Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.1: For Labeling Books"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[File:EN_KC_A_1_1.png|right|frame|'''ISBN–10'''? Or '''ISBN–13'''?]] | [[File:EN_KC_A_1_1.png|right|frame|'''ISBN–10'''? Or '''ISBN–13'''?]] | ||
| − | Since the 1960s, all books are provided with a 10-digit | + | Since the 1960s, all books are provided with a 10-digit "International Standard Book Number" $\rm (ISBN)$. The last digit of this so-called '''ISBN-10 specification''' is calculated according to the following rule: |
:$$ z_{10}= \left ( \sum_{i=1}^{9} \hspace{0.2cm} i \cdot z_i \right ) \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 11 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ z_{10}= \left ( \sum_{i=1}^{9} \hspace{0.2cm} i \cdot z_i \right ) \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 11 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | Since 2007, the specification according to the standard '''ISBN-13''' is additionally mandatory, whereby the check digit $z_{\rm 13}$ then results as follows: | + | Since 2007, the specification according to the standard '''ISBN-13''' is additionally mandatory, whereby the check digit $z_{\rm 13}$ then results as follows: |
:$$z_{13} = 10 - \left ( \sum_{i=1}^{12} \hspace{0.2cm} z_i \cdot 3^{(i+1)\mod 2} \right ) \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 10 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$z_{13} = 10 - \left ( \sum_{i=1}^{12} \hspace{0.2cm} z_i \cdot 3^{(i+1)\mod 2} \right ) \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 10 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | Some exemplary "ISBNs" are given opposite. The following questions refer to these. | + | Some exemplary "ISBNs" are given opposite. The following questions refer to these. |
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| − | Hints: | + | Hints: This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Objective_of_Channel_Coding|"Objective of Channel Coding"]] |
| − | |||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
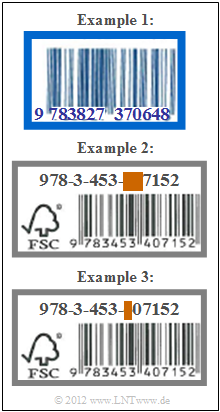
| − | What is the standard for $\text{ | + | What is the standard for $\text{Example 1}$? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- ISBN-10, | - ISBN-10, | ||
+ISBN-13. | +ISBN-13. | ||
| − | {Accordingly $\text{ | + | {Accordingly $\text{Example 2}$ two digits of an ISBN-13 are deleted. Is it possible to reconstruct the ISBN? If yes: Specify the ISBN-13. |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- Yes, | - Yes, | ||
+No. | +No. | ||
| − | {According to $\text{ | + | {According to $\text{Example 3}$ one digit of an ISBN-13 is erased. Can the ISBN be reconstructed? If Yes: Specify the ISBN-13. |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
+Yes, | +Yes, | ||
| Line 50: | Line 49: | ||
$M \ = \ $ { 11 3% } $\ \rm$ | $M \ = \ $ { 11 3% } $\ \rm$ | ||
| − | {Assumed as ISBN-10 is 3-8273-7064-7. Which statement is true? | + | {Assumed as ISBN-10 is "3-8273-7064-7". Which statement is true? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- This is not a valid ISBN. | - This is not a valid ISBN. | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 6 June 2022
Since the 1960s, all books are provided with a 10-digit "International Standard Book Number" $\rm (ISBN)$. The last digit of this so-called ISBN-10 specification is calculated according to the following rule:
- $$ z_{10}= \left ( \sum_{i=1}^{9} \hspace{0.2cm} i \cdot z_i \right ) \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 11 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Since 2007, the specification according to the standard ISBN-13 is additionally mandatory, whereby the check digit $z_{\rm 13}$ then results as follows:
- $$z_{13} = 10 - \left ( \sum_{i=1}^{12} \hspace{0.2cm} z_i \cdot 3^{(i+1)\mod 2} \right ) \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 10 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Some exemplary "ISBNs" are given opposite. The following questions refer to these.
Hints: This exercise belongs to the chapter "Objective of Channel Coding"
Questions
Solution
- The weighted sum over all digits is a multiple of 10:
- $$S \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \sum_{i=1}^{13} \hspace{0.2cm} z_i \cdot 3^{(i+1) \hspace{-0.2cm} \cdot 2} = (9+8+8+7+6+8) \cdot 1 + (7+3+2+3+0+4) \cdot 3 = 110\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} S \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 10 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) The answer is No. Only one cancellation can be reconstructed with a single check digit.
(3) One digit can be reconstructed ⇒ Yes. For the digit $z_{\rm 8}$, it must hold:
- $$[(9+8+4+3+0+1+2) \cdot 1 + (7+3+5+z_8+7+5) \cdot 3] \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 10 = 0\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} [108 + 3z_8] \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 10 = 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} z_8 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 4} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) By the modulo 11 operation $z_{10}$ can take the values $0, 1, \text{...} , 10$ ⇒ $\underline{M =11}$.
- Since "10" is not a digit, one makes do with $z_{10} = \rm X$.
- This corresponds to the Roman representation of the number "10".
(5) The test condition is:
- $$\ \ S= \left ( \sum_{i=1}^{10} \hspace{0.2cm} i \cdot z_i \right ) \hspace{-0.2cm} \mod 11 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The given ISBN satisfies this condition:
- $$3 \cdot 1 + 8 \cdot 2 + 2 \cdot 3 + 7 \cdot 4 + 3 \cdot 5 + 7 \cdot 6 + 0 \cdot 7 + 6 \cdot 8 + 4 \cdot 9 + 7 \cdot 10 = 264\hspace{0.3cm} ⇒\hspace{0.3cm} S= 264 \hspace{-0.3cm} \mod 11 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Correct statement 2, since the checksum $S = 0$ could result even with more than one error.