\rm{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''5 | + | '''(5)''' <u>Solution 2</u> is correct because: |
| + | *At large symbol duration, the relative fraction extending from the predecessor symbol into the symbol under consideration and thus causing intersymbol interference $\rm (ISI)$ is smaller than at small symbol duration. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 67: | Line 80: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Modulation Methods: Exercises|^5.5 General Description of OFDM^]] |
Latest revision as of 12:00, 10 January 2022
In this exercise, a comparison is to be made between
- a single-carrier $\rm (SC)$ system $(N = 1)$, and
- a multi-carrier $\rm (MC)$ system with $N = 32$ carriers.
For both transmission systems (see diagram), a data bit rate of $R_{\rm B} = 1 \ \rm Mbit/s$ is required in each case.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter General Description of OFDM.
- Reference is also made to the chapter Quadrature Amplitude Modulation.
Questions
Solution
(1) From the diagram on the front page, it is immediately apparent that the single-carrier system is based on "binary phase modulation" $\rm (BPSK)$ ⇒ solution 2.
(2) In contrast, the multi-carrier system is based on $\rm 16–QAM$ ⇒ solution 4.
(3) In general, for an OFDM system with $N$ carriers and $M$ signal space points, the symbol duration is:
- $$T = N \cdot {\rm{log}_2}\hspace{0.04cm}(M) \cdot T_{\rm{B}}.$$
- Because of $R_{\rm{B}} = 1 \ \rm Mbit/s$, the bit duration for BPSK is equal to $T_{\rm{B}} = 1 \ \rm µ s$.
- From this, the symbol duration of the single-carrier system with $N = 1$ and $M = 2$ is:
- $$ T_{\rm{SC}} = 1 \cdot {\rm{log}_2}\hspace{0.04cm}(2) \cdot T_{\rm{B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1\,\,{\rm µ s}}.$$
(4) Similarly, for the multi-carrier system with $N = 32$ and $M = 16$, we obtain:
- $$T_{\rm{MC}} = 32 \cdot {\rm{log}_2}\hspace{0.04cm}(16) \cdot T_{\rm{B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 128\,\,{\rm µ s}}.$$
(5) Solution 2 is correct because:
- At large symbol duration, the relative fraction extending from the predecessor symbol into the symbol under consideration and thus causing intersymbol interference $\rm (ISI)$ is smaller than at small symbol duration.