Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.08: Identical Codes"
| (18 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/General_Description_of_Linear_Block_Codes |
}} | }} | ||
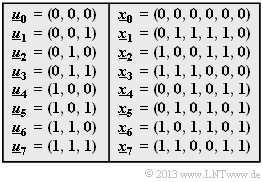
| − | [[File:P_ID2393__KC_A_1_8_neu.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2393__KC_A_1_8_neu.png|right|frame|Assignment of the $(6, 3)$ block code]] |
| − | + | We consider a block code $\mathcal{C}$ described by the following generator matrix: | |
:$${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1\\ 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &1 &1 &0 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1\\ 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &1 &1 &0 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The mapping between the information words $\underline{u}$ and the code words $\underline{x}$ can be seen in the table. It can be seen that this is not a "systematic code". | |
| − | + | By manipulating the generator matrix $\boldsymbol {\rm G}$, identical codes can be constructed from it. This refers to codes with the same code words but different assignments $\underline{u} \rightarrow \underline{x}$. | |
| − | + | The following operations are allowed to obtain identical code: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *swapping or permuting the rows, | |
| − | + | *Multiplying all rows by a constant vector not equal to "$\underline{0}$". | |
| − | + | *Replacing a row with a linear combination between this row and another one. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | For the code $\mathcal{C}_{\rm sys}$ sought in subtask '''(3)''' it is further required to be systematic ⇒ generator matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm G}_{\rm sys}$. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Hints: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/General_Description_of_Linear_Block_Codes|"General Description of Linear Block Codes"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reference is made in particular to the section [[Channel_Coding/General_Description_of_Linear_Block_Codes#Systematic_Codes|"Systematic Codes"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reference is also made to the so-called "Singleton bound". | ||
| + | |||
| + | *This states that the minimum Hamming distance of a $(n, k)$ block code is upper bounded: $d_{\rm min} \le n - k +1.$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Give the characteristics of the given code $\mathcal{C}$ . |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $n \ = \ $ { 6 | + | $n \hspace{0.3cm} = \ $ { 6 } |
| − | $k \ = \ $ { 3 | + | $k \hspace{0.3cm} = \ $ { 3 } |
| − | $ | + | $m \hspace{0.15cm} = \ $ { 3 } |
| − | $R \ = \ ${ 0.5 3% } | + | $R \hspace{0.2cm} = \ ${ 0.5 3% } |
| − | $ | + | $|\hspace{0.05cm}\mathcal{C}\hspace{0.05cm}| \hspace{-0.05cm} = \ ${ 8 } |
| − | $d_{\rm min}$ | + | $d_{\rm min} \hspace{0.01cm} = \ $ { 3 } |
| − | { | + | {Is there any $(6, 3)$ block code with larger minimum distance? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
| − | + | + | + Yes. |
| − | - | + | - No. |
| − | { | + | {What is the generator matrix ${\boldsymbol{\rm G}}_{\rm sys}$ of the identical systematic code? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The 1st row is "$1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 1 \ 0 \ 1$". |
| − | + | + | + The 2nd row is "$0 \ 1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0 \ 1$". |
| − | + | + | + The 3rd row is "$0 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 1$". |
| − | { | + | {What assignments result from this coding? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + $\underline{u} = (0, 0, 0) \Rightarrow | + | + $\underline{u} = (0, 0, 0) \ \Rightarrow \ \underline{x}_{\rm sys} = (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)$. |
| − | + $\underline{u} = (0, 0, 1) | + | + $\underline{u} = (0, 0, 1) \ \Rightarrow \ \underline{x}_{\rm sys}= (0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1)$. |
| − | - $\underline{u} = (0, 1, 0) | + | - $\underline{u} = (0, 1, 0) \ \Rightarrow \ \underline{x}_{\rm sys} = (0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0)$. |
| − | { | + | {Which parity bits has the systematic code $\underline{x}_{\rm sys} = (u_{1},\ u_{2},\ u_{3},\ p_{1},\ p_{2},\ p_{3})$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+$p_{1} = u_{1} \oplus u_{2},$ | +$p_{1} = u_{1} \oplus u_{2},$ | ||
| Line 66: | Line 80: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The given code $\mathcal{C}$ is characterized by the following parameters: |
| − | + | *Number of bits of the code words: $\underline{n = 6}$, | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *Number of bits of the information words: $\underline{k = 3}$, | ||
| + | *Number of parity bit equations: $\underline{m = n - k = 3}$, | ||
| − | + | *Code rate: $R = k/n = 3/6 \Rightarrow \underline{R = 0.5}$, | |
| − | + | *Number of code words (code size): $|\mathcal{C}| = 2^k \Rightarrow \underline{|C| = 8}$, | |
| − | * | + | *minimum Hamming distance (see table): $\underline{d}_{\rm min} \underline{= 3}$. |
| − | |||
| + | '''(2)''' Correct is $\underline{\rm Yes}$: | ||
| + | *According to the singleton bound ⇒ $d_{\rm min} ≤ n - k + 1$. With $n = 6$ and $k = 3$ one obtains $d_{\rm min} ≤ 4$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *It is thus quite possible to construct a $(6, 3)$ block code with larger minimal distance. How such a code looks, was kindly not asked. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The minimum distance of all Hamming codes is $d_{\rm min} = 3$, and only the special case with $n = 3$ and $k = 1$ reaches the limit. In contrast, the maximum reach according to the Singleton bound: | |
| + | |||
| + | *all [[Channel_Coding/Examples_of_Binary_Block_Codes#Repetition_Codes|repetition codes]] $\rm (RC)$ because $k = 1$ and $d_{\rm min} = n$; this includes the $\rm (3, 1)$ Hamming code, which is known to be identical to $\rm RC\ (3, 1)$, | ||
| + | |||
| + | *all [[Channel_Coding/Examples_of_Binary_Block_Codes#Single_Parity-check_Codes|single parity–check codes]] $\rm (SPC)$: $k = n - 1,\ d_{\rm min} = 2$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(3)''' Correct are th e <u>solutions 2 and 3</u>: | |
| − | + | *If we swap rows in the generator matrix $\boldsymbol {\rm G}$, we arrive at an identical code $\mathcal{C}'$. That is, the codes $\mathcal{C}$ and $\mathcal{C}'$ contain the exact same code words. | |
| + | |||
| + | *For example, after cyclic row swapping $2 \rightarrow 1,\ 3 \rightarrow 2$, and $1 \rightarrow 3$, one obtains the new matrix | ||
| + | :$${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}}' = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The first and the last row of the new matrix already comply with the requirements of a systematic code ⇒ matrix ${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}_{\rm sys}}$ must start with a diagonal matrix. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | *Replacing row 2 by the modulo 2 sum of rows 2 and 3, we get: | ||
| − | + | :$${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}}_{\rm sys} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &0 &1 &0 &1\\ 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | |
| − | |||
| + | *This systematic code contains exactly the same code words as the codes $\mathcal{C}$ and $\mathcal{C}'$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | '''( | + | '''(4)''' Correct are the <u>solutions 1 and 2</u>: |
| + | *Applying the equation $\underline{x}_{\rm sys} = \underline{u} \cdot \boldsymbol{\rm G}_{\rm sys}$ to the above examples, we see that the first two statements are correct, but not the last one. | ||
| + | *Without calculation one comes to the same result, if one considers that | ||
| − | :$ | + | :*the systematic code word $\underline{x}_{\rm sys}$ must start with $\underline{u}$, |
| + | :*the code $\mathcal{C}_{\rm sys}$ contains the same code words as the given code $\mathcal{C}$. | ||
| − | + | *For $\underline{u} = (0, 1, 0)$, the code word is thus $(0, 1, 0, ?, ?, ?)$. | |
| − | + | *A comparison with the code table of $\mathcal{C}$ in the information section leads to $\underline{x}_{\rm sys} = (0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1)$. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(5)''' Only <u>statement 1</u> is correct. The statements for $p_{2}$ and $p_{3}$, on the other hand, are exactly reversed. | |
| + | *With systematic coding, the following relationship exists between the generator matrix and the parity-check matrix: | ||
| + | :$${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}} =\left({ \boldsymbol{\rm I}}_k \: ; \:{ \boldsymbol{\rm P}} \right) \hspace{0.3cm}\Leftrightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H}} =\left({ \boldsymbol{\rm P}}^{\rm T}\: ; \:{ \boldsymbol{\rm I}}_m \right) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
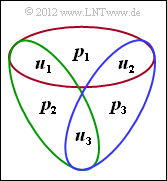
| − | $\Rightarrow | + | [[File:P_ID2395__KC_A_1_8_ML.png|right|frame|Chart of parity-check equations]] |
| + | *Applied to the current example, we obtain thus: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :$${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}}_{\rm sys} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &0 &1 &0 &1\\ 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm sys} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &1 &0 &1 &0 &0\\ 1 &0 &1 &0 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &0 &0 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *This results in parity-check equations (see graph): | ||
| + | :$$u_1 \oplus u_2 \oplus p_1 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} p_1 = u_1 \oplus u_2 \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$ u_1 \oplus u_3 \oplus p_2 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} p_2 = u_1 \oplus u_3 \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$ u_2 \oplus u_3 \oplus p_3 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} p_3 = u_2 \oplus u_3 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 134: | Line 162: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Channel Coding: Exercises|^1.4 Linear Block Code Description |
^]] | ^]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:00, 23 January 2023
We consider a block code $\mathcal{C}$ described by the following generator matrix:
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1\\ 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &1 &1 &0 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The mapping between the information words $\underline{u}$ and the code words $\underline{x}$ can be seen in the table. It can be seen that this is not a "systematic code".
By manipulating the generator matrix $\boldsymbol {\rm G}$, identical codes can be constructed from it. This refers to codes with the same code words but different assignments $\underline{u} \rightarrow \underline{x}$.
The following operations are allowed to obtain identical code:
- swapping or permuting the rows,
- Multiplying all rows by a constant vector not equal to "$\underline{0}$".
- Replacing a row with a linear combination between this row and another one.
For the code $\mathcal{C}_{\rm sys}$ sought in subtask (3) it is further required to be systematic ⇒ generator matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm G}_{\rm sys}$.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "General Description of Linear Block Codes".
- Reference is made in particular to the section "Systematic Codes".
- Reference is also made to the so-called "Singleton bound".
- This states that the minimum Hamming distance of a $(n, k)$ block code is upper bounded: $d_{\rm min} \le n - k +1.$
Questions
Solution
- Number of bits of the code words: $\underline{n = 6}$,
- Number of bits of the information words: $\underline{k = 3}$,
- Number of parity bit equations: $\underline{m = n - k = 3}$,
- Code rate: $R = k/n = 3/6 \Rightarrow \underline{R = 0.5}$,
- Number of code words (code size): $|\mathcal{C}| = 2^k \Rightarrow \underline{|C| = 8}$,
- minimum Hamming distance (see table): $\underline{d}_{\rm min} \underline{= 3}$.
(2) Correct is $\underline{\rm Yes}$:
- According to the singleton bound ⇒ $d_{\rm min} ≤ n - k + 1$. With $n = 6$ and $k = 3$ one obtains $d_{\rm min} ≤ 4$.
- It is thus quite possible to construct a $(6, 3)$ block code with larger minimal distance. How such a code looks, was kindly not asked.
The minimum distance of all Hamming codes is $d_{\rm min} = 3$, and only the special case with $n = 3$ and $k = 1$ reaches the limit. In contrast, the maximum reach according to the Singleton bound:
- all repetition codes $\rm (RC)$ because $k = 1$ and $d_{\rm min} = n$; this includes the $\rm (3, 1)$ Hamming code, which is known to be identical to $\rm RC\ (3, 1)$,
- all single parity–check codes $\rm (SPC)$: $k = n - 1,\ d_{\rm min} = 2$.
(3) Correct are th e solutions 2 and 3:
- If we swap rows in the generator matrix $\boldsymbol {\rm G}$, we arrive at an identical code $\mathcal{C}'$. That is, the codes $\mathcal{C}$ and $\mathcal{C}'$ contain the exact same code words.
- For example, after cyclic row swapping $2 \rightarrow 1,\ 3 \rightarrow 2$, and $1 \rightarrow 3$, one obtains the new matrix
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}}' = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The first and the last row of the new matrix already comply with the requirements of a systematic code ⇒ matrix ${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}_{\rm sys}}$ must start with a diagonal matrix.
- Replacing row 2 by the modulo 2 sum of rows 2 and 3, we get:
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}}_{\rm sys} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &0 &1 &0 &1\\ 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This systematic code contains exactly the same code words as the codes $\mathcal{C}$ and $\mathcal{C}'$.
(4) Correct are the solutions 1 and 2:
- Applying the equation $\underline{x}_{\rm sys} = \underline{u} \cdot \boldsymbol{\rm G}_{\rm sys}$ to the above examples, we see that the first two statements are correct, but not the last one.
- Without calculation one comes to the same result, if one considers that
- the systematic code word $\underline{x}_{\rm sys}$ must start with $\underline{u}$,
- the code $\mathcal{C}_{\rm sys}$ contains the same code words as the given code $\mathcal{C}$.
- For $\underline{u} = (0, 1, 0)$, the code word is thus $(0, 1, 0, ?, ?, ?)$.
- A comparison with the code table of $\mathcal{C}$ in the information section leads to $\underline{x}_{\rm sys} = (0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1)$.
(5) Only statement 1 is correct. The statements for $p_{2}$ and $p_{3}$, on the other hand, are exactly reversed.
- With systematic coding, the following relationship exists between the generator matrix and the parity-check matrix:
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}} =\left({ \boldsymbol{\rm I}}_k \: ; \:{ \boldsymbol{\rm P}} \right) \hspace{0.3cm}\Leftrightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H}} =\left({ \boldsymbol{\rm P}}^{\rm T}\: ; \:{ \boldsymbol{\rm I}}_m \right) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Applied to the current example, we obtain thus:
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm G}}_{\rm sys} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &0 &0 &1 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &0 &1 &0 &1\\ 0 &0 &1 &0 &1 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm sys} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &1 &0 &1 &0 &0\\ 1 &0 &1 &0 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &0 &0 &1 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This results in parity-check equations (see graph):
- $$u_1 \oplus u_2 \oplus p_1 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} p_1 = u_1 \oplus u_2 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ u_1 \oplus u_3 \oplus p_2 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} p_2 = u_1 \oplus u_3 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ u_2 \oplus u_3 \oplus p_3 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} p_3 = u_2 \oplus u_3 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$