Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.3Z: DSB-AM due to Nonlinearity"
m |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/Double-Sideband_Amplitude_Modulation |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID999__Mod_Z_2_3.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID999__Mod_Z_2_3.png|right|frame|DSB–AM with nonlinearity]] |
| − | In | + | In this task, we consider the realization of a double-sideband amplitude modulation $\text{DSB-AM}$ using the nonlinear characteristic curve: |
:$$y = g(x) = c_1 \cdot x + c_2 \cdot x^2+ c_3 \cdot x^3\hspace{0.05cm}$$ | :$$y = g(x) = c_1 \cdot x + c_2 \cdot x^2+ c_3 \cdot x^3\hspace{0.05cm}$$ | ||
| − | :$$ \Rightarrow | + | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm} c_1 = 2,\hspace{0.5cm}c_2 = 0.25/{\rm V},\hspace{0.5cm}c_3 = 0 \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm or}\hspace{0.5cm}c_3 = 0.01/{\rm V^2}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | The sum of the carrier signal $ z(t)$ and the source signal $ q(t)$ is present at the input of this characteristic curve: | |
:$$ x(t) = z(t) + q(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t)+ q(t),\hspace{0.2cm} A_{\rm T} = 4\,{\rm V}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ x(t) = z(t) + q(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t)+ q(t),\hspace{0.2cm} A_{\rm T} = 4\,{\rm V}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *It is known that the source signal $q(t)$ contains spectral components between $1 \ \rm kHz$ and $9 \ \rm kHz$ (up to and including these limits). | |
| + | *From subtask '''(5)''' onwards, the following source signal should be assumed: | ||
:$$q(t) = A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$q(t) = A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *Let the angular frequencies be $ω_1 = 2 π · 1 \ \rm kHz$ and $ω_9 = 2 π · 9\ \rm kHz$. The corresponding amplitudes are given as: $A_1 = 1\ \rm V$ and $A_9 = 2\ \rm V$. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | The following abbreviations are used in the questions for this task: | ||
:$$ y(t) = y_1(t) + y_2(t)+y_3(t),$$ | :$$ y(t) = y_1(t) + y_2(t)+y_3(t),$$ | ||
:$$y_1(t) = c_1 \cdot [z(t) + q(t)],$$ | :$$y_1(t) = c_1 \cdot [z(t) + q(t)],$$ | ||
:$$ y_2(t) = c_2 \cdot[z(t) + q(t)]^2,$$ | :$$ y_2(t) = c_2 \cdot[z(t) + q(t)]^2,$$ | ||
:$$y_3(t) = c_3 \cdot [z(t) + q(t)]^3 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$y_3(t) = c_3 \cdot [z(t) + q(t)]^3 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Thus, the transmitted signals $s(t)$ i.e., $s_1(t)$, $s_2(t)$ and $s_3(t)$, result from band-limiting to the range from $90 \ \rm kHz$ to $110 \ \rm kHz$. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Double-Sideband_Amplitude_Modulation|Double-Sideband Amplitude Modulation]]. |
| − | * | + | *Particular reference is made to the page [[Modulation_Methods/Double-Sideband_Amplitude_Modulation#Amplitude_modulation_with_a_quadratic_characteristic_curve|Amplitude modulation with a quadratic characteristic curve]]. |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | *The following trigonometric transformations are given: |
:$$ \cos^2(\alpha) = {1}/{2} \cdot \left[ 1 + \cos(2\alpha)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} | :$$ \cos^2(\alpha) = {1}/{2} \cdot \left[ 1 + \cos(2\alpha)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} | ||
\cos^3(\alpha) = {1}/{4} \cdot \left[ 3 \cdot \cos(\alpha) + \cos(3\alpha)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \cos^3(\alpha) = {1}/{4} \cdot \left[ 3 \cdot \cos(\alpha) + \cos(3\alpha)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is a reasonable choice for the carrier frequency? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$f_{\rm T} \ = \ $ { 100 3% } $\ \text{kHz}$ | $f_{\rm T} \ = \ $ { 100 3% } $\ \text{kHz}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What signal components does $s_1(t)$ include? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The term $c_1 \cdot z(t)$, |
| − | - | + | - the term $c_1 \cdot q(t)$. |
| − | { | + | {What signal components does $s_2(t)$ include? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The term $c_2 · z^2(t)$, |
| − | - | + | - the term $c_2 · q^2(t)$, |
| − | + | + | + the term $2c_2 · z(t) · q(t)$. |
| − | { | + | {What signal components does $s_3(t)$ (at least partially) include? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The term $c_3 · z^3(t)$, |
| − | - | + | - the term $3 · c_3 · z^2(t) · q(t)$, |
| − | + | + | + the term $3 · c_3 · z(t) · q^2(t)$, |
| − | - | + | - the term $c_3 · q^3(t)$. |
| − | { | + | {Calculate $s(t)$, when $c_3 = 0$ and the source signal $q(t)$ is composed of two cosine oscillations. What is the modulation depth $m$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$m \ = \ $ { 0.75 3% } | $m \ = \ $ { 0.75 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Now calculate the transmitted signal $s(t)$ given $c_3 = \rm 0.01/V^{2}$. Which of the following statements are true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + Because $c_3 ≠ 0$ the spectral line changes at $f_{\rm T}$. |
| − | - | + | - Because $c_3 ≠ 0$ linear distortions arise, which can be compensated for. |
| − | + | + | + Because $c_3 ≠ 0$ nonlinear (i.e. irreversible) distortions arise. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The carrier frequency is most sensibly equal to the center frequency of the bandpass: $f_{\rm T}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 100\ \rm kHz}$. |
| + | *If $f_{\rm T}$ does not deviate from this by more than $±1 \ \rm kHz$, this also results in a "DSB-AM". | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' $s_1(t)$ includes only the carrier $z(t)$ ⇒ <u>Answer 1</u>. The source signal $q(t)$ is removed by the band-pass. | ||
| + | |||
| − | '''( | + | '''(3)''' The quadratic term $z^2(t)$ consists of a DC component $($at $f = 0)$ and a component at $2f_{\rm T}$. |
| + | *Additionally, all spectral components of $q^2(t)$ are outside the band-pass. | ||
| + | *Therefore the <u>last answer</u> is correct. | ||
| − | |||
| + | '''(4)''' <u>Answers 1 and 3</u> are correct: | ||
| + | *The term $\cos^3(ω_Tt)$ has its largest signal component at $f = f_{\rm T}$. | ||
| + | *The third answer $(3 · c_3 · z(t) · q^2(t))$ lies between $100\ \rm kHz ± 18 \ \rm kHz $. | ||
| + | *Some parts – namely the frequency components between $90\ \rm kHz $ and $110 \ \rm kHz$ – are not removed by the band-pass and are thus also included in $s(t)$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''(5)''' | + | [[File:P_ID993__Mod_Z_2_3_f.png|right|frame|Generated DSB-AM spectrum]] |
| + | '''(5)''' The transmitted signal consists of a total of five frequencies: | ||
:$$s(t) = c_1 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t)+ c_2 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 1})t) + c_2 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot A_{\rm 2} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 2})t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$s(t) = c_1 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t)+ c_2 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 1})t) + c_2 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot A_{\rm 2} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 2})t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *Note that the second term and the third term each contain two signal frequencies:: | |
| − | + | **$\text{99 kHz}$ and $\text{101 kHz}$ and | |
| − | + | **$\text{91 kHz}$ and $\text{109 kHz}$, respectively. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Given $A_{\rm T} = 4 \ \rm V$, $A_1 = 1 V$, $A_9 = 2 \ \rm V$, $c_1 = 1$ and $c_2 = 1/A_{\rm T} = \rm 0.25/V$, it holds that: | ||
:$$s(t) = 4\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t) + 1\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 1})t) + 2\,{\rm V}\cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 2})t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$s(t) = 4\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t) + 1\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 1})t) + 2\,{\rm V}\cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 2})t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *From this it can be seen that for the modulation depth: | |
:$$m =\frac{A_1 + A_9}{A_{\rm T}} = \rm \frac{1\ V + 2 \ V}{4 \ V} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=0.75}.$$ | :$$m =\frac{A_1 + A_9}{A_{\rm T}} = \rm \frac{1\ V + 2 \ V}{4 \ V} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=0.75}.$$ | ||
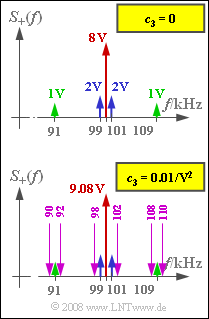
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' The graph above shows the spectrum $S_+(f)$ – that is, only positive frequencies – where $c_3 = 0$. |
| + | * When $c_3 ≠ 0$ the following additional spectral components arise: | ||
:$$c_3 \cdot z^3(t)= \frac{c_3 \cdot A_{\rm T}^3}{4} \cdot \left[ 3 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t) + \cos(3\omega_{\rm T} t)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$c_3 \cdot z^3(t)= \frac{c_3 \cdot A_{\rm T}^3}{4} \cdot \left[ 3 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t) + \cos(3\omega_{\rm T} t)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The first component falls in the pass-band of the band-pass. As a result, the Dirac weight at $f_{\rm T} = 100\ \rm kHz$ is increased from the original $8 \ \rm V$ to |
| − | * | + | :$$\text{8 V + 0.75 · 0.01/V}^2 · 4^3 \text{ V}^3 = 8.48 \ \rm V.$$ |
| + | |||
| + | *Furthermore, the third spectral component of subtask '''(4)''' provides an unwanted contribution to $S_+(f)$. In this case: | ||
:$$q^2(t) = \left[A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t)\right]^2 = A_{\rm 1}^2 \cdot \cos^2(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+ A_{\rm 9}^2 \cdot \cos^2(\omega_{\rm 9}t) + | :$$q^2(t) = \left[A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t)\right]^2 = A_{\rm 1}^2 \cdot \cos^2(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+ A_{\rm 9}^2 \cdot \cos^2(\omega_{\rm 9}t) + | ||
2 \cdot A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)\cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t)$$ | 2 \cdot A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)\cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t)$$ | ||
:$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} q^2(t) = \frac{A_{\rm 1}^2}{2} +\frac{A_{\rm 1}^2}{2} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 2} t)+ \frac{A_{\rm 9}^2}{2} + \frac{A_{\rm 9}^2}{2} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 18} t) + A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 8} t)+ A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 10} t).$$ | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} q^2(t) = \frac{A_{\rm 1}^2}{2} +\frac{A_{\rm 1}^2}{2} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 2} t)+ \frac{A_{\rm 9}^2}{2} + \frac{A_{\rm 9}^2}{2} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 18} t) + A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 8} t)+ A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 10} t).$$ | ||
| − | + | *After multiplying by $z(t)$, all but the fourth of these contributions fall within the $\text{90 kHz}$ to $\text{110 kHz}$ range. The weight at $f_{\rm T} = 100\ \rm kHz$ is further increased by $3 · c_3 · A_{\rm T} · 0.5 (A_1^2 + A_9^2) = 0.6\ \rm V$ and is thus $9.08 \ \rm V$. | |
| − | *$98 \ \rm kHz$ | + | |
| − | * $92 \ \rm kHz$ | + | |
| − | * $90 \ \rm kHz$ | + | Further components are obtained at: |
| + | *$98 \ \rm kHz$ and $102 \ \rm kHz$ with weights $c_3 · A_{\rm T}/2 · A_1^2/2 = 0.03\ \rm V$, | ||
| + | * $92 \ \rm kHz$ and $108 \ \rm kHz$ with weights $3c_3 · A_{\rm T}/2 · A_1 · A_9 = 0.12\ \rm V$, | ||
| + | * $90 \ \rm kHz$ and $110 \ \rm kHz$ with weights $3c_3 · A_{\rm T}/2 · A_1 · A_9 = 0.12\ \rm V$. | ||
| − | + | The lower plot in the above graph shows the spectrum $S_+(f)$ considering the cubic components. It can be seen that new frequencies have appeared, indicating nonlinear distortions. The correct solutions are therefore <u>Answers 1 and 3</u>. | |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 118: | Line 139: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Modulation Methods: Exercises|^2.1 Double Sideband Amplitude Modulation^]] |
Latest revision as of 17:02, 24 March 2022
In this task, we consider the realization of a double-sideband amplitude modulation $\text{DSB-AM}$ using the nonlinear characteristic curve:
- $$y = g(x) = c_1 \cdot x + c_2 \cdot x^2+ c_3 \cdot x^3\hspace{0.05cm}$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm} c_1 = 2,\hspace{0.5cm}c_2 = 0.25/{\rm V},\hspace{0.5cm}c_3 = 0 \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm or}\hspace{0.5cm}c_3 = 0.01/{\rm V^2}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The sum of the carrier signal $ z(t)$ and the source signal $ q(t)$ is present at the input of this characteristic curve:
- $$ x(t) = z(t) + q(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t)+ q(t),\hspace{0.2cm} A_{\rm T} = 4\,{\rm V}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- It is known that the source signal $q(t)$ contains spectral components between $1 \ \rm kHz$ and $9 \ \rm kHz$ (up to and including these limits).
- From subtask (5) onwards, the following source signal should be assumed:
- $$q(t) = A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Let the angular frequencies be $ω_1 = 2 π · 1 \ \rm kHz$ and $ω_9 = 2 π · 9\ \rm kHz$. The corresponding amplitudes are given as: $A_1 = 1\ \rm V$ and $A_9 = 2\ \rm V$.
The following abbreviations are used in the questions for this task:
- $$ y(t) = y_1(t) + y_2(t)+y_3(t),$$
- $$y_1(t) = c_1 \cdot [z(t) + q(t)],$$
- $$ y_2(t) = c_2 \cdot[z(t) + q(t)]^2,$$
- $$y_3(t) = c_3 \cdot [z(t) + q(t)]^3 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Thus, the transmitted signals $s(t)$ i.e., $s_1(t)$, $s_2(t)$ and $s_3(t)$, result from band-limiting to the range from $90 \ \rm kHz$ to $110 \ \rm kHz$.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Double-Sideband Amplitude Modulation.
- Particular reference is made to the page Amplitude modulation with a quadratic characteristic curve.
- The following trigonometric transformations are given:
- $$ \cos^2(\alpha) = {1}/{2} \cdot \left[ 1 + \cos(2\alpha)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} \cos^3(\alpha) = {1}/{4} \cdot \left[ 3 \cdot \cos(\alpha) + \cos(3\alpha)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
- If $f_{\rm T}$ does not deviate from this by more than $±1 \ \rm kHz$, this also results in a "DSB-AM".
(2) $s_1(t)$ includes only the carrier $z(t)$ ⇒ Answer 1. The source signal $q(t)$ is removed by the band-pass.
(3) The quadratic term $z^2(t)$ consists of a DC component $($at $f = 0)$ and a component at $2f_{\rm T}$.
- Additionally, all spectral components of $q^2(t)$ are outside the band-pass.
- Therefore the last answer is correct.
(4) Answers 1 and 3 are correct:
- The term $\cos^3(ω_Tt)$ has its largest signal component at $f = f_{\rm T}$.
- The third answer $(3 · c_3 · z(t) · q^2(t))$ lies between $100\ \rm kHz ± 18 \ \rm kHz $.
- Some parts – namely the frequency components between $90\ \rm kHz $ and $110 \ \rm kHz$ – are not removed by the band-pass and are thus also included in $s(t)$.
(5) The transmitted signal consists of a total of five frequencies:
- $$s(t) = c_1 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t)+ c_2 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 1})t) + c_2 \cdot A_{\rm T} \cdot A_{\rm 2} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 2})t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Note that the second term and the third term each contain two signal frequencies::
- $\text{99 kHz}$ and $\text{101 kHz}$ and
- $\text{91 kHz}$ and $\text{109 kHz}$, respectively.
- Given $A_{\rm T} = 4 \ \rm V$, $A_1 = 1 V$, $A_9 = 2 \ \rm V$, $c_1 = 1$ and $c_2 = 1/A_{\rm T} = \rm 0.25/V$, it holds that:
- $$s(t) = 4\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t) + 1\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 1})t) + 2\,{\rm V}\cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} \pm \omega_{\rm 2})t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- From this it can be seen that for the modulation depth:
- $$m =\frac{A_1 + A_9}{A_{\rm T}} = \rm \frac{1\ V + 2 \ V}{4 \ V} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=0.75}.$$
(6) The graph above shows the spectrum $S_+(f)$ – that is, only positive frequencies – where $c_3 = 0$.
- When $c_3 ≠ 0$ the following additional spectral components arise:
- $$c_3 \cdot z^3(t)= \frac{c_3 \cdot A_{\rm T}^3}{4} \cdot \left[ 3 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} t) + \cos(3\omega_{\rm T} t)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The first component falls in the pass-band of the band-pass. As a result, the Dirac weight at $f_{\rm T} = 100\ \rm kHz$ is increased from the original $8 \ \rm V$ to
- $$\text{8 V + 0.75 · 0.01/V}^2 · 4^3 \text{ V}^3 = 8.48 \ \rm V.$$
- Furthermore, the third spectral component of subtask (4) provides an unwanted contribution to $S_+(f)$. In this case:
- $$q^2(t) = \left[A_{\rm 1} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t)\right]^2 = A_{\rm 1}^2 \cdot \cos^2(\omega_{\rm 1} t)+ A_{\rm 9}^2 \cdot \cos^2(\omega_{\rm 9}t) + 2 \cdot A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} t)\cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 9} t)$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} q^2(t) = \frac{A_{\rm 1}^2}{2} +\frac{A_{\rm 1}^2}{2} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 2} t)+ \frac{A_{\rm 9}^2}{2} + \frac{A_{\rm 9}^2}{2} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 18} t) + A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 8} t)+ A_{\rm 1} \cdot A_{\rm 9} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 10} t).$$
- After multiplying by $z(t)$, all but the fourth of these contributions fall within the $\text{90 kHz}$ to $\text{110 kHz}$ range. The weight at $f_{\rm T} = 100\ \rm kHz$ is further increased by $3 · c_3 · A_{\rm T} · 0.5 (A_1^2 + A_9^2) = 0.6\ \rm V$ and is thus $9.08 \ \rm V$.
Further components are obtained at:
- $98 \ \rm kHz$ and $102 \ \rm kHz$ with weights $c_3 · A_{\rm T}/2 · A_1^2/2 = 0.03\ \rm V$,
- $92 \ \rm kHz$ and $108 \ \rm kHz$ with weights $3c_3 · A_{\rm T}/2 · A_1 · A_9 = 0.12\ \rm V$,
- $90 \ \rm kHz$ and $110 \ \rm kHz$ with weights $3c_3 · A_{\rm T}/2 · A_1 · A_9 = 0.12\ \rm V$.
The lower plot in the above graph shows the spectrum $S_+(f)$ considering the cubic components. It can be seen that new frequencies have appeared, indicating nonlinear distortions. The correct solutions are therefore Answers 1 and 3.