Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.4: Simple Phase Modulator"
m (→Questions) |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/Phase_Modulation_(PM) |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1086__Mod_A_3_4.png|right|frame|& | + | [[File:P_ID1086__Mod_A_3_4.png|right|frame|"Approximate phase modulator"]] |
| − | + | The adjacent circuit allows the approximate realization of a phase-modulated signal. | |
| + | |||
| + | From the cosinusoidal carrier, $z(t)$ , the $90^\circ$ phase shifter forms a sinusoidal signal of the same frequency, such that the modulated signal can be written as: | ||
:$$ s(t) = z(t) + q(t) \cdot \frac{z(t- T_0/4)}{A_{\rm T}} | :$$ s(t) = z(t) + q(t) \cdot \frac{z(t- T_0/4)}{A_{\rm T}} | ||
= A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + q(t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + q(t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The second term describes a "DSB–AM without carrier". Additionally, the carrier, phase-shifted by $90^\circ$ , is added. Thus, with a cosine source signal $q(t) = A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)$ , we get: | |
:$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) $$ | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) $$ | ||
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \ | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \big[\cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | We refer to the ratio $η = A_{\rm N}/A_{\rm T}$ as the modulation index; in the following, the carrier amplitude is set to $A_{\rm T} = 1$ for simplicity. | |
| + | |||
| + | *In contrast to [[Modulation_Methods/Phasenmodulation_(PM)#Signalverl.C3.A4ufe_bei_Phasenmodulation|ideal phase modulation]] the modulation index $η$ and the phase deviation $ϕ_{\rm max}$ may differ in this "approximate phase modulation". | ||
| + | *Additionally, we can see that the envelope $a(t) ≠ 1$ . This means that an unwanted amplitude modulation is superimposed on the phase modulation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | From the representation of the equivalent low-pass signal $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ in the complex plane (locus curve), the following are to be calculated in this task: | ||
| + | *the envelope $a(t)$ and | ||
| + | *the phase function $ϕ(t)$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Then, you are to analyse the distortions arising when an ideal PM demodulator, which sets the sink signal $v(t)$ proportional to the phase $ϕ(t)$ , is used on the receiving side of this nonideal PM modulator. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '' | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | ''Hints:'' |
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Phase_Modulation_(PM)|Phase Modulation]]. | ||
| + | *Particular reference is made to the page [[Modulation_Methods/Phase_Modulation_(PM)#Equivalent_low-pass_signal_in_phase_modulation|Equivalent low-pass signal in phase modulation]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *You can use the following equations to approximate the distortion factor: | ||
:$$\arctan(\gamma) \approx \gamma - {\gamma^3}/{3} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \cos^3(\gamma) ={3}/{4} \cdot \cos(\gamma) +{1}/{4} \cdot \cos(3 \cdot \gamma) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\arctan(\gamma) \approx \gamma - {\gamma^3}/{3} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \cos^3(\gamma) ={3}/{4} \cdot \cos(\gamma) +{1}/{4} \cdot \cos(3 \cdot \gamma) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the equivalent low-pass signal. Which statement is true? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
| − | - | + | - The locus curve $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ is a circular arc. |
| − | - | + | - The locus curve $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ is a horizontal straight line. |
| − | + | + | + The locus curve $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ is a vertical straight line. |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the (normalized) envelope $a(t)$ for $A_{\rm T} = 1$. What are its minimum and maximum values when $η = 1$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$a_{\rm min} \ = \ $ { 1 3% } | $a_{\rm min} \ = \ $ { 1 3% } | ||
$a_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 1.414 3% } | $a_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 1.414 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the maximum value of the phase $ϕ(t)$ for $η = 1$ and $η = 0.5$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$η = 1.0\text{:} \ \ \ ϕ_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 45 3% } $\ \rm Grad$ | $η = 1.0\text{:} \ \ \ ϕ_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 45 3% } $\ \rm Grad$ | ||
$η = 0.5\text{:} \ \ \ ϕ_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 26.6 3% } $\ \rm Grad$ | $η = 0.5\text{:} \ \ \ ϕ_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 26.6 3% } $\ \rm Grad$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What distortions result after ideal phase demodulation of $s(t)$? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
| − | - | + | - No distortions occur. |
| − | - | + | - Linear distortions occur. |
| − | + | + | + Nonlinear distortions occur. |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the distortion factor $K$ considering the trigonometric relationships given on the exercise page. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$η = 1.0\text{:} \ \ \ K \ = \ $ { 11.1 3% } $\ \text{%}$ | $η = 1.0\text{:} \ \ \ K \ = \ $ { 11.1 3% } $\ \text{%}$ | ||
| Line 67: | Line 76: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1087__Mod_A_3_4_a.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1087__Mod_A_3_4_a.png|right|frame|Construction of the "vertical locus" from the pointers]] |
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' <u>Answer 3</u> is correct: |
| − | * | + | *The equivalent low-pass signal is::$$s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \left ( 1 + {\rm j}\cdot \frac {\eta}{2}\cdot \left ({\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t} + {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{-\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t}\right) \right) |
| − | :$$s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \left ( 1 + {\rm j}\cdot \frac {\eta}{2}\cdot \left ({\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t} + {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{-\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t}\right) \right) | + | = A_{\rm T} \cdot \big ( 1 + {\rm j}\cdot {\eta}\cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \big)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | = A_{\rm T} \cdot \ | + | *The graph illustrates that the locus curve $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ is now a a vertical straight line in contrast to the ideal PM (circular arc) and DSB–AM (horizontal straight line). |
| − | * | + | *In the following, we set $A_{\rm T} = 1$ . |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' The envelope is obtained from the time-dependent pointer length as |
:$$a(t) = \sqrt{1 + \eta^2 \cdot \cos^2 (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)} \hspace{0.3cm} | :$$a(t) = \sqrt{1 + \eta^2 \cdot \cos^2 (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)} \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm min} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 1}, \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm max} = \sqrt{1 + \eta^2 }\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm min} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 1}, \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm max} = \sqrt{1 + \eta^2 }\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *For $η = 1$ the maximum value becomes $a_{\rm max} = \sqrt{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { ≈ 1.414}$. | |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | |
| + | '''(3)''' The phase function of this simple phase demodulator is given by: | ||
:$$\phi(t) = \arctan \frac{{\rm Im}[s_{\rm TP}(t)]}{{\rm Re}[s_{\rm TP}(t)]} = \arctan (\eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\phi(t) = \arctan \frac{{\rm Im}[s_{\rm TP}(t)]}{{\rm Re}[s_{\rm TP}(t)]} = \arctan (\eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The maximum value occurs at time $t = 0$ , for example, and is $ϕ_{\rm max} = \arctan(η)$. | |
| − | * | + | :*When $η = 1$ , one obtains $ϕ_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 45^\circ}$ $($to compare: for ideal PM $57.3^\circ)$, |
| − | * | + | :*When $η = 0.5$ one gets $ϕ_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { \approx 26.6^\circ}$ $($for ideal PM $28.7^\circ)$. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(4)''' <u>Answer 3</u> is correct: | ||
| + | *It is '''not''' true that: $\arctan\big [η · \cos(γ)\big ] = η · \cos(γ)$. | ||
| + | *This means that the sink signal is not cosine, in contrast to the source signal. | ||
| + | *This points to nonlinear distortions. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' Using $γ = η · \cos(ω_N · t)$ and $\arctan(γ) ≈ γ – γ^3/3$ , we get: |
:$$ \phi(t) = \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - \frac{\eta^3}{3}\cdot \cos^3 (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t))= | :$$ \phi(t) = \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - \frac{\eta^3}{3}\cdot \cos^3 (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t))= | ||
\eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - \frac{\eta^3}{3}\cdot \left [ {3}/{4}\cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) + {1}/{4}\cdot \cos (3 \omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\right ] $$ | \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - \frac{\eta^3}{3}\cdot \left [ {3}/{4}\cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) + {1}/{4}\cdot \cos (3 \omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\right ] $$ | ||
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \phi(t) = \left(\eta - {\eta^3}/{4} \right) \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - {\eta^3}/{12}\cdot \cos (3\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \phi(t) = \left(\eta - {\eta^3}/{4} \right) \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - {\eta^3}/{12}\cdot \cos (3\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | *This means: using the given series expansion (where 5th and higher order terms are ignored), only the third-order harmonic distortion is non-zero. Thus: | |
:$$K = K_3 = \frac{\eta^3/12}{\eta-\eta^3/4}= \frac{1}{12/\eta^2 -3} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$K = K_3 = \frac{\eta^3/12}{\eta-\eta^3/4}= \frac{1}{12/\eta^2 -3} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *When $η = 1$ the numerical value is $K = 1/9 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { ≈ 11.1\%}$. |
| − | * | + | *When $η = 0.5$ the distortion factor is $K = 1/45 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {≈ 2.2\%}$. |
| − | + | A simulation shows that by stopping the series after the third order term, we have made the error of over-estimating the distortion factor: | |
| − | * | + | *The values obtained by simulation are $K ≈ 6%$ $($for $η = 1)$ and $K ≈ 2%$ $($for $η = 0.5)$. |
| − | * | + | *Thus, the error increases more than proportionally with increasing $η$ . |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 114: | Line 126: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Modulation Methods: Exercises|^3.1 Phase Modulation^]] |
Latest revision as of 16:04, 9 April 2022
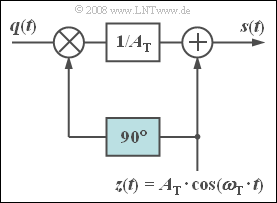
The adjacent circuit allows the approximate realization of a phase-modulated signal.
From the cosinusoidal carrier, $z(t)$ , the $90^\circ$ phase shifter forms a sinusoidal signal of the same frequency, such that the modulated signal can be written as:
- $$ s(t) = z(t) + q(t) \cdot \frac{z(t- T_0/4)}{A_{\rm T}} = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + q(t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The second term describes a "DSB–AM without carrier". Additionally, the carrier, phase-shifted by $90^\circ$ , is added. Thus, with a cosine source signal $q(t) = A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)$ , we get:
- $$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \big[\cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
We refer to the ratio $η = A_{\rm N}/A_{\rm T}$ as the modulation index; in the following, the carrier amplitude is set to $A_{\rm T} = 1$ for simplicity.
- In contrast to ideal phase modulation the modulation index $η$ and the phase deviation $ϕ_{\rm max}$ may differ in this "approximate phase modulation".
- Additionally, we can see that the envelope $a(t) ≠ 1$ . This means that an unwanted amplitude modulation is superimposed on the phase modulation.
From the representation of the equivalent low-pass signal $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ in the complex plane (locus curve), the following are to be calculated in this task:
- the envelope $a(t)$ and
- the phase function $ϕ(t)$.
Then, you are to analyse the distortions arising when an ideal PM demodulator, which sets the sink signal $v(t)$ proportional to the phase $ϕ(t)$ , is used on the receiving side of this nonideal PM modulator.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Phase Modulation.
- Particular reference is made to the page Equivalent low-pass signal in phase modulation.
- You can use the following equations to approximate the distortion factor:
- $$\arctan(\gamma) \approx \gamma - {\gamma^3}/{3} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \cos^3(\gamma) ={3}/{4} \cdot \cos(\gamma) +{1}/{4} \cdot \cos(3 \cdot \gamma) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
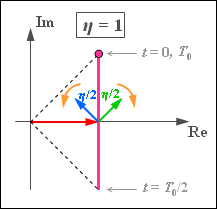
(1) Answer 3 is correct:
- The equivalent low-pass signal is::$$s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \left ( 1 + {\rm j}\cdot \frac {\eta}{2}\cdot \left ({\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t} + {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{-\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t}\right) \right) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \big ( 1 + {\rm j}\cdot {\eta}\cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \big)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The graph illustrates that the locus curve $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ is now a a vertical straight line in contrast to the ideal PM (circular arc) and DSB–AM (horizontal straight line).
- In the following, we set $A_{\rm T} = 1$ .
(2) The envelope is obtained from the time-dependent pointer length as
- $$a(t) = \sqrt{1 + \eta^2 \cdot \cos^2 (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm min} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 1}, \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm max} = \sqrt{1 + \eta^2 }\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- For $η = 1$ the maximum value becomes $a_{\rm max} = \sqrt{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { ≈ 1.414}$.
(3) The phase function of this simple phase demodulator is given by:
- $$\phi(t) = \arctan \frac{{\rm Im}[s_{\rm TP}(t)]}{{\rm Re}[s_{\rm TP}(t)]} = \arctan (\eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The maximum value occurs at time $t = 0$ , for example, and is $ϕ_{\rm max} = \arctan(η)$.
- When $η = 1$ , one obtains $ϕ_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 45^\circ}$ $($to compare: for ideal PM $57.3^\circ)$,
- When $η = 0.5$ one gets $ϕ_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { \approx 26.6^\circ}$ $($for ideal PM $28.7^\circ)$.
(4) Answer 3 is correct:
- It is not true that: $\arctan\big [η · \cos(γ)\big ] = η · \cos(γ)$.
- This means that the sink signal is not cosine, in contrast to the source signal.
- This points to nonlinear distortions.
(5) Using $γ = η · \cos(ω_N · t)$ and $\arctan(γ) ≈ γ – γ^3/3$ , we get:
- $$ \phi(t) = \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - \frac{\eta^3}{3}\cdot \cos^3 (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t))= \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - \frac{\eta^3}{3}\cdot \left [ {3}/{4}\cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) + {1}/{4}\cdot \cos (3 \omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\right ] $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \phi(t) = \left(\eta - {\eta^3}/{4} \right) \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) - {\eta^3}/{12}\cdot \cos (3\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This means: using the given series expansion (where 5th and higher order terms are ignored), only the third-order harmonic distortion is non-zero. Thus:
- $$K = K_3 = \frac{\eta^3/12}{\eta-\eta^3/4}= \frac{1}{12/\eta^2 -3} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- When $η = 1$ the numerical value is $K = 1/9 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { ≈ 11.1\%}$.
- When $η = 0.5$ the distortion factor is $K = 1/45 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {≈ 2.2\%}$.
A simulation shows that by stopping the series after the third order term, we have made the error of over-estimating the distortion factor:
- The values obtained by simulation are $K ≈ 6%$ $($for $η = 1)$ and $K ≈ 2%$ $($for $η = 0.5)$.
- Thus, the error increases more than proportionally with increasing $η$ .