Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.10Z: Rayleigh? Or Rice?"
From LNTwww
m (Nabil verschob die Seite Zusatzaufgaben:3.10 Rayleigh oder Rice nach 3.10Z Rayleigh oder Rice) |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Further_Distributions |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID149__Sto_Z_3_10.png|right|]] | + | [[File:P_ID149__Sto_Z_3_10.png|right|frame|Does the present PDF describe "Rayleigh" or "Rice"?]] |
| − | + | The probability density function of the random variable $x$ is given as follows: | |
| − | :$$f_x(x)=\frac{\it x}{\lambda^{2}}\cdot\rm e^{- | + | :$$f_x(x)=\frac{\it x}{\lambda^{2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{-x^{\rm 2}/(\lambda^{\rm 2})}.$$ |
| − | + | Correspondingly, for the associated distribution function: | |
| − | :$$F_x(r)= {\rm Pr}(x \le r) = 1-\rm e^{- | + | :$$F_x(r)= {\rm Pr}(x \le r) = 1-{\rm e}^{- r^{\rm 2}/(2 \lambda^{\rm 2})}.$$ |
| − | + | *It is known that the value $x_0 = 2$ occurs most frequently. | |
| + | *This also means that the PDF $f_x(x)$ is maximum at $x = x_0 $. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | : | + | Hints: |
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Further_Distributions|"Further Distributions"]]. | ||
| + | *In particular, reference is made to the sections [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Further_Distributions#Rayleigh_PDF|"Rayleigh PDF"]] and [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Further_Distributions#Rice_PDF|"Rice PDF"]] . | ||
| + | *You can check your results with interactive applet [[Applets:PDF,_CDF_and_Moments_of_Special_Distributions|"PDF, CDF and moments of special distributions"]]. | ||
| + | *Consider the following definite integral in the solution: | ||
| + | :$$\int_{0}^{\infty}x^{\rm 2}\cdot {\rm e}^{ -x^{\rm 2}/\rm 2} \, {\rm d}x=\sqrt{{\pi}/{\rm 2}}.$$ | ||
| − | === | + | |
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | { Which of the following statements are true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - It is a rice-distributed random variable. |
| − | + | + It is a rayleigh distributed random variable. | |
| − | - | + | - The 3rd order central moment ⇒ $\mu_3$ is zero. |
| − | + | - The kurtosis has the value $K_x = 3$. | |
| − | { | + | {What is the numerical value of the distribution parameter $\lambda$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\lambda$ | + | $\lambda \ = \ $ { 2 3% } |
| − | { | + | {What is the probability that $x$ is less than $x_0 = 2$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $Pr(x < x_0 )$ | + | ${\rm Pr}(x < x_0 ) \ = \ $ { 39.3 3% } $\ \%$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the mean value of the random variable $x$? Interpretation. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $m_x$ | + | $m_x \ = \ $ { 2.506 3% } |
| − | { | + | {With what probability is $x$ larger than its mean $m_x$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $Pr (x > m_x)$ | + | ${\rm Pr}(x > m_x) \ = \ $ { 45.6 3% } $\ \%$ |
| − | |||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | + | '''(1)''' Correct is <u>only the second proposed solution</u>. | |
| + | *Because of the given PDF there is no Rice distribution, but a <u>Rayleigh distribution</u>. | ||
| + | *This is asymmetric around the mean $m_x$ so that $\mu_3 \ne 0$ . | ||
| + | *Only in the case of a Gaussian distributed random variable does the kurtosis $K = 3$. | ||
| + | *For the Rayleigh distribution, a larger value $(K = 3.245)$ is obtained due to more pronounced PDF emitters, independent of $\lambda$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' The derivative of the PDF with respect to $x$ yields: | ||
| + | :$$\frac{{\rm d} f_x(x)}{{\rm d} x} = \frac{\rm 1}{\lambda^{\rm 2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{ -{x^{\rm 2}}/({2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}+\frac{ x}{ \lambda^{\rm 2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{ -{x^{\rm 2}}/({ 2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}\cdot(-\frac{2 x}{2 \lambda^{\rm 2}}).$$ | ||
| + | *From this follows as the equation of determination for $x_0$ (only the positive solution is meaningful): | ||
| + | :$$\frac{1}{\lambda^{\rm 2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{ -{x_{\rm 0}^{\rm 2}}/{(2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}\cdot(\rm 1-{\it x_{\rm 0}^{\rm 2}}/{\it \lambda^{\rm 2}})=0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad {\it x}_0=\it \lambda.$$ | ||
| − | + | *Thus, we obtain for the distribution parameter $\lambda = x_0\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2}$. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(3)''' The probability we are looking for is equal to the cumulative distribution function $\rm (CDF)$ at the point $r = x_0 = \lambda$: | |
| + | :$${\rm Pr}(x<x_{\rm 0})={\rm Pr}( x \le x_{\rm 0})= | ||
| + | F_x(x_{\rm 0})=1-{\rm e}^{-{\lambda^{\rm 2}}/({ 2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}=1-{\rm e}^{-0.5}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\rm 39.3\%}.$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | '''(4)''' For example, the mean can be calculated using the following equation: | ||
:$$m_x=\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\hspace{-0.45cm}x\cdot f_x(x)\,{\rm d}x=\int_{\rm 0}^{\infty}\frac{\it x^{\rm 2}}{\it \lambda^{\rm 2}} \cdot \rm e^{-{\it x^{\rm 2}}/({\rm 2\it \lambda^{\rm 2}})}\,{\rm d}\it x = \sqrt{{\rm \pi}/{\rm 2}}\cdot \it \lambda\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\rm 2.506}.$$ | :$$m_x=\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\hspace{-0.45cm}x\cdot f_x(x)\,{\rm d}x=\int_{\rm 0}^{\infty}\frac{\it x^{\rm 2}}{\it \lambda^{\rm 2}} \cdot \rm e^{-{\it x^{\rm 2}}/({\rm 2\it \lambda^{\rm 2}})}\,{\rm d}\it x = \sqrt{{\rm \pi}/{\rm 2}}\cdot \it \lambda\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\rm 2.506}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The mean $m_x$ is of course larger than $x_0$ $(=$ maximum value of the PDF$)$, since the PDF is bounded downward but not upward. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | '''(5)''' In general, for the sought probability: | |
| − | :$$\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr}(x>m_x)=1- F_x(m_x).$$ |
| − | + | *With the given CDF and the result of the subtask '''(4)''' we obtain: | |
| − | :$$\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr}(x>m_x)={\rm e}^{-{m_x^{\rm 2}}/({ 2\lambda^{\rm 2})}}={\rm e}^{-\pi/ 4}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx \rm 45.6\%}.$$ |
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Theory of Stochastic Signals: Exercises|^3.7 Further Distributions^]] |
Latest revision as of 11:59, 3 February 2022
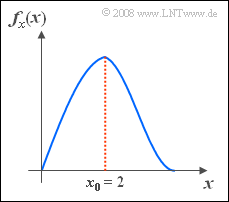
The probability density function of the random variable $x$ is given as follows:
- $$f_x(x)=\frac{\it x}{\lambda^{2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{-x^{\rm 2}/(\lambda^{\rm 2})}.$$
Correspondingly, for the associated distribution function:
- $$F_x(r)= {\rm Pr}(x \le r) = 1-{\rm e}^{- r^{\rm 2}/(2 \lambda^{\rm 2})}.$$
- It is known that the value $x_0 = 2$ occurs most frequently.
- This also means that the PDF $f_x(x)$ is maximum at $x = x_0 $.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Further Distributions".
- In particular, reference is made to the sections "Rayleigh PDF" and "Rice PDF" .
- You can check your results with interactive applet "PDF, CDF and moments of special distributions".
- Consider the following definite integral in the solution:
- $$\int_{0}^{\infty}x^{\rm 2}\cdot {\rm e}^{ -x^{\rm 2}/\rm 2} \, {\rm d}x=\sqrt{{\pi}/{\rm 2}}.$$
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct is only the second proposed solution.
- Because of the given PDF there is no Rice distribution, but a Rayleigh distribution.
- This is asymmetric around the mean $m_x$ so that $\mu_3 \ne 0$ .
- Only in the case of a Gaussian distributed random variable does the kurtosis $K = 3$.
- For the Rayleigh distribution, a larger value $(K = 3.245)$ is obtained due to more pronounced PDF emitters, independent of $\lambda$.
(2) The derivative of the PDF with respect to $x$ yields:
- $$\frac{{\rm d} f_x(x)}{{\rm d} x} = \frac{\rm 1}{\lambda^{\rm 2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{ -{x^{\rm 2}}/({2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}+\frac{ x}{ \lambda^{\rm 2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{ -{x^{\rm 2}}/({ 2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}\cdot(-\frac{2 x}{2 \lambda^{\rm 2}}).$$
- From this follows as the equation of determination for $x_0$ (only the positive solution is meaningful):
- $$\frac{1}{\lambda^{\rm 2}}\cdot{\rm e}^{ -{x_{\rm 0}^{\rm 2}}/{(2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}\cdot(\rm 1-{\it x_{\rm 0}^{\rm 2}}/{\it \lambda^{\rm 2}})=0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad {\it x}_0=\it \lambda.$$
- Thus, we obtain for the distribution parameter $\lambda = x_0\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2}$.
(3) The probability we are looking for is equal to the cumulative distribution function $\rm (CDF)$ at the point $r = x_0 = \lambda$:
- $${\rm Pr}(x<x_{\rm 0})={\rm Pr}( x \le x_{\rm 0})= F_x(x_{\rm 0})=1-{\rm e}^{-{\lambda^{\rm 2}}/({ 2 \lambda^{\rm 2}})}=1-{\rm e}^{-0.5}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\rm 39.3\%}.$$
(4) For example, the mean can be calculated using the following equation:
- $$m_x=\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\hspace{-0.45cm}x\cdot f_x(x)\,{\rm d}x=\int_{\rm 0}^{\infty}\frac{\it x^{\rm 2}}{\it \lambda^{\rm 2}} \cdot \rm e^{-{\it x^{\rm 2}}/({\rm 2\it \lambda^{\rm 2}})}\,{\rm d}\it x = \sqrt{{\rm \pi}/{\rm 2}}\cdot \it \lambda\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=\rm 2.506}.$$
- The mean $m_x$ is of course larger than $x_0$ $(=$ maximum value of the PDF$)$, since the PDF is bounded downward but not upward.
(5) In general, for the sought probability:
- $${\rm Pr}(x>m_x)=1- F_x(m_x).$$
- With the given CDF and the result of the subtask (4) we obtain:
- $${\rm Pr}(x>m_x)={\rm e}^{-{m_x^{\rm 2}}/({ 2\lambda^{\rm 2})}}={\rm e}^{-\pi/ 4}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx \rm 45.6\%}.$$