Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.4Z: Eye Opening and Level Number"
| (20 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Digital_Signal_Transmission/Intersymbol_Interference_for_Multi-Level_Transmission |
}} | }} | ||
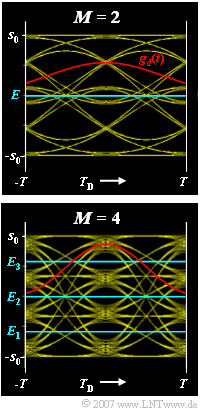
| − | [[File:P_ID1420__Dig_Z_3_4.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1420__Dig_Z_3_4.png|right|frame|Binary and quaternary <br>eye diagrams]] |
| − | In | + | In this exercise, a redundancy-free binary system and a redundancy-free quaternary system are compared with respect to vertical eye opening. The same boundary conditions apply to the two transmission systems: |
| − | * | + | * The basic transmission pulse $g_s(t)$ is NRZ rectangular in each case and has the height $s_0 = 1 \, {\rm V}$. |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | * The (equivalent) bit rate is $R_{\rm B} = 100 \, {\rm Mbit/s}$. |
| − | * | + | |
| + | * The AWGN noise has the (one-sided) noise power density $N_0$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Let the receiver filter be a Gaussian low-pass filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} = 30 \, {\rm MHz}$: | ||
:$$H_{\rm G}(f) = {\rm e}^{{- \pi \cdot f^2}/{(2f_{\rm G})^2}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$H_{\rm G}(f) = {\rm e}^{{- \pi \cdot f^2}/{(2f_{\rm G})^2}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * The decision thresholds are optimal. The detection time is $T_{\rm D} = 0$. |
| − | + | For the half-eye opening of an M-level transmission system, the following holds in general: | |
:$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} = \frac{g_0}{ M-1} - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} |g_\nu | - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} |g_{-\nu} |\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} = \frac{g_0}{ M-1} - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} |g_\nu | - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} |g_{-\nu} |\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *Here, $g_0 = g_d(t = 0)$ is the "main value" of the basic detection pulse $g_d(t) = g_s(t) * h_{\rm G}(t)$. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | *The second term describes the trailers ("postcursors") $g_{\rm \nu} = g_d(t = \nu T)$. |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | *The last term describes the "precursors" $g_{\rm -\nu} = g_d(t = -\nu T)$. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Note that in the present configuration with Gaussian low-pass | ||
| + | * all the basic detection pulse values $\text{...} \, g_{\rm -1}, \, g_0, \, g_1, \, \text{...}$ are positive, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * the (infinite) sum $\text{...} \, + \, g_{\rm -1} + g_0 + g_1\,\text{...}$ gives the constant value $s_0$, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * the main value can be calculated with the complementary Gaussian error function ${\rm Q}(x)$: | ||
:$$g_0 = s_0 | :$$g_0 = s_0 | ||
| − | \cdot\ | + | \cdot\big [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( |
\sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot T | \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot T | ||
| − | \right)\ | + | \right)\big] |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The graph shows the (noiseless) eye diagrams of the binary and quaternary systems and, in red, the corresponding basic detection pulses $g_d(t)$: | |
| + | *The optimal decision thresholds $E$ $($for $M = 2)$ and $E_1$, $E_2$, $E_3$ $($for $M = 4)$ are also drawn. | ||
| − | '' | + | *In subtask '''(7)''' these are to be determined numerically. |
| − | * | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Notes: | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Intersymbol_Interference_for_Multi-Level_Transmission|"Intersymbol Interference for Multi-Level Transmission"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *For the complementary Gaussian error function applies: | ||
:$${\rm Q}(0.25) = 0.4013,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(0.50) = 0.3085,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(0.75) = 0.2266,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.00) = 0.1587,$$ | :$${\rm Q}(0.25) = 0.4013,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(0.50) = 0.3085,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(0.75) = 0.2266,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.00) = 0.1587,$$ | ||
:$${\rm Q}(1.25) = 0.1057,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.50) = 0.0668,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.75) = 0.0401,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(2.00) = | :$${\rm Q}(1.25) = 0.1057,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.50) = 0.0668,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.75) = 0.0401,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(2.00) = | ||
0.0228.$$ | 0.0228.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the symbol duration $T$ for the binary and the quaternary system? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $M = 2: T$ | + | $M = 2\text{:}\hspace{0.4cm} T \ = \ $ { 10 3% } $\ {\rm ns}$ |
| − | $M = 4: T$ | + | $M = 4\text{:}\hspace{0.4cm} T \ = \ $ { 20 3% } $\ {\rm ns}$ |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the main value $g_0$ for the binary system. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $M = 2: g_0$ | + | $M = 2\text{:}\hspace{0.4cm} g_0\ = \ $ { 0.547 3% } $\ {\rm V}$ |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the main value $g_0$ for the quaternary system. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $M = 4: g_0$ | + | $M = 4\text{:}\hspace{0.4cm} g_0\ = \ $ { 0.867 3% } $\ {\rm V}$ |
| − | { | + | {Which equations are valid considering the Gaussian low-pass? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2 = M \cdot g_0/(M | + | + $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2 = M \cdot g_0/(M - 1) - s_0,$ |
| − | - $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2 = M \cdot s_0/(M | + | - $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2 = M \cdot s_0/(M - 1) - g_0,$ |
| − | + $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2 = s_0/(M | + | + $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2 = s_0/(M - 1) \cdot \big [1 - 2 \cdot M \cdot {\rm Q}(\sqrt{2\pi} \cdot {\rm log_2} \, (M) \cdot f_{\rm G}/R_{\rm B}) \big ].$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the eye opening for the binary system? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $M = 2: \ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})$ | + | $M = 2\text{:}\hspace{0.4cm} \ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})\ = \ $ { 0.188 3% } $\ {\rm V}$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the eye opening for the quaternary system? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $M = 4: \ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})$ | + | $M = 4\text{:}\hspace{0.4cm} \ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})\ = \ $ { 0.312 3% } $\ {\rm V}$ |
| − | { | + | {Determine the optimal thresholds of the quaternary system. Enter the lower threshold $E_1$ as a control. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $M = 4: E_1$ | + | $M = 4\text{:}\hspace{0.4cm} E_1\ = \ $ { -0.595--0.561 } $\ {\rm V}$ |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' In the binary system, the bit duration is equal to the reciprocal of the equivalent bit rate: |
:$$T = \frac{1}{R_{\rm B}}= \frac{1}{100\,{\rm Mbit/s}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 10\,{\rm ns}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$T = \frac{1}{R_{\rm B}}= \frac{1}{100\,{\rm Mbit/s}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 10\,{\rm ns}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The symbol duration of the quaternary system is twice as large: | |
:$$T = \frac{{\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}4}{R_{\rm B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 20\,{\rm ns}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$T = \frac{{\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}4}{R_{\rm B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 20\,{\rm ns}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' According to the given equation, the following holds for the binary system: |
:$$g_0 \ = \ s_0 \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot | :$$g_0 \ = \ s_0 \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot | ||
T \right)\right]= 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot 30\,{\rm MHz} \cdot | T \right)\right]= 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot 30\,{\rm MHz} \cdot | ||
10\,{\rm ns} \right)\right] $$ | 10\,{\rm ns} \right)\right] $$ | ||
| − | :$$ \ \approx \ 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( 0.75 \right)\right] | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} g_0 \ \approx \ 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( 0.75 \right)\right] |
= 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot 0.2266 \right]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 0.547\,{\rm V}} | = 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot 0.2266 \right]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 0.547\,{\rm V}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' Due to the double symbol duration, with the same cutoff frequency for $M = 4$: |
:$$g_0 \ = 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( 1.5 \right)\right] | :$$g_0 \ = 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( 1.5 \right)\right] | ||
= 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot 0.0668 \right] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.867\,{\rm V}} | = 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot 0.0668 \right] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.867\,{\rm V}} | ||
| Line 94: | Line 113: | ||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Extending the given equation by $\pm g_0$, we obtain: |
:$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} = \frac{g_0}{ M-1} + g_0 - g_0 - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} g_\nu - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} g_{-\nu} | :$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} = \frac{g_0}{ M-1} + g_0 - g_0 - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} g_\nu - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} g_{-\nu} | ||
= \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot g_0 - s_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | = \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot g_0 - s_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Here is taken into account: | |
| + | *In the case of the Gaussian low-pass filter, the magnitude formation can be omitted. | ||
| + | *The sum over all detection pulse values is equal to $s_0$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The <u>first, but also the last solution</u> is correct: | ||
:$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} \ = \ \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot g_0 - s_0 | :$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} \ = \ \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot g_0 - s_0 | ||
= \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot s_0 \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot | = \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot s_0 \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot | ||
| − | T \right)\right]- s_0 | + | T \right)\right]- s_0 $$ |
| − | :$$ \ = \ \frac{s_0}{ M-1} \cdot \left [ 1- 2 \cdot M \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} \ = \ \frac{s_0}{ M-1} \cdot \left [ 1- 2 \cdot M \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot |
T \right)\right] | T \right)\right] | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | Using the relation $T = {\rm log_2} \,(M)/R_{\rm B}$, we arrive at the third proposed solution, which is also applicable. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(5)''' Using the results from '''(2)''' and '''(4)''', one obtains with $M = 2$: | |
| − | '''(5)''' | ||
:$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})} = 2 \cdot (2 \cdot g_0 - s_0) = 2 \cdot (2 \cdot 0.547\,{\rm V} - 1\,{\rm V}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.188\,{\rm V}} | :$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})} = 2 \cdot (2 \cdot g_0 - s_0) = 2 \cdot (2 \cdot 0.547\,{\rm V} - 1\,{\rm V}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.188\,{\rm V}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' On the other hand, with $g_0 = 0.867 \, {\rm V}$, $s_0 = 1 \, {\rm V}$ and $M = 4$, we get: |
:$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})} = 2 \cdot ({4}/{3} \cdot 0.867\,{\rm V} - 1\,{\rm V}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.312\,{\rm V}} | :$${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})} = 2 \cdot ({4}/{3} \cdot 0.867\,{\rm V} - 1\,{\rm V}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.312\,{\rm V}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(7)''' | + | '''(7)''' According to subtask '''(3)''', $g_0 = 0.867 \, {\rm V}$ and correspondingly $g_{\rm VN} = 0.133 \, {\rm V}$ (sum of all precursors and trailers). |
| + | *The eye opening is $\ddot{o} = 0.312 \, {\rm V}$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *From the sketch on the information section, we can see that the upper boundary $($German: "obere Grenzlinie" ⇒ "o"$)$ of the upper eye has the following value $($for $T_{\rm D} = 0)$: | ||
:$$o = s_0 - 2 \cdot g_{\rm VN}= g_0 - g_{\rm VN}= 0.867\,{\rm V} - 0.133\,{\rm V} = 0.734\,{\rm V} | :$$o = s_0 - 2 \cdot g_{\rm VN}= g_0 - g_{\rm VN}= 0.867\,{\rm V} - 0.133\,{\rm V} = 0.734\,{\rm V} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The lower limit $($German: "untere Grenzlinie" ⇒ "u"$)$ is at: | |
:$$u = o -{\ddot{o}} = 0.734\,{\rm V} - 0.312\,{\rm V} = 0.422\,{\rm V} | :$$u = o -{\ddot{o}} = 0.734\,{\rm V} - 0.312\,{\rm V} = 0.422\,{\rm V} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *From this follows for the optimal decision threshold of the upper eye: | |
:$$E_3 = \frac{o + u}{2} = \frac{0.734\,{\rm V} + 0.422\,{\rm V}}{2} { = 0.578\,{\rm V}} | :$$E_3 = \frac{o + u}{2} = \frac{0.734\,{\rm V} + 0.422\,{\rm V}}{2} { = 0.578\,{\rm V}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The sought threshold (for the lower eye) is $E_1 \, \underline {= \, –0.578 \, V}$. | |
| + | |||
| + | *The average decision threshold is $E_2 = 0$ for symmetry reasons. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Digital Signal Transmission: Exercises|^3.4 Eye Opening with Multilevel Systems^]] |
Latest revision as of 16:09, 20 June 2022
In this exercise, a redundancy-free binary system and a redundancy-free quaternary system are compared with respect to vertical eye opening. The same boundary conditions apply to the two transmission systems:
- The basic transmission pulse $g_s(t)$ is NRZ rectangular in each case and has the height $s_0 = 1 \, {\rm V}$.
- The (equivalent) bit rate is $R_{\rm B} = 100 \, {\rm Mbit/s}$.
- The AWGN noise has the (one-sided) noise power density $N_0$.
- Let the receiver filter be a Gaussian low-pass filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} = 30 \, {\rm MHz}$:
- $$H_{\rm G}(f) = {\rm e}^{{- \pi \cdot f^2}/{(2f_{\rm G})^2}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The decision thresholds are optimal. The detection time is $T_{\rm D} = 0$.
For the half-eye opening of an M-level transmission system, the following holds in general:
- $${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} = \frac{g_0}{ M-1} - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} |g_\nu | - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} |g_{-\nu} |\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Here, $g_0 = g_d(t = 0)$ is the "main value" of the basic detection pulse $g_d(t) = g_s(t) * h_{\rm G}(t)$.
- The second term describes the trailers ("postcursors") $g_{\rm \nu} = g_d(t = \nu T)$.
- The last term describes the "precursors" $g_{\rm -\nu} = g_d(t = -\nu T)$.
Note that in the present configuration with Gaussian low-pass
- all the basic detection pulse values $\text{...} \, g_{\rm -1}, \, g_0, \, g_1, \, \text{...}$ are positive,
- the (infinite) sum $\text{...} \, + \, g_{\rm -1} + g_0 + g_1\,\text{...}$ gives the constant value $s_0$,
- the main value can be calculated with the complementary Gaussian error function ${\rm Q}(x)$:
- $$g_0 = s_0 \cdot\big [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot T \right)\big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The graph shows the (noiseless) eye diagrams of the binary and quaternary systems and, in red, the corresponding basic detection pulses $g_d(t)$:
- The optimal decision thresholds $E$ $($for $M = 2)$ and $E_1$, $E_2$, $E_3$ $($for $M = 4)$ are also drawn.
- In subtask (7) these are to be determined numerically.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Intersymbol Interference for Multi-Level Transmission".
- For the complementary Gaussian error function applies:
- $${\rm Q}(0.25) = 0.4013,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(0.50) = 0.3085,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(0.75) = 0.2266,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.00) = 0.1587,$$
- $${\rm Q}(1.25) = 0.1057,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.50) = 0.0668,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(1.75) = 0.0401,\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Q}(2.00) = 0.0228.$$
Questions
Solution
- $$T = \frac{1}{R_{\rm B}}= \frac{1}{100\,{\rm Mbit/s}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 10\,{\rm ns}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The symbol duration of the quaternary system is twice as large:
- $$T = \frac{{\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}4}{R_{\rm B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 20\,{\rm ns}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) According to the given equation, the following holds for the binary system:
- $$g_0 \ = \ s_0 \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot T \right)\right]= 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot 30\,{\rm MHz} \cdot 10\,{\rm ns} \right)\right] $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} g_0 \ \approx \ 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( 0.75 \right)\right] = 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot 0.2266 \right]\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 0.547\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) Due to the double symbol duration, with the same cutoff frequency for $M = 4$:
- $$g_0 \ = 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( 1.5 \right)\right] = 1\,{\rm V} \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot 0.0668 \right] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.867\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Extending the given equation by $\pm g_0$, we obtain:
- $${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} = \frac{g_0}{ M-1} + g_0 - g_0 - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} g_\nu - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{\infty} g_{-\nu} = \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot g_0 - s_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Here is taken into account:
- In the case of the Gaussian low-pass filter, the magnitude formation can be omitted.
- The sum over all detection pulse values is equal to $s_0$.
The first, but also the last solution is correct:
- $${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} \ = \ \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot g_0 - s_0 = \frac{M}{ M-1} \cdot s_0 \cdot\left [ 1- 2 \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot T \right)\right]- s_0 $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})}/{ 2} \ = \ \frac{s_0}{ M-1} \cdot \left [ 1- 2 \cdot M \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{2\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G} \cdot T \right)\right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Using the relation $T = {\rm log_2} \,(M)/R_{\rm B}$, we arrive at the third proposed solution, which is also applicable.
(5) Using the results from (2) and (4), one obtains with $M = 2$:
- $${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})} = 2 \cdot (2 \cdot g_0 - s_0) = 2 \cdot (2 \cdot 0.547\,{\rm V} - 1\,{\rm V}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.188\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) On the other hand, with $g_0 = 0.867 \, {\rm V}$, $s_0 = 1 \, {\rm V}$ and $M = 4$, we get:
- $${\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})} = 2 \cdot ({4}/{3} \cdot 0.867\,{\rm V} - 1\,{\rm V}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.312\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(7) According to subtask (3), $g_0 = 0.867 \, {\rm V}$ and correspondingly $g_{\rm VN} = 0.133 \, {\rm V}$ (sum of all precursors and trailers).
- The eye opening is $\ddot{o} = 0.312 \, {\rm V}$.
- From the sketch on the information section, we can see that the upper boundary $($German: "obere Grenzlinie" ⇒ "o"$)$ of the upper eye has the following value $($for $T_{\rm D} = 0)$:
- $$o = s_0 - 2 \cdot g_{\rm VN}= g_0 - g_{\rm VN}= 0.867\,{\rm V} - 0.133\,{\rm V} = 0.734\,{\rm V} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The lower limit $($German: "untere Grenzlinie" ⇒ "u"$)$ is at:
- $$u = o -{\ddot{o}} = 0.734\,{\rm V} - 0.312\,{\rm V} = 0.422\,{\rm V} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- From this follows for the optimal decision threshold of the upper eye:
- $$E_3 = \frac{o + u}{2} = \frac{0.734\,{\rm V} + 0.422\,{\rm V}}{2} { = 0.578\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The sought threshold (for the lower eye) is $E_1 \, \underline {= \, –0.578 \, V}$.
- The average decision threshold is $E_2 = 0$ for symmetry reasons.