Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.3: UMTS Access Level"
From LNTwww
| (14 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Examples_of_Communication_Systems/UMTS_Network_Architecture |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_Bei_A_4_3_v2.png|right|frame|UMTS access network]] |
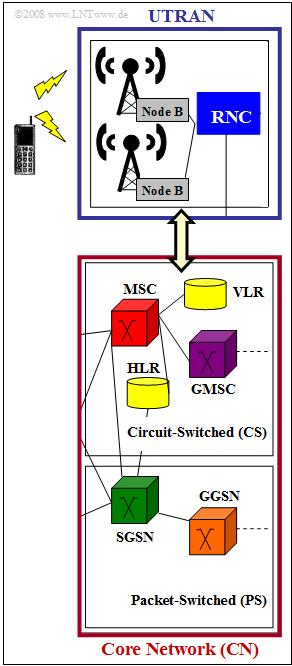
| − | + | The figure shows the UMTS access network with the two main blocks: | |
| − | *$ | + | *${\rm UTRAN}$ $($"UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network", upper graph$)$: This monitors the radio transmission between the radio network layer and the transport layer; |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *${\rm CN}$$($"Core Network", lower graph$)$: This is responsible for switching data within the UMTS network. | ||
| + | The exercise will explain some of the abbreviations used in the figure. | ||
| + | <u>Hints:</u> | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/UMTS_Network_Architecture|"UMTS Network Architecture"]]. | ||
| + | *Reference is made in particular to the section [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/UMTS_Network_Architecture#Access_level_architecture|"Access level architecture"]]. | ||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
| + | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| + | {Which switching types are supported by UMTS? | ||
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | - Circuit-switching only, | ||
| + | - packet-switching only, | ||
| + | + both circuit-switching and packet-switching. | ||
| + | {What does UTRAN include? | ||
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | + The base stations, | ||
| + | + the "Radio Network Controller" $\rm (RNC)$, | ||
| + | - the "Mobile Service Switching Center" $\rm (MSC)$. | ||
| + | {Which registers are required for circuit-switching? | ||
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | + the "Home Location Register" $\rm (HLR)$, | ||
| + | + the "Visitor Location Register" $\rm (VLR)$, | ||
| + | - the GPRS register. | ||
| + | {Which of the following statements are true? | ||
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | + $\rm GMSC$ and $\rm GGSN$ forward to other data networks. | ||
| + | - $\rm GMSC$ and $\rm GGSN$ are active only when there is circuit-switching. | ||
| + | + $\rm SGSN$ has a similar function to $\rm MSC$ and $\rm HLR$. | ||
| + | </quiz> | ||
| + | ===Solutions=== | ||
| + | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| + | '''(1)''' Correct is the <u>Answer 3</u>: UMTS networks support: | ||
| + | *Circuit-switching $\rm (CS)$: In this case, the radio channel is not available to other users during the entire switching period. | ||
| + | *Packet-switching $\rm (PS)$: The data stream is divided into small data packets in the transmitter and then sent together with other packets. The channel can thus be shared by several users. | ||
| + | '''(2)''' Correct are the <u>Answers 1 and 2</u>: | ||
| + | *As can be seen from the diagram, UTRAN includes various base stations, usually called "Node B" in UMTS, and various "Radio Network Controllers" in each case. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *$\rm MSC$ $($"Mobile Service Switching Center"$)$ is a part of the core network. | ||
| − | + | '''(3)''' Correct are the <u>Answers 1 and 2</u>: | |
| + | *The "Home Location Register" $\rm HLR$ contains all subscriber data, for example rate model, telephone number, service-specific authorizations, and keys of a network operator's own customers. | ||
| − | + | *In contrast, the "Visitor Location Register" $\rm VLR$ contains information about locally registered users and copies of the records from the HLR of its network operator. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *This data is dynamic: As soon as the subscriber changes his location, this information is changed. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *The GPRS register $\rm (GR)$ is part of the HLR. It contains additional subscriber information, but it is only needed for packet-switched transmission. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''( | + | '''(4)''' Correct are the <u>Answers 1 and 3</u>: |
| − | + | *The "Gateway Mobile Switching Center" $\rm (GMSC)$ is the switching center in mobile systems for forwarding data to the $($circuit-switched$)$ fixed network. | |
| − | + | *For packet data networks such as the Internet, the "Gateway GRRS Support Node" $\rm (GGSN)$ is responsible for this. | |
| + | |||
| + | *The "Serving GRRS Support Node" $\rm (SGSN)$ has similar tasks for packet-switching as the MSC and the HLR have for circuit-switched transmission. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 91: | Line 93: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Examples of Communication Systems: Exercises|^4.2 UMTS Network Architecture |
^]] | ^]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:49, 15 February 2023
The figure shows the UMTS access network with the two main blocks:
- ${\rm UTRAN}$ $($"UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network", upper graph$)$: This monitors the radio transmission between the radio network layer and the transport layer;
- ${\rm CN}$$($"Core Network", lower graph$)$: This is responsible for switching data within the UMTS network.
The exercise will explain some of the abbreviations used in the figure.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "UMTS Network Architecture".
- Reference is made in particular to the section "Access level architecture".
Questions
Solutions
(1) Correct is the Answer 3: UMTS networks support:
- Circuit-switching $\rm (CS)$: In this case, the radio channel is not available to other users during the entire switching period.
- Packet-switching $\rm (PS)$: The data stream is divided into small data packets in the transmitter and then sent together with other packets. The channel can thus be shared by several users.
(2) Correct are the Answers 1 and 2:
- As can be seen from the diagram, UTRAN includes various base stations, usually called "Node B" in UMTS, and various "Radio Network Controllers" in each case.
- $\rm MSC$ $($"Mobile Service Switching Center"$)$ is a part of the core network.
(3) Correct are the Answers 1 and 2:
- The "Home Location Register" $\rm HLR$ contains all subscriber data, for example rate model, telephone number, service-specific authorizations, and keys of a network operator's own customers.
- In contrast, the "Visitor Location Register" $\rm VLR$ contains information about locally registered users and copies of the records from the HLR of its network operator.
- This data is dynamic: As soon as the subscriber changes his location, this information is changed.
- The GPRS register $\rm (GR)$ is part of the HLR. It contains additional subscriber information, but it is only needed for packet-switched transmission.
(4) Correct are the Answers 1 and 3:
- The "Gateway Mobile Switching Center" $\rm (GMSC)$ is the switching center in mobile systems for forwarding data to the $($circuit-switched$)$ fixed network.
- For packet data networks such as the Internet, the "Gateway GRRS Support Node" $\rm (GGSN)$ is responsible for this.
- The "Serving GRRS Support Node" $\rm (SGSN)$ has similar tasks for packet-switching as the MSC and the HLR have for circuit-switched transmission.