Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.11: Chebyshev's Inequality"
From LNTwww
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_Sto_A_3_11_neu.png|right|frame|Exemplary Chebyshev bound]] |
[[File:P_ID921__Sto_A_3_11_b.png|frame|Values of the "complementary Gaussian error function"]] | [[File:P_ID921__Sto_A_3_11_b.png|frame|Values of the "complementary Gaussian error function"]] | ||
If nothing else is known about a random variable $x$ than only | If nothing else is known about a random variable $x$ than only | ||
| − | *the mean value $m_x$ and | + | *the mean value $m_x$, and |
| − | *the | + | *the standard deviation $\sigma_x$, |
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| − | From this plot it can be seen that the "Chebyshev's Inequality" is only a very rough bound. <br>It should be used only if really only the mean and the | + | From this plot it can be seen that the "Chebyshev's Inequality" is only a very rough bound. <br>It should be used only if really only the mean and the standard deviation are known from the random size. |
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' Correct are <u>the proposed solutions 2 and 3</u>: | + | '''(1)''' Correct are <u>the proposed solutions 2 and 3</u>: |
| − | *The first statement is false. Chebyshev's inequality provides the bound | + | *The first statement is false. Here, Chebyshev's inequality provides the bound $1/9$. |
| − | *For no distribution | + | *For no distribution the probability considered here can be equal $1/4$. |
| − | *For $\varepsilon < \sigma_x$ Chebyshev yields a probability greater $1$. This information is useless. | + | *For $\varepsilon < \sigma_x$ ⇒ Chebyshev yields a probability greater $1$. This information is useless. |
| − | *The last statement is true. For example, | + | *The last statement is true. For example, with the uniform distribution: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr}(| x- m_x | \ge \varepsilon)=\left\{ \begin{array}{*{4}{c}} 1-{\varepsilon}/{\varepsilon_{\rm 0}} & \rm | + | :$${\rm Pr}(| x- m_x | \ge \varepsilon)=\left\{ \begin{array}{*{4}{c}} 1-{\varepsilon}/{\varepsilon_{\rm 0}} & \rm for\hspace{0.1cm}{\it \varepsilon<\varepsilon_{\rm 0}=\sqrt{\rm 3}\cdot\sigma_x},\\\rm 0 & \rm else. \end{array} \right. $$ |
| + | |||
'''(2)''' For the Gaussian distribution holds: | '''(2)''' For the Gaussian distribution holds: | ||
:$$p_k={\rm Pr}(| x-m_x| \ge k\cdot\sigma_{x})=\rm 2\cdot \rm Q(\it k).$$ | :$$p_k={\rm Pr}(| x-m_x| \ge k\cdot\sigma_{x})=\rm 2\cdot \rm Q(\it k).$$ | ||
| − | *This results in the following numerical values (in brackets: bound according to Chebyshev): | + | *This results in the following numerical values $($in brackets: bound according to Chebyshev$)$: |
:$$k= 1\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge \sigma_{x}) = 31.7 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(100 \%),$$ | :$$k= 1\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge \sigma_{x}) = 31.7 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(100 \%),$$ | ||
:$$k= 2\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 2 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = 4.54 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(25 \%),$$ | :$$k= 2\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 2 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = 4.54 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(25 \%),$$ | ||
| Line 75: | Line 76: | ||
:$$k= 4\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 4 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = 0.0064 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(6.25 \%).$$ | :$$k= 4\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 4 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = 0.0064 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(6.25 \%).$$ | ||
| − | '''(3)''' Without restricting generality, we set $\lambda = 1$ | + | |
| + | '''(3)''' Without restricting generality, we set $\lambda = 1$ | ||
⇒ $m_x = \sigma_x = 1$. Then holds: | ⇒ $m_x = \sigma_x = 1$. Then holds: | ||
:$${\rm Pr}(|x - m_x| \ge k\cdot\sigma_{x}) = {\rm Pr}(| x-1| \ge k).$$ | :$${\rm Pr}(|x - m_x| \ge k\cdot\sigma_{x}) = {\rm Pr}(| x-1| \ge k).$$ | ||
| − | *Since in this special case the random variable is always $x >0$ | + | *Since in this special case the random variable is always $x >0$, it further holds: |
:$$p_k= {\rm Pr}( x \ge k+1)=\int_{k+\rm 1}^{\infty}\hspace{-0.15cm} | :$$p_k= {\rm Pr}( x \ge k+1)=\int_{k+\rm 1}^{\infty}\hspace{-0.15cm} | ||
{\rm e}^{-x}\, {\rm d} x={\rm e}^{-( k + 1)}.$$ | {\rm e}^{-x}\, {\rm d} x={\rm e}^{-( k + 1)}.$$ | ||
*This yields the following numerical values for the exponential distribution: | *This yields the following numerical values for the exponential distribution: | ||
| − | :$$k= 1\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge \sigma_{x}) \rm e^{-2}= \rm 13.53\%,$$ | + | :$$k= 1\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge \sigma_{x})= \rm e^{-2}= \rm 13.53\%,$$ |
:$$k= 2\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 2 \cdot \sigma_{x})= \rm \rm e^{-3}=\rm 4.97\% ,$$ | :$$k= 2\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 2 \cdot \sigma_{x})= \rm \rm e^{-3}=\rm 4.97\% ,$$ | ||
| − | :$$k= 3 | + | :$$k= 3\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 3 \cdot\sigma_{x})= \rm \rm e^{-4}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =\rm 1.83\% },$$ |
:$$k= 4\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 4 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = \rm e^{-5}= \rm 0.67\%.$$ | :$$k= 4\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 4 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = \rm e^{-5}= \rm 0.67\%.$$ | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:39, 13 March 2023
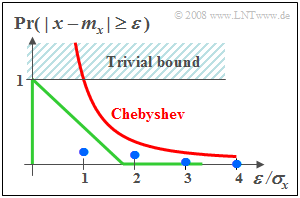
If nothing else is known about a random variable $x$ than only
- the mean value $m_x$, and
- the standard deviation $\sigma_x$,
so the "Chebyshev's Inequality" gives an upper bound on the probability that $x$ deviates by more than a value $\varepsilon$ from its mean. This bound is:
- $${\rm Pr}(|x-m_x|\ge \varepsilon) \le {\sigma_x^{\rm 2}}/{\varepsilon^{\rm 2}}.$$
To explain:
- In the graph, this upper bound is drawn in red.
- The green curve shows the actual probability for the uniform distribution.
- The blue points are for the exponential distribution.
From this plot it can be seen that the "Chebyshev's Inequality" is only a very rough bound.
It should be used only if really only the mean and the standard deviation are known from the random size.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Further Distributions".
- In particular, reference is made to the section "Chebyshev's inequality" .
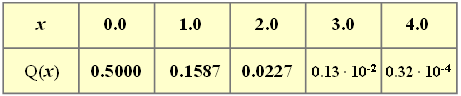
- On the right, values of the complementary Gaussian error function ${\rm Q}(x)$ are given.
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct are the proposed solutions 2 and 3:
- The first statement is false. Here, Chebyshev's inequality provides the bound $1/9$.
- For no distribution the probability considered here can be equal $1/4$.
- For $\varepsilon < \sigma_x$ ⇒ Chebyshev yields a probability greater $1$. This information is useless.
- The last statement is true. For example, with the uniform distribution:
- $${\rm Pr}(| x- m_x | \ge \varepsilon)=\left\{ \begin{array}{*{4}{c}} 1-{\varepsilon}/{\varepsilon_{\rm 0}} & \rm for\hspace{0.1cm}{\it \varepsilon<\varepsilon_{\rm 0}=\sqrt{\rm 3}\cdot\sigma_x},\\\rm 0 & \rm else. \end{array} \right. $$
(2) For the Gaussian distribution holds:
- $$p_k={\rm Pr}(| x-m_x| \ge k\cdot\sigma_{x})=\rm 2\cdot \rm Q(\it k).$$
- This results in the following numerical values $($in brackets: bound according to Chebyshev$)$:
- $$k= 1\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge \sigma_{x}) = 31.7 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(100 \%),$$
- $$k= 2\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 2 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = 4.54 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(25 \%),$$
- $$k= 3\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 3 \cdot\sigma_{x})\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0.26 \%} \hspace{0.3cm}(11.1 \%),$$
- $$k= 4\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 4 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = 0.0064 \% \hspace{0.3cm}(6.25 \%).$$
(3) Without restricting generality, we set $\lambda = 1$
⇒ $m_x = \sigma_x = 1$. Then holds:
- $${\rm Pr}(|x - m_x| \ge k\cdot\sigma_{x}) = {\rm Pr}(| x-1| \ge k).$$
- Since in this special case the random variable is always $x >0$, it further holds:
- $$p_k= {\rm Pr}( x \ge k+1)=\int_{k+\rm 1}^{\infty}\hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm e}^{-x}\, {\rm d} x={\rm e}^{-( k + 1)}.$$
- This yields the following numerical values for the exponential distribution:
- $$k= 1\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge \sigma_{x})= \rm e^{-2}= \rm 13.53\%,$$
- $$k= 2\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 2 \cdot \sigma_{x})= \rm \rm e^{-3}=\rm 4.97\% ,$$
- $$k= 3\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 3 \cdot\sigma_{x})= \rm \rm e^{-4}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =\rm 1.83\% },$$
- $$k= 4\text{:}\hspace{0.5cm} {\rm Pr}(|x-m_x| \ge 4 \cdot \sigma_{x}) = \rm e^{-5}= \rm 0.67\%.$$