Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.6Z:Optimum Nyquist Equalizer for Exponential Pulse"
From LNTwww
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Digital_Signal_Transmission/Linear_Nyquist_Equalization}} | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Digital_Signal_Transmission/Linear_Nyquist_Equalization}} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1434__Dig_Z_3_6.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1434__Dig_Z_3_6.png|right|frame|Two-sided exponential pulse]] |
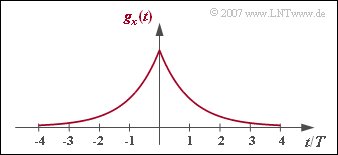
| − | + | As in [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.6:_Transversal_Filter_of_the_Optimal_Nyquist_Equalizer|"Exercise 3.6"]] we consider again the optimal Nyquist equalizer, but now the input pulse $g_x(t)$ is a two-sided exponential function: | |
:$$g_x(t) = {\rm e }^{ - |t|/T}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$g_x(t) = {\rm e }^{ - |t|/T}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Through a transversal filter of $N$–th order with the impulse response |
:$$h_{\rm TF}(t) = \sum_{\lambda = -N}^{+N} k_\lambda \cdot \delta(t - \lambda \cdot T)$$ | :$$h_{\rm TF}(t) = \sum_{\lambda = -N}^{+N} k_\lambda \cdot \delta(t - \lambda \cdot T)$$ | ||
| − | : | + | :it is always possible that the output pulse $g_y(t)$ has zero crossings at $t/T = ±1, \ \text{...} \ , \ t/T = ±N$ and $g_y(t = 0) = 1$. |
| − | * | + | *However, in the general case, the precursors and trailers with $| \nu | > N$ then lead to intersymbol interference. |
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Note:'' |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Linear_Nyquist_Equalization|"Linear Nyquist Equalization"]]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Give the signal values $g_x(\nu) = g_x(t = \nu T)$ at multiples of $T$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$g_x(0)\ = \ $ { 1 3% } | $g_x(0)\ = \ $ { 1 3% } | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
$g_x(2)\ = \ $ { 0.135 3% } | $g_x(2)\ = \ $ { 0.135 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the optimal filter coefficients for $N = 1$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$k_0 \ = \ $ { 1.313 3% } | $k_0 \ = \ $ { 1.313 3% } | ||
$k_1 \ = \ $ { -0.43775--0.41225 } | $k_1 \ = \ $ { -0.43775--0.41225 } | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the output values $g_2 = g_{\rm \nu}(t = 2T)$ and $g_3 = g_{\rm \nu}(t = 3T)$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$g_2 \ = \ $ { 0. } | $g_2 \ = \ $ { 0. } | ||
$g_3\ = \ $ { 0. } | $g_3\ = \ $ { 0. } | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements is true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + For the given input pulse $g_x(t)$, no improvement is possible with a second-order transversal filter. |
| − | - | + | - The first statement is independent of the input pulse $g_x(t)$. |
| − | - | + | - For the given input pulse, a further improvement is obtained with an "infinite" transversal filter. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
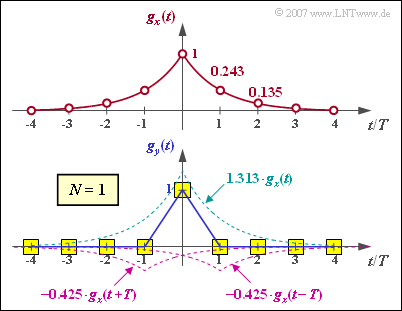
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The five first samples of the input pulse at distance $T$ are: |
:$$g_x(0)\hspace{0.25cm}\underline{ = 1},\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(1) \hspace{0.25cm}\underline{= 0.368},\hspace{0.25cm}g_x(2) \hspace{0.25cm}\underline{= | :$$g_x(0)\hspace{0.25cm}\underline{ = 1},\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(1) \hspace{0.25cm}\underline{= 0.368},\hspace{0.25cm}g_x(2) \hspace{0.25cm}\underline{= | ||
0.135},\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(3) = 0.050,\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(4) {= 0.018} | 0.135},\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(3) = 0.050,\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(4) {= 0.018} | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' According to the [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.6:_Transversal_Filter_of_the_Optimal_Nyquist_Equalizer|"solution to Exercise 3.6"]], we arrive at the following system of equations: |
:$$2t = T \hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm}g_1 \hspace{-0.2cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.2cm} k_0 \cdot g_x(1) +k_1 \cdot | :$$2t = T \hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm}g_1 \hspace{-0.2cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.2cm} k_0 \cdot g_x(1) +k_1 \cdot | ||
[g_x(0)+g_x(2)]= 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | [g_x(0)+g_x(2)]= 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
\frac{1-k_0}{0.736} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \frac{1-k_0}{0.736} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *This leads to the result: |
:$$k_0 - 0.324 \cdot 0.736 \cdot k_0 = 1 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow | :$$k_0 - 0.324 \cdot 0.736 \cdot k_0 = 1 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow | ||
\hspace{0.3cm} k_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1.313}, \hspace{0.2cm}k_1\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = -0.425} | \hspace{0.3cm} k_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1.313}, \hspace{0.2cm}k_1\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = -0.425} | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' For time $t = 2T$ holds: |
:$$g_2 \ = \ k_0 \cdot g_x(2) +k_1 \cdot [g_x(1)+g_x(3)]= \ 1.313 \cdot 0.050 -0.425 \cdot [0.135+0.018]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0} | :$$g_2 \ = \ k_0 \cdot g_x(2) +k_1 \cdot [g_x(1)+g_x(3)]= \ 1.313 \cdot 0.050 -0.425 \cdot [0.135+0.018]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Similarly, the output pulse at time $t = 3T$ is also zero: |
:$$g_3 \ = \ k_0 \cdot g_x(3) +k_1 \cdot [g_x(2)+g_x(4)]= 1.313 \cdot 0.135 -0.425 \cdot [0.368+0.050]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0} | :$$g_3 \ = \ k_0 \cdot g_x(3) +k_1 \cdot [g_x(2)+g_x(4)]= 1.313 \cdot 0.135 -0.425 \cdot [0.368+0.050]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1440__Dig_Z_3_6_c.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1440__Dig_Z_3_6_c.png|right|frame|Input pulse (top), output pulse for <i>N</i> = 1 (bottom)]] |
| − | * | + | *The figure shows that for this exponentially decaying pulse, the first-order transversal filter provides complete equalization. |
| − | * | + | *Outside the interval $-T < t < T$, $g_y(t)$ is identically zero, inside it results in a triangular shape. |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Only the <u>first statement</u> is correct: |
| − | * | + | *Since already with a first-order delay filter all precursors and trailers are compensated, also with a second-order filter and also for $N → ∞$ no further improvements result. |
| − | * | + | *However, this result applies exclusively to the (bilaterally) exponentially decaying input pulse. |
| − | * | + | *For almost any other pulse shape, the larger $N$ is, the better the result. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Revision as of 17:53, 25 May 2022
As in "Exercise 3.6" we consider again the optimal Nyquist equalizer, but now the input pulse $g_x(t)$ is a two-sided exponential function:
- $$g_x(t) = {\rm e }^{ - |t|/T}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Through a transversal filter of $N$–th order with the impulse response
- $$h_{\rm TF}(t) = \sum_{\lambda = -N}^{+N} k_\lambda \cdot \delta(t - \lambda \cdot T)$$
- it is always possible that the output pulse $g_y(t)$ has zero crossings at $t/T = ±1, \ \text{...} \ , \ t/T = ±N$ and $g_y(t = 0) = 1$.
- However, in the general case, the precursors and trailers with $| \nu | > N$ then lead to intersymbol interference.
Note:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Linear Nyquist Equalization".
Questions
Solution
(1) The five first samples of the input pulse at distance $T$ are:
- $$g_x(0)\hspace{0.25cm}\underline{ = 1},\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(1) \hspace{0.25cm}\underline{= 0.368},\hspace{0.25cm}g_x(2) \hspace{0.25cm}\underline{= 0.135},\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(3) = 0.050,\hspace{0.2cm}g_x(4) {= 0.018} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) According to the "solution to Exercise 3.6", we arrive at the following system of equations:
- $$2t = T \hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm}g_1 \hspace{-0.2cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.2cm} k_0 \cdot g_x(1) +k_1 \cdot [g_x(0)+g_x(2)]= 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{k_1}{k_0} = - \frac{g_x(1)}{g_x(0)+g_x(2)} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$t = 0 \hspace{-0.1cm}:\hspace{0.2cm}g_0 \hspace{-0.2cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.2cm} k_0 \cdot g_x(0) + k_1 \cdot 2 \cdot g_x(1) = 1\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} k_1 = \frac{1-k_0}{0.736} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This leads to the result:
- $$k_0 - 0.324 \cdot 0.736 \cdot k_0 = 1 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} k_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1.313}, \hspace{0.2cm}k_1\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = -0.425} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) For time $t = 2T$ holds:
- $$g_2 \ = \ k_0 \cdot g_x(2) +k_1 \cdot [g_x(1)+g_x(3)]= \ 1.313 \cdot 0.050 -0.425 \cdot [0.135+0.018]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Similarly, the output pulse at time $t = 3T$ is also zero:
- $$g_3 \ = \ k_0 \cdot g_x(3) +k_1 \cdot [g_x(2)+g_x(4)]= 1.313 \cdot 0.135 -0.425 \cdot [0.368+0.050]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The figure shows that for this exponentially decaying pulse, the first-order transversal filter provides complete equalization.
- Outside the interval $-T < t < T$, $g_y(t)$ is identically zero, inside it results in a triangular shape.
(4) Only the first statement is correct:
- Since already with a first-order delay filter all precursors and trailers are compensated, also with a second-order filter and also for $N → ∞$ no further improvements result.
- However, this result applies exclusively to the (bilaterally) exponentially decaying input pulse.
- For almost any other pulse shape, the larger $N$ is, the better the result.