Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.11: Analysis of Parity-check Matrices"
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Kanalcodierung/Grundlegendes zu den Low–density Parity–check Codes }} [[File:|right|]] ===Fragebogen=== <quiz display…“) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/The_Basics_of_Low-Density_Parity_Check_Codes}} |
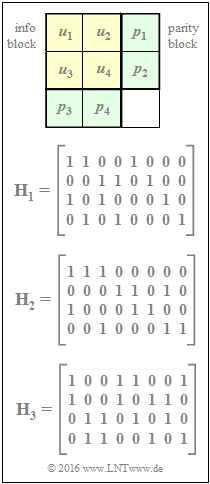
| + | [[File:EN_KC_A_4_11_v2.png|right|frame|Product code described by the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$]] | ||
| + | In the adjacent graphic, a product code is indicated at the top, which is characterized by the following parity-check equations: | ||
| + | :$$p_1 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u_1 \oplus u_2\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$p_2 = u_3 \oplus u_4\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$p_3 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u_1 \oplus u_3\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$p_4 = u_2 \oplus u_4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | Below are given the check matrices $\mathbf{H}_1, \ \mathbf{H}_2$ and $\mathbf{H}_3$. To be checked: Which of the matrices correctly describe the given product code according to the equation $\underline{x} = \underline{u} \cdot \mathbf{H}^{\rm T}$ assuming the following definitions: | ||
| + | * the code word $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$, | ||
| + | * the code word $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$. | ||
| + | All $\mathbf{H}$ matrices contain fewer "ones" than "zeros". This is a characteristic of the so-called "low–density parity–check codes" $($short: $\rm LDPC$ codes$)$. In the case of LDPC codes relevant to practice, however, the share of "ones" is still significantly lower than in these examples. | ||
| + | Furthermore, note for the exercise: | ||
| + | * An $(n, \ k)$ $\underline{x} = \underline{u} \cdot \mathbf{H}^{\rm T}$ block code is systematic if the first $k$ bits of the code word $\underline{x}$ contains the information word $\underline{u}$. With the code word $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$ the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$ must then end with a $k × k$ diagonal matrix. | ||
| + | * A "regular code" $($with respect to the LDPC application$)$ exists, if the Hamming weight of all rows ⇒ $w_{\rm R}$ and the Hamming weight of all columns ⇒ $w_{\rm C}$ are equal in each case. Otherwise, one speaks of an "irregular LDPC code". | ||
| + | * The parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$ of a conventional linear $(n, \ k)$ block code consists of exactly $m = n - k$ rows and $n$ columns. For LDPC codes, the requirement is $m ≥ n - k$. The equal sign is true if the $m$ parity-check equations are statistically independent. | ||
| − | }} | + | * From the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$ a lower bound for the code rate $R$ can be given: |
| + | :$$R \ge 1 - \frac{{\rm E}[w_{\rm C}]}{{\rm E}[w_{\rm R}]} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm with}\hspace{0.5cm} | ||
| + | {\rm E}[w_{\rm C}] =\frac{1}{n} \cdot \sum_{i = 1}^{n}w_{\rm C}(i) | ||
| + | \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm and}\hspace{0.5cm} | ||
| + | {\rm E}[w_{\rm R}] =\frac{1}{m} \cdot \sum_{j = 1}^{ m}w_{\rm R}(j) | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | [[ | + | *This equation applies equally to regular and irregular LDPC codes, where for regular codes holds ${\rm E}[w_{\rm C}] = w_{\rm C}$ and ${\rm E}[w_{\rm R}] = w_{\rm R}$. |
| − | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Hints:</u> | ||
| + | * This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/The_Basics_of_Low-Density_Parity_Check_Codes|"Basics of the Low–density Parity–check codes"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Reference is made in particular to the page [[Channel_Coding/The_Basics_of_Low-Density_Parity_Check_Codes#Some_characteristics_of_LDPC_codes|"Some characteristics of LDPC codes"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which parity-check matrix describes the given product code according to the sketch above? |
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | + $\mathbf{H}_1$ given $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$. | ||
| + | - $\mathbf{H}_1$ given $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$. | ||
| + | + $\mathbf{H}_2$ given $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$. | ||
| + | - $\mathbf{H}_3$ given $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {For the remaining subtasks we shall always assume $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$. <br>Which statements are valid for the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_1$? | ||
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | + The code is systematic. | ||
| + | - The code is regular. | ||
| + | - For the code rate holds $R > 1/2$. | ||
| + | + For the code rate holds $R = 1/2$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {What statements hold for the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_3$? | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - No relation between $\mathbf{H}_1$ and $\mathbf{H}_3$ is discernible. |
| − | + | + | + The $\mathbf{H}_3$ rows are linear combinations of two $\mathbf{H}_1$ rows each. |
| + | + The four parity-check equations according to $\mathbf{H}_3$ are linearly independent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Which statements apply to the code denoted by $\mathbf{H}_3$ ? | ||
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | - The code is systematic. | ||
| + | + The code is regular. | ||
| + | + For the code rate holds $R ≥ 1/2$. | ||
| + | + For the code rate holds $R = 1/2$. | ||
| + | </quiz> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Solution=== | ||
| + | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| + | '''(1)''' Correct are the <u>solutions 1 and 3</u>: | ||
| + | *With the code word definition $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$, the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_1$ denotes the following check equations: | ||
| + | :$$u_1 \oplus u_2 \oplus p_1 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | u_3 \oplus u_4 \oplus p_2 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | u_1 \oplus u_3 \oplus p_3 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | u_2 \oplus u_4 \oplus p_4 = 0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *This corresponds exactly to the assumptions made above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The same result is obtained for $\mathbf{H}_2$ and the code word definition $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | With the same code word definition $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$ the other parity-check matrices do not yield a meaningful set of equations: | ||
| + | * According to parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_1$: | ||
| + | :$$u_1 \oplus p_1 \oplus u_3 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | u_2 \oplus p_2 \oplus p_3 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | u_1 \oplus u_2 \oplus u_4 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | p_1 \oplus p_2 \oplus p_4 = 0\hspace{0.05cm};$$ | ||
| + | * corresponding to parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_3$: | ||
| + | :$$u_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} | ||
| + | u_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm}u_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} | ||
| + | p_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm}u_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} | ||
| + | p_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' Correct are the <u>proposed solutions 1 and 4</u>: | ||
| + | * The code is systematic because $\mathbf{H}_1$ ends with a $4 × 4$ diagonal matrix. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *For a regular (LDPC) code, there should be an equal number of "ones" in each row and in each column. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The first condition is satisfied $(w_{\rm R} = 3)$, but not the second. Rather, there is (equally often) one "one" or two "ones" per column ⇒ ${\rm E}[w_{\rm C}] = 1.5$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For an irregular code, the lower bound for the code rate is: | ||
| + | :$$R \ge 1 - \frac{{\rm E}[w_{\rm C}]}{{\rm E}[w_{\rm R}]} | ||
| + | = 1 - \frac{1.5}{3} = 1/2 | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Because of the given code structure $(k = 4$ information bits, $m = 4$ check bits ⇒ $n = 8$ encoded bits$)$ the code rate can also be given in the conventional form: $R = k/n$ ⇒ Correct is solution 4 in contrast to answer 3. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''(3)''' The $\mathbf{H}_3$ rows result from linear combinations of $\mathbf{H}_1$ rows: | ||
| + | * The first $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 1 and row 4. | ||
| + | * The second $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 2 and row 3. | ||
| − | + | * The third $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 1 and row 3. | |
| − | + | * The fourth $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 2 and row 4. | |
| − | { | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | By linear combinations, the four linearly independent equations with respect to $\mathbf{H}_1$ now become four linearly independent equations with respect to $\mathbf{H}_3$ <br>⇒ Therefore, the <u>proposed solutions 2 and 3</u> are correct. | ||
| − | |||
| + | '''(4)''' Here, <u>solutions 2, 3, and 4</u> are correct: | ||
| + | * If the code described by $\mathbf{H}_3$ were systematic, $\mathbf{H}_3$ should end with a $4 × 4$ diagonal matrix. This is not the case here. | ||
| + | * The Hamming weights of all rows are equal $(w_{\rm R} = 4)$ and also all columns each have the same Hamming weight $(w_{\rm C} = 2)$ ⇒ the code is regular. | ||
| + | * This gives $R ≥ 1 - 2/4 = 1/2$ for the code rate. | ||
| + | *But since the four rows of $\mathbf{H}_3$ also describe four independent equations, the equal sign ⇒ $R = 1/2$ also holds. | ||
| + | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | ^]] | + | [[Category:Channel Coding: Exercises|^4.4 Low–density Parity–check Codes^]] |
Latest revision as of 17:20, 19 December 2022
In the adjacent graphic, a product code is indicated at the top, which is characterized by the following parity-check equations:
- $$p_1 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u_1 \oplus u_2\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$p_2 = u_3 \oplus u_4\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$p_3 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u_1 \oplus u_3\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$p_4 = u_2 \oplus u_4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Below are given the check matrices $\mathbf{H}_1, \ \mathbf{H}_2$ and $\mathbf{H}_3$. To be checked: Which of the matrices correctly describe the given product code according to the equation $\underline{x} = \underline{u} \cdot \mathbf{H}^{\rm T}$ assuming the following definitions:
- the code word $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$,
- the code word $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$.
All $\mathbf{H}$ matrices contain fewer "ones" than "zeros". This is a characteristic of the so-called "low–density parity–check codes" $($short: $\rm LDPC$ codes$)$. In the case of LDPC codes relevant to practice, however, the share of "ones" is still significantly lower than in these examples.
Furthermore, note for the exercise:
- An $(n, \ k)$ $\underline{x} = \underline{u} \cdot \mathbf{H}^{\rm T}$ block code is systematic if the first $k$ bits of the code word $\underline{x}$ contains the information word $\underline{u}$. With the code word $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$ the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$ must then end with a $k × k$ diagonal matrix.
- A "regular code" $($with respect to the LDPC application$)$ exists, if the Hamming weight of all rows ⇒ $w_{\rm R}$ and the Hamming weight of all columns ⇒ $w_{\rm C}$ are equal in each case. Otherwise, one speaks of an "irregular LDPC code".
- The parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$ of a conventional linear $(n, \ k)$ block code consists of exactly $m = n - k$ rows and $n$ columns. For LDPC codes, the requirement is $m ≥ n - k$. The equal sign is true if the $m$ parity-check equations are statistically independent.
- From the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$ a lower bound for the code rate $R$ can be given:
- $$R \ge 1 - \frac{{\rm E}[w_{\rm C}]}{{\rm E}[w_{\rm R}]} \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm with}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm E}[w_{\rm C}] =\frac{1}{n} \cdot \sum_{i = 1}^{n}w_{\rm C}(i) \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm and}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm E}[w_{\rm R}] =\frac{1}{m} \cdot \sum_{j = 1}^{ m}w_{\rm R}(j) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This equation applies equally to regular and irregular LDPC codes, where for regular codes holds ${\rm E}[w_{\rm C}] = w_{\rm C}$ and ${\rm E}[w_{\rm R}] = w_{\rm R}$.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Basics of the Low–density Parity–check codes".
- Reference is made in particular to the page "Some characteristics of LDPC codes".
Questions
Solution
- With the code word definition $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, u_2, \, u_3, \, u_4, \, p_1, \, p_2, \, p_3, \, p_4)$, the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_1$ denotes the following check equations:
- $$u_1 \oplus u_2 \oplus p_1 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} u_3 \oplus u_4 \oplus p_2 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} u_1 \oplus u_3 \oplus p_3 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} u_2 \oplus u_4 \oplus p_4 = 0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This corresponds exactly to the assumptions made above.
- The same result is obtained for $\mathbf{H}_2$ and the code word definition $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$.
With the same code word definition $\underline{x} = (u_1, \, p_1, \, u_2, \, p_2, \, u_3, \, p_3, \, u_4, \, p_4)$ the other parity-check matrices do not yield a meaningful set of equations:
- According to parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_1$:
- $$u_1 \oplus p_1 \oplus u_3 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} u_2 \oplus p_2 \oplus p_3 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} u_1 \oplus u_2 \oplus u_4 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} p_1 \oplus p_2 \oplus p_4 = 0\hspace{0.05cm};$$
- corresponding to parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_3$:
- $$u_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} u_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm}u_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} p_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm}u_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} p_1 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} u_2 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_3 \hspace{-0.12cm}\oplus\hspace{-0.06cm} p_4 \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Correct are the proposed solutions 1 and 4:
- The code is systematic because $\mathbf{H}_1$ ends with a $4 × 4$ diagonal matrix.
- For a regular (LDPC) code, there should be an equal number of "ones" in each row and in each column.
- The first condition is satisfied $(w_{\rm R} = 3)$, but not the second. Rather, there is (equally often) one "one" or two "ones" per column ⇒ ${\rm E}[w_{\rm C}] = 1.5$.
- For an irregular code, the lower bound for the code rate is:
- $$R \ge 1 - \frac{{\rm E}[w_{\rm C}]}{{\rm E}[w_{\rm R}]} = 1 - \frac{1.5}{3} = 1/2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Because of the given code structure $(k = 4$ information bits, $m = 4$ check bits ⇒ $n = 8$ encoded bits$)$ the code rate can also be given in the conventional form: $R = k/n$ ⇒ Correct is solution 4 in contrast to answer 3.
(3) The $\mathbf{H}_3$ rows result from linear combinations of $\mathbf{H}_1$ rows:
- The first $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 1 and row 4.
- The second $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 2 and row 3.
- The third $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 1 and row 3.
- The fourth $\mathbf{H}_3$ row is the sum of row 2 and row 4.
By linear combinations, the four linearly independent equations with respect to $\mathbf{H}_1$ now become four linearly independent equations with respect to $\mathbf{H}_3$
⇒ Therefore, the proposed solutions 2 and 3 are correct.
(4) Here, solutions 2, 3, and 4 are correct:
- If the code described by $\mathbf{H}_3$ were systematic, $\mathbf{H}_3$ should end with a $4 × 4$ diagonal matrix. This is not the case here.
- The Hamming weights of all rows are equal $(w_{\rm R} = 4)$ and also all columns each have the same Hamming weight $(w_{\rm C} = 2)$ ⇒ the code is regular.
- This gives $R ≥ 1 - 2/4 = 1/2$ for the code rate.
- But since the four rows of $\mathbf{H}_3$ also describe four independent equations, the equal sign ⇒ $R = 1/2$ also holds.