Difference between revisions of "Modulation Methods/Frequency Modulation (FM)"
| (95 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Header | {{Header | ||
| − | |Untermenü= | + | |Untermenü=Angle Modulation and Demodulation |
| − | |Vorherige Seite= | + | |Vorherige Seite=Phase Modulation (PM) |
| − | |Nächste Seite= | + | |Nächste Seite=Influence of Noise on Systems with Angle Modulation |
}} | }} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Instantaneous frequency== |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos | + | We will once again assume an angle-modulated signal: |
| − | + | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \big[\psi(t)\big].$$ | |
| − | * | + | All the information about the source signal $q(t)$ |
| − | * | + | *is thus exclusively captured by the angular function $ψ(t)$, |
| + | |||
| + | *while the envelope $a(t) = A_{\rm T}$ is constant. | ||
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | $\text{Definitions:}$ |
| + | *The »'''instantaneous angular frequency'''« is the derivative of the angular function with respect to time: | ||
:$$\omega_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{ {\rm d}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\omega_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{ {\rm d}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | *Accordingly, the »'''instantaneous frequency'''« is captured by: | ||
:$$f_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{\omega_{\rm A}(t)}{2\pi} = \frac{1}{2\pi} \cdot \frac{ {\rm d}\hspace{0.03cm}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$f_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{\omega_{\rm A}(t)}{2\pi} = \frac{1}{2\pi} \cdot \frac{ {\rm d}\hspace{0.03cm}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | *The »'''frequency deviation'''« is the maximum deviation $Δf_{\rm A}$ of the time-dependent instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ from the constant carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$. }} | ||
| − | + | For an angle modulation with carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$ , the instantaneous frequency oscillates in the range | |
:$$f_{\rm T} - \Delta f_{\rm A} \le f_{\rm A}(t) \le f_{\rm T} + \Delta f_{\rm A}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$f_{\rm T} - \Delta f_{\rm A} \le f_{\rm A}(t) \le f_{\rm T} + \Delta f_{\rm A}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | It should be emphasized: | |
| + | # There is a fundamental difference between the instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ and the spectrum $S(f)$ of an angle-modulated signal $s(t)$. | ||
| + | #This is illustrated by the following example. $S(f)$ can be measured with a spectrum analyzer. | ||
| + | |||
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | [[File:P_ID1101__Mod_T_3_2_S1_neu.png |right|frame| Illustration of the instantaneous frequency]] |
| − | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos | + | $\text{Example 1:}$ The graph shows the phase-modulated signal |
| + | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\psi(t)\big] = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[2 \pi f_{\rm T} \hspace{0.05cm}t + \eta \cdot \sin (2 \pi f_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm} t)\big]$$ | ||
| − | + | as well as the instantaneous frequency plotted beneath | |
:$$f_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{1}{2 \pi} \cdot \frac{ {\rm d}\hspace{0.03cm}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t} = f_{\rm T} + \Delta f_{\rm A}\cdot \cos (2 \pi f_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm} t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$f_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{1}{2 \pi} \cdot \frac{ {\rm d}\hspace{0.03cm}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t} = f_{\rm T} + \Delta f_{\rm A}\cdot \cos (2 \pi f_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm} t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Here, the system parameters are: | |
| + | * carrier frequency $f_{\rm T} = 50 \ \rm kHz$ ⇒ frequency of $z(t)$, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * message frequency $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ ⇒ frequency of $q(t)$, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * message modulation index $η = 3$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | From this, we derive the (maximum) frequency deviation | |
| − | * | + | * $Δf_{\rm A} = η · f_{\rm N} = 15 \ \rm kHz$. |
| − | |||
| − | + | In the middle, the qualitative progression of the sinusoidal source signal $q(t)$ is plotted for reference. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | From these graphs, one can see: | ||
| + | *The instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ can take on arbitrary values between $f_{\rm T} + Δf_{\rm A} = 65 \ \rm kHz$ $($at $t = 50\ \rm µ s,\ 250 \ µ s$, etc.$)$ and $f_{\rm T} \ – Δf_{\rm A} = 35 \ \rm kHz$ $($at $t = 150\ \rm µ s, \ 350 \ µ s$, etc.$)$ ⇒ green marks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *At time $t ≈ 16.7 \ \rm µ s$ , for example, $f_{\rm A}(t) = 57.5 \ \rm kHz$ holds ⇒ purple arrow. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In contrast, the spectral function $S(f)$ consists of discrete Bessel lines at the frequencies ... , $30,\ 35,\ 40,\ 45,\ \mathbf{50},\ 55,\ 60,\ 65,\ 70$, ... $($each in $\rm kHz)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *There is no spectral line at $f = 57.5 \ \rm kHz$, though there is one at $f = 70 \ \rm kHz$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In contrast, at no time does $f_{\rm A}(t) = 70 \ \rm kHz$ hold. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | $\text{Therefore:}$ | ||
| − | + | The '''instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ is thus not a physically measurable frequency''' in the conventional sense, but only an »'''abstract mathematical quantity'''«, namely the derivative of the angular function $ψ(t)$.}} | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Signal characteristics with frequency modulation== | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | As in the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Phase_Modulation_(PM)|"Phase Modulation"]] we will assume that the carrier signal $z(t)$ has a cosine waveform and the source signal $q(t)$ is peak-limited. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | |
| + | $\text{Definition:}$ If the instantaneous angular frequency $ω_{\rm A}(t)$ of a communication system is linearly dependent on the instantaneous value of the source signal $q(t)$, we call this »'''frequency modulation'''« $\rm (FM)$: | ||
| + | :$$\omega_{\rm A}(t) = 2 \pi \cdot f_{\rm A}(t) = \omega_{\rm T} + K_{\rm FM} \cdot q(t) | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | Here, $K_{\rm FM}$ denotes a dimensionally restricted constant. If $q(t)$ represents a voltage waveform, $K_{\rm FM}$ has the unit $\rm V^{–1}s^{–1}$. }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In frequency modulation, the angular function $\psi(t)$ and the modulated signal $s(t)$ are given by: | |
| − | + | :$$\psi(t) = \omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + K_{\rm FM} \cdot \int q(t)\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}t \hspace{0.05cm}\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \big[\psi(t)\big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | |
| − | $$ | ||
| + | [[File:EN_Mod_T_3_2_S2_v1.png |right|frame|Relationship between phase and frequency modulation]] | ||
| − | + | From these equations, we can immediately see: | |
| − | $ | + | *Even in the case of frequency modulation, the equivalent low-pass signal moves on an circular arc because of the constant envelope ⇒ $a(t) = A_{\rm T}$. |
| + | |||
| + | *A frequency modulator can be implemented using an integrator and a phase modulator. | ||
| + | *Consequently, the FM demodulator consists of a PM demodulator and a differentiator, as shown in the upper part of the diagram. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The lower graph shows the inverse relationship ⇒ a possible description of PM modulator and demodulator in terms of corresponding FM components. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= |
| + | $\text{It can also be seen from the above equation:}$ | ||
| + | * The equation encountered earlier in the section [[Modulation_Methods/General_Model_of_Modulation#A_very_simple_.28though_unfortunately_not_always_correct.29_modulator_equation|"A very simple (though unfortunately not always correct) modulator equation"]] in the first chapter of this book, will only hold for frequency modulation in very special cases. | ||
| + | *In frequency modulation, the conversion | ||
| + | :$$s(t) = a(t) \cdot \cos (\omega (t) \cdot t + \phi(t)) \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega (t) \cdot t + \phi_{\rm T})$$ | ||
| + | :is only allowed sometimes, such as in the non-linear digital modulation method [[Modulation_Methods/Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation#FSK_.E2.80.93_Frequency_Shift_Keying|$\text{Frequency Shift Keying}$]] $\rm (FSK)$ with rectangular basic pulse.}} | ||
| − | + | ==Frequency modulation of a cosine signal== | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | For a cosine source signal $q(t)$ with frequency modulation, the instantaneous angular frequency is: | ||
| + | :$$q(t) = A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \omega_{\rm A}(t) = \omega_{\rm T} + K_{\rm FM} \cdot A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | Integrating this over time, we get the angular function: | ||
| + | :$$\psi(t) = \omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \frac {K_{\rm FM} \cdot A_{\rm N}}{\omega_{\rm N}} \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | A comparison with the propositions in the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Phase_Modulation_(PM)|"Phase Modulation"]] makes clear: |
| − | + | *The frequency modulation of a cosine signal yields a qualitatively identical transmitted signal $s(t)$ as the phase modulation of a sinusoidal source signal $q(t)$. However, this requires that the modulator constants are matched according to the ratio $K_{\rm FM}/K_{\rm PM} = ω_{\rm N}$ . | |
| − | * | + | |
| + | *The transmitted signal $s(t)$ can thus be described uniformly for the two configurations "PM – sine signal" as well as "FM – cosine signal": | ||
| + | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \eta \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *However, when using this equation for the modulation index $η$, different equations must be used for phase and frequency modulation: | ||
| + | :$$\eta_{\rm PM} = {K_{\rm PM} \cdot A_{\rm N}},$$ | ||
| + | :$$\eta_{\rm FM} = \frac {K_{\rm FM} \cdot A_{\rm N}}{\omega_{\rm N}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *If the source signal is not a harmonic oscillation, but is instead composed of several frequencies, the time signals also differ qualitatively for phase and frequency modulation. This can be seen in the [[Modulation_Methods/General_Model_of_Modulation#Modulated_signals_with_a_digital_source_signal|$\text{earlier comparison of PSK and FSK}$]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | |
| − | $ | + | $\text{Example 2:}$ |
| + | We will now assume a cosine source signal $q(t)$ with amplitude $A_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm V$ and frequency $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ and we consider the signal characteristics of phase modulation $\rm (PM)$ and frequency modulation $\rm (FM)$ with the same modulation index $η = 1.5$. | ||
| + | [[File:P_ID1094__Mod_T_3_2_S3_neu.png|right|frame|$\rm PM$ and $\rm FM$ of a cosine source signal with $η = 1.5$]] | ||
| − | + | The <u>middle graph</u> shows the phase-modulated signal (red curve) for the modulator parameters $f_{\rm T} = 50 \ \rm kHz$ and $K_{\rm PM} = \rm 0.5 V^{–1}$: | |
| − | + | :$$s_{\rm PM}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\big ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | |
| + | *In phase modulation, $A_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm V$ yields $η = 1.5 ≈ π/2$ for the phase deviation (modulation index). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The maximum deviation of the zero crossings from their (equidistant) nominal positions is about a quarter of the carrier period. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If the source signal is $q(t) > 0$, the zero crossings arrive earlier, and if $q(t) < 0$ , they come somewhat too late. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The <u>lower graph</u> shows the frequency-modulated signal with the same modulation index $η$: | |
| − | + | :$$s_{\rm FM}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \eta \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\big ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In this case, $η = 1.5$ is achieved by the modulator constant | |
| − | + | :$$K_{\rm FM} = \frac {\eta \cdot \omega_{\rm N} }{A_{\rm N} } = {K_{\rm PM} \cdot \omega_{\rm N} } $$ | |
| − | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} K_{\rm FM} = 0.5\,{\rm V}^{-1} \cdot 2 \pi \cdot 5\,{\rm kHz} = 15708\,{\rm V}^{-1}{\rm s}^{-1} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | |
| − | |||
| − | + | *Here, the frequency deviation is $Δf_{\rm A} = η · f_{\rm N} = 7.5 \ \rm kHz$, and instantaneous frequencies occur between $f_{\rm T}-Δf_{\rm A} = 42.5$ and $f_{\rm T}+Δf_{\rm A} =57.5 \ \rm kHz$. | |
| − | { | + | |
| − | + | *The zero crossings now match those of the carrier signal $z(t)$ at the maxima and minima of the source signal $q(t)$, while the maximum phase deviations can be seen at the zero crossings of $q(t)$. The exact opposite is the case in phase modulation.}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Angle modulation spectrum of a harmonic oscillation== | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Now we assume a harmonic oscillation with phase $ϕ_{\rm N}$ for the source signal in general: | ||
| + | :$$q(t) = A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[2 \pi f_{\rm N} \cdot t + \phi_{\rm N}\big ].$$ | ||
| + | We are interested in the spectrum $S(f)$. For simplicity, in what follows we will consider the magnitude spectrum $|S_+(f)|$ of the analytical signal, from which $|S(f)|$ can be derived in the familiar way. | ||
| + | For any type of angle modulation described here – whether it is phase or frequency modulation – and regardless of the phase $ϕ_{\rm N}$ of the source signal, the following holds: | ||
| + | :$$|S_{\rm +}(f)| = A_{\rm T} \cdot \sum_{n = - \infty}^{+\infty}|{\rm J}_n (\eta)| \cdot \delta \big[f - (f_{\rm T} + n \cdot f_{\rm N})\big]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | [[ | + | This equation can be explained as follows: |
| + | *In the section [[Modulation_Methods/Phase_Modulation_(PM)#Equivalent_low-pass_signal_in_phase_modulation|"Equivalent low-pass signal in PM"]] this equation was derived for a phase-modulated sine signal, where $η = A_{\rm N} · K_{\rm PM}$ denotes the modulation index and ${\rm J}_n(η)$ denotes the $n$–th order Bessel functions of the first kind. $K_{\rm PM}$ is the modulator constant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *When the message phase $ϕ_{\rm N}$ changes, only the phase function ${\rm arc} \ S_+(f)$ changes, but not the magnitude spectrum $|S_+(f)|$. This important result is confirmed in [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.3Z:_Characteristics_Determination|"Exercise 3.3Z"]]. | ||
| + | *In the [[Modulation_Methods/Frequency_Modulation_(FM)#Frequency_modulation_of_a_cosine_signal|"Frequency modulation of a cosine signal"]] section, it was shown that a frequency-modulated signal can be represented in the same way as a phase-modulated signal if the modulation index $η = K_{\rm FM} · A_{\rm N}/ω_{\rm N}$ is used. Consequently, the magnitude spectra for $\rm PM$ and $\rm FM$ can also be represented in the same way. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | We would like to refer you to the second part of the (German language) learning video [[Winkelmodulation_-_Frequenz-_und_Phasenmodulation_(Lernvideo)|"Winkelmodulation - FM und PM"]] ⇒ "Angle modulation – FM and PM". | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{GraueBox|TEXT= |
| + | $\text{Example 3:}$ | ||
| + | Let us again consider a harmonic oscillation, here with amplitude $A_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm V$ according to | ||
| + | [[File:P_ID1095__Mod_T_3_2_S4_neu.png|right|frame|Discrete spectra in phase and frequency modulation]] | ||
| + | *phase modulation $\rm (PM)$ with $K_{\rm PM} = \rm 0.5 \ \rm V^{–1}$, | ||
| − | + | *frequency modulation $\rm (FM)$ with $K_{\rm FM} = \rm 15708 \ \rm V^{–1}s^{–1}$. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The corresponding signal characteristics are shown in [[Modulation_Methods/Frequency_Modulation_(FM)#Frequency_modulation_of_a_cosine_signal|$\text{Example 2}$]]. | |
| + | *For both transmission systems, a Bessel spectrum with modulation index $η = 1.5$ is obtained for $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The identical magnitude spectra of the analytical signal (positive frequencies only) are shown in the <u>two upper diagrams</u>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Bessel lines with values smaller than $0.03$ are ignored in both cases. | ||
| − | + | The <u>lower diagrams</u> are valid for the message frequency $f_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm kHz$: | |
| + | *In PM, there is a narrower spectrum compared to $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$, since the spacing of the Bessel lines is only $3 \ \rm kHz$ (left diagram). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Since the modulation index $η = 1.5$ does not changes, we get the same Bessel weights as for $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ (upper diagram). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Also in FM, the Bessel lines now occur at $3 \ \rm kHz$ spacing (lower graph on the right). However, there are significantly more Bessel lines than in the upper right graph (valid for $η = 1.5$ ) due to the larger modulation index $η = 2.5$ . | ||
| − | * | + | *This follows from the fact that for FM, the index $η$ is inversely proportional to $f_{\rm N}$ .}} |
| + | ==Influence of band-limiting in angle modulation== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Let us briefly summarize some previous results of this section, by assuming an example with | ||
| + | *carrier frequency $f_{\rm T} = 100 \ \rm kHz$, | ||
| + | |||
| + | *message frequency $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ and | ||
| − | * | + | *modulation index $η = π/2 \approx 1.5$: |
| + | #The spectrum of an angle-modulated oscillation consists of Bessel lines around the carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$ at a distance $f_{\rm N}$ between neighboring samplesand is infinitely extended in theory. | ||
| + | #Even if we ignore all spectral lines with magnitudes smaller than $0.01$, the now finite bandwidth for $η = π/2$ is still $B_{\rm HF} = 8 · f_{\rm N} = 40 \ \rm kHz$. | ||
| + | #The locus curve – i.e., the course of the equivalent low-pass signal in the complex plane – is ideally a circular arc with an opening angle of $±1.57 \ {\rm rad} = ±90^\circ$. | ||
| + | #However, this circular arc after vector summation results only if all Bessel lines on the locus rotate with the correct pointer lengths, the correct phase positions and the correct angular frequencies. | ||
| + | #Logically, the circular locus curve is altered when the spectral lines are distorted (e.g. by linear channel distortions) or missing altogether (e.g. by band-limiting). | ||
| + | #Since the ideal angle demodulator detects the phase $ϕ_r(t)$ of the received signal and obtains the sink signal $v(t)$ from it, the demodulator causes non-linear distortions. This means: The distortions are irreversible and cannot be compensated for by a linear filter. | ||
| + | #At the same time, this means: '''Due to linear distortions in the channel, nonlinear distortions occur in the demodulated signal''' $v(t)$. | ||
| + | #As a result, new frequencies ("harmonics") are created, which were not in the original source signal $q(t)$. | ||
| + | #The smaller the available bandwidth $B_{\rm HF}$ and the larger the chosen modulation index $η$, the larger becomes the distortion factor $K$, which captures nonlinear distortions. | ||
| + | #As a rule of thumb for the required high-frequency bandwidth for a desired distortion factor $K$, one can use the so-called »'''Carson Rule'''«: | ||
| + | ::$$K < 10\%\text{:}\hspace{0.6cm} B_{\rm HF} \ge 2 \cdot f_{\rm N} \cdot (\eta +1)\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | ::$$K < 1\%\text{:}\hspace{0.72cm} B_{\rm HF} \ge 2 \cdot f_{\rm N} \cdot(\eta +2)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | |
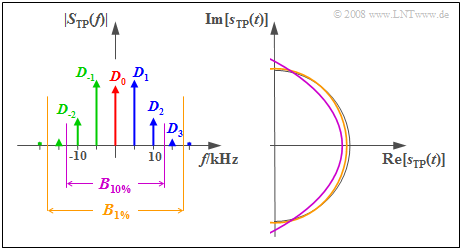
| + | $\text{Example 4:}$ We continue to assume the system parameters $f_{\rm T} = 100 \ \rm kHz$, $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ and $η = π/2$. For this case, the graph displays the magnitude spectrum $ \vert S_{\rm TP}(f) \vert$ of the equivalent low-pass signal on the left and the corresponding complex time function $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ on the right. | ||
| + | [[File:P_ID1104__Mod_T_3_2_S5_neu.png|right|frame| Influence of band limiting in the case of angle modulation]] | ||
| + | *According to Carson's rule to limit the harmonic distortion to the value $K < 1\%$, an RF bandwidth of $B_{1 \%} ≈ 36 \ \rm kHz$ is required. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The equivalent low-pass signal is composed of the constant $D_0$ and three clockwise $(D_1,\ D_2,\ D_3)$ and three counterclockwise $(D_{-1},\ D_{-2},\ D_{-3})$ rotating pointers: | ||
| + | :$$\begin{align*}s_{\rm TP}(t) & = \sum_{n = - 3}^{+3}D_n \cdot{\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}n \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.02cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t }\end{align*}$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The ochre curve in the time domain plot makes it clear that the equivalent low-pass signal differs only slightly from the distortion-free semicircle (thin black line) due to this bandwidth limitation. |
| − | * | + | If one is satisfied with a distortion factor $K < 10\%$ , the RF bandwidth $B_{10 \%} ≈ 26\ \rm kHz$ is already sufficient. |
| + | *This also truncates the two Fourier coefficients $D_3$ and $D_{-3}$ and so the locus curve shown in purple represents a section of a parabola. | ||
| + | *The simulation of this case study yields a distortion factor of $K ≈ 6\%$. | ||
| − | * | + | *Evidently, Carson's Rule often gives a somewhat overly pessimistic result $(10\%$ instead of $6\%)$. }} |
| + | ==Realization of a FM modulator== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | A frequency modulation $s(t)$ is obtained when the oscillation frequency of an oscillator is changed to the rhythm of the modulating signal $u(t)$. RC elements or oscillating circuits usually serve as frequency-determining elements. The left graph shows the form of a possible circuit realization; the exact circuit description can be found in [Mäu 88]<ref name= "Mäu 88">Mäusl, R.: Analoge Modulationsverfahren. Heidelberg: Dr. Hüthig, 1988.</ref>. The idealized frequency-voltage characteristic is shown on the right. | ||
| − | + | [[File:EN_Mod_T_3_2_S6.png |right|frame| Realization of a FM modulator and its characteristic curve]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Only a few remarks should be made here: | |
| − | { | + | *The applied voltage $u(t)$ is additively composed of the source signal $q(t)$ and a DC component $A_0$ which defines the <u>operating point</u>. |
| − | + | ||
| + | *The capacitance $C$ of the <u>capacitance diode</u> is approximately proportional to $1/u^{2}(t)$, so the oscillation frequency of the LC oscillator changes depending on $q(t)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *When the change in frequency is small, $u(t)$ and $f_{\rm A}(t)$ are linearly dependent. Thus, the <u>instantaneous angular frequency</u> with slope $K_{\rm FM}$ of the modulator characteristic is given as | ||
| + | :$$\omega_{\rm A}(t) = \omega_{\rm T} + K_{\rm FM} \cdot q(t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *The <u>push-pull circuit</u> consisting of both capacitance diodes is used, among other things, to compensate for imbalances and thus reduce quadratic distortion. | ||
| − | + | *With an input of $A_0+{\rm d}q(t)/{\rm d}t$, the frequency-modulated signal $s(t)$ is obtained at the output. | |
| + | ==PLL realization of FM demodulator== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The following diagram shows a second possible realization of an FM demodulator. A detailed circuit description of the PLL FM demodulator and further demodulators – for example, using an edge discriminator – can be found in [Mäu 88]<ref name="Mäu 88"/>. | ||
| − | + | [[File:EN_Mod_T_3_2_S7.png|right|frame| PLL realization of a FM demodulator]] | |
| − | + | In short, this circuit, which operates as a $($"Phase–Locked–Loop", $\rm PLL)$, can be described as follows: | |
| − | + | *The phase detector determines the phase differences (distances of zero crossings) between the received signal $r(t)$ and the comparison signal provided by the VCO. | |
| − | + | *After low-pass filtering and amplification, the output signal $v(t)$ is approximately equal to the source signal $q(t)$ if it has been FM-modulated at the transmit end. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | *The output signal $v(t)$ is simultaneously applied to the input of the "Voltage Controlled Oscillator", abbreviated as "$\rm VCO$". | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The VCO output signal is permanently readjusted in such a way that its frequency corresponds as closely to the instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ of the received signal $r(t)$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Exercises for the chapter== |
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.5:_PM_and_FM_for_Rectangular_Signals|Exercise 3.5: PM and FM for Rectangular Signals]] | ||
| + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.5Z:_Phase_Modulation_of_a_Trapezoidal_Signal| Exercise 3.5Z: Phase Modulation of a Trapezoidal Signal]] | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.6:_PM_or_FM%3F_Or_AM%3F|Exercise 3.6: PM or FM? Or AM?]] |
| + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.7:_Angular_Modulation_of_a_Harmonic_Oscillation| Exercise 3.7: Angular Modulation of a Harmonic Oscillation]] | ||
| − | + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.8:_Modulation_Index_and_Bandwidth|Exercise 3.8: Modulation Index and Bandwidth]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.9:_Circular_Arc_and_Parabola|Exercise 3.9: Circular Arc and Parabola]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| + | <br> | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
{{Display}} | {{Display}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:35, 13 January 2023
Contents
- 1 Instantaneous frequency
- 2 Signal characteristics with frequency modulation
- 3 Frequency modulation of a cosine signal
- 4 Angle modulation spectrum of a harmonic oscillation
- 5 Influence of band-limiting in angle modulation
- 6 Realization of a FM modulator
- 7 PLL realization of FM demodulator
- 8 Exercises for the chapter
- 9 References
Instantaneous frequency
We will once again assume an angle-modulated signal:
- $$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \big[\psi(t)\big].$$
All the information about the source signal $q(t)$
- is thus exclusively captured by the angular function $ψ(t)$,
- while the envelope $a(t) = A_{\rm T}$ is constant.
$\text{Definitions:}$
- The »instantaneous angular frequency« is the derivative of the angular function with respect to time:
- $$\omega_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{ {\rm d}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Accordingly, the »instantaneous frequency« is captured by:
- $$f_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{\omega_{\rm A}(t)}{2\pi} = \frac{1}{2\pi} \cdot \frac{ {\rm d}\hspace{0.03cm}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The »frequency deviation« is the maximum deviation $Δf_{\rm A}$ of the time-dependent instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ from the constant carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$.
For an angle modulation with carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$ , the instantaneous frequency oscillates in the range
- $$f_{\rm T} - \Delta f_{\rm A} \le f_{\rm A}(t) \le f_{\rm T} + \Delta f_{\rm A}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
It should be emphasized:
- There is a fundamental difference between the instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ and the spectrum $S(f)$ of an angle-modulated signal $s(t)$.
- This is illustrated by the following example. $S(f)$ can be measured with a spectrum analyzer.
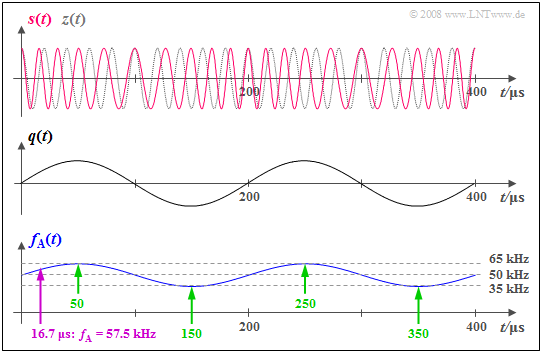
$\text{Example 1:}$ The graph shows the phase-modulated signal
- $$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\psi(t)\big] = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[2 \pi f_{\rm T} \hspace{0.05cm}t + \eta \cdot \sin (2 \pi f_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm} t)\big]$$
as well as the instantaneous frequency plotted beneath
- $$f_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{1}{2 \pi} \cdot \frac{ {\rm d}\hspace{0.03cm}\psi(t)}{ {\rm d}t} = f_{\rm T} + \Delta f_{\rm A}\cdot \cos (2 \pi f_{\rm N} \hspace{0.05cm} t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Here, the system parameters are:
- carrier frequency $f_{\rm T} = 50 \ \rm kHz$ ⇒ frequency of $z(t)$,
- message frequency $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ ⇒ frequency of $q(t)$,
- message modulation index $η = 3$.
From this, we derive the (maximum) frequency deviation
- $Δf_{\rm A} = η · f_{\rm N} = 15 \ \rm kHz$.
In the middle, the qualitative progression of the sinusoidal source signal $q(t)$ is plotted for reference.
From these graphs, one can see:
- The instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ can take on arbitrary values between $f_{\rm T} + Δf_{\rm A} = 65 \ \rm kHz$ $($at $t = 50\ \rm µ s,\ 250 \ µ s$, etc.$)$ and $f_{\rm T} \ – Δf_{\rm A} = 35 \ \rm kHz$ $($at $t = 150\ \rm µ s, \ 350 \ µ s$, etc.$)$ ⇒ green marks.
- At time $t ≈ 16.7 \ \rm µ s$ , for example, $f_{\rm A}(t) = 57.5 \ \rm kHz$ holds ⇒ purple arrow.
- In contrast, the spectral function $S(f)$ consists of discrete Bessel lines at the frequencies ... , $30,\ 35,\ 40,\ 45,\ \mathbf{50},\ 55,\ 60,\ 65,\ 70$, ... $($each in $\rm kHz)$.
- There is no spectral line at $f = 57.5 \ \rm kHz$, though there is one at $f = 70 \ \rm kHz$.
- In contrast, at no time does $f_{\rm A}(t) = 70 \ \rm kHz$ hold.
$\text{Therefore:}$
The instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ is thus not a physically measurable frequency in the conventional sense, but only an »abstract mathematical quantity«, namely the derivative of the angular function $ψ(t)$.
Signal characteristics with frequency modulation
As in the chapter "Phase Modulation" we will assume that the carrier signal $z(t)$ has a cosine waveform and the source signal $q(t)$ is peak-limited.
$\text{Definition:}$ If the instantaneous angular frequency $ω_{\rm A}(t)$ of a communication system is linearly dependent on the instantaneous value of the source signal $q(t)$, we call this »frequency modulation« $\rm (FM)$:
- $$\omega_{\rm A}(t) = 2 \pi \cdot f_{\rm A}(t) = \omega_{\rm T} + K_{\rm FM} \cdot q(t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Here, $K_{\rm FM}$ denotes a dimensionally restricted constant. If $q(t)$ represents a voltage waveform, $K_{\rm FM}$ has the unit $\rm V^{–1}s^{–1}$.
In frequency modulation, the angular function $\psi(t)$ and the modulated signal $s(t)$ are given by:
- $$\psi(t) = \omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + K_{\rm FM} \cdot \int q(t)\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}t \hspace{0.05cm}\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \big[\psi(t)\big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
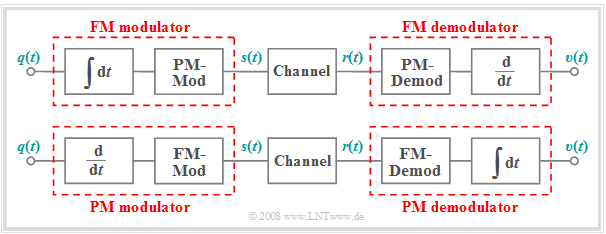
From these equations, we can immediately see:
- Even in the case of frequency modulation, the equivalent low-pass signal moves on an circular arc because of the constant envelope ⇒ $a(t) = A_{\rm T}$.
- A frequency modulator can be implemented using an integrator and a phase modulator.
- Consequently, the FM demodulator consists of a PM demodulator and a differentiator, as shown in the upper part of the diagram.
The lower graph shows the inverse relationship ⇒ a possible description of PM modulator and demodulator in terms of corresponding FM components.
$\text{It can also be seen from the above equation:}$
- The equation encountered earlier in the section "A very simple (though unfortunately not always correct) modulator equation" in the first chapter of this book, will only hold for frequency modulation in very special cases.
- In frequency modulation, the conversion
- $$s(t) = a(t) \cdot \cos (\omega (t) \cdot t + \phi(t)) \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega (t) \cdot t + \phi_{\rm T})$$
- is only allowed sometimes, such as in the non-linear digital modulation method $\text{Frequency Shift Keying}$ $\rm (FSK)$ with rectangular basic pulse.
Frequency modulation of a cosine signal
For a cosine source signal $q(t)$ with frequency modulation, the instantaneous angular frequency is:
- $$q(t) = A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \omega_{\rm A}(t) = \omega_{\rm T} + K_{\rm FM} \cdot A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Integrating this over time, we get the angular function:
- $$\psi(t) = \omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \frac {K_{\rm FM} \cdot A_{\rm N}}{\omega_{\rm N}} \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
A comparison with the propositions in the chapter "Phase Modulation" makes clear:
- The frequency modulation of a cosine signal yields a qualitatively identical transmitted signal $s(t)$ as the phase modulation of a sinusoidal source signal $q(t)$. However, this requires that the modulator constants are matched according to the ratio $K_{\rm FM}/K_{\rm PM} = ω_{\rm N}$ .
- The transmitted signal $s(t)$ can thus be described uniformly for the two configurations "PM – sine signal" as well as "FM – cosine signal":
- $$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \eta \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- However, when using this equation for the modulation index $η$, different equations must be used for phase and frequency modulation:
- $$\eta_{\rm PM} = {K_{\rm PM} \cdot A_{\rm N}},$$
- $$\eta_{\rm FM} = \frac {K_{\rm FM} \cdot A_{\rm N}}{\omega_{\rm N}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- If the source signal is not a harmonic oscillation, but is instead composed of several frequencies, the time signals also differ qualitatively for phase and frequency modulation. This can be seen in the $\text{earlier comparison of PSK and FSK}$.
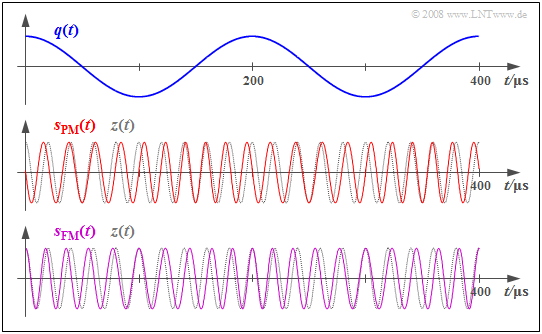
$\text{Example 2:}$ We will now assume a cosine source signal $q(t)$ with amplitude $A_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm V$ and frequency $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ and we consider the signal characteristics of phase modulation $\rm (PM)$ and frequency modulation $\rm (FM)$ with the same modulation index $η = 1.5$.
The middle graph shows the phase-modulated signal (red curve) for the modulator parameters $f_{\rm T} = 50 \ \rm kHz$ and $K_{\rm PM} = \rm 0.5 V^{–1}$:
- $$s_{\rm PM}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \eta \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\big ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In phase modulation, $A_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm V$ yields $η = 1.5 ≈ π/2$ for the phase deviation (modulation index).
- The maximum deviation of the zero crossings from their (equidistant) nominal positions is about a quarter of the carrier period.
- If the source signal is $q(t) > 0$, the zero crossings arrive earlier, and if $q(t) < 0$ , they come somewhat too late.
The lower graph shows the frequency-modulated signal with the same modulation index $η$:
- $$s_{\rm FM}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \eta \cdot \sin (\omega_{\rm N} \cdot t)\big ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In this case, $η = 1.5$ is achieved by the modulator constant
- $$K_{\rm FM} = \frac {\eta \cdot \omega_{\rm N} }{A_{\rm N} } = {K_{\rm PM} \cdot \omega_{\rm N} } $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} K_{\rm FM} = 0.5\,{\rm V}^{-1} \cdot 2 \pi \cdot 5\,{\rm kHz} = 15708\,{\rm V}^{-1}{\rm s}^{-1} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Here, the frequency deviation is $Δf_{\rm A} = η · f_{\rm N} = 7.5 \ \rm kHz$, and instantaneous frequencies occur between $f_{\rm T}-Δf_{\rm A} = 42.5$ and $f_{\rm T}+Δf_{\rm A} =57.5 \ \rm kHz$.
- The zero crossings now match those of the carrier signal $z(t)$ at the maxima and minima of the source signal $q(t)$, while the maximum phase deviations can be seen at the zero crossings of $q(t)$. The exact opposite is the case in phase modulation.
Angle modulation spectrum of a harmonic oscillation
Now we assume a harmonic oscillation with phase $ϕ_{\rm N}$ for the source signal in general:
- $$q(t) = A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[2 \pi f_{\rm N} \cdot t + \phi_{\rm N}\big ].$$
We are interested in the spectrum $S(f)$. For simplicity, in what follows we will consider the magnitude spectrum $|S_+(f)|$ of the analytical signal, from which $|S(f)|$ can be derived in the familiar way.
For any type of angle modulation described here – whether it is phase or frequency modulation – and regardless of the phase $ϕ_{\rm N}$ of the source signal, the following holds:
- $$|S_{\rm +}(f)| = A_{\rm T} \cdot \sum_{n = - \infty}^{+\infty}|{\rm J}_n (\eta)| \cdot \delta \big[f - (f_{\rm T} + n \cdot f_{\rm N})\big]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
This equation can be explained as follows:
- In the section "Equivalent low-pass signal in PM" this equation was derived for a phase-modulated sine signal, where $η = A_{\rm N} · K_{\rm PM}$ denotes the modulation index and ${\rm J}_n(η)$ denotes the $n$–th order Bessel functions of the first kind. $K_{\rm PM}$ is the modulator constant.
- When the message phase $ϕ_{\rm N}$ changes, only the phase function ${\rm arc} \ S_+(f)$ changes, but not the magnitude spectrum $|S_+(f)|$. This important result is confirmed in "Exercise 3.3Z".
- In the "Frequency modulation of a cosine signal" section, it was shown that a frequency-modulated signal can be represented in the same way as a phase-modulated signal if the modulation index $η = K_{\rm FM} · A_{\rm N}/ω_{\rm N}$ is used. Consequently, the magnitude spectra for $\rm PM$ and $\rm FM$ can also be represented in the same way.
We would like to refer you to the second part of the (German language) learning video "Winkelmodulation - FM und PM" ⇒ "Angle modulation – FM and PM".
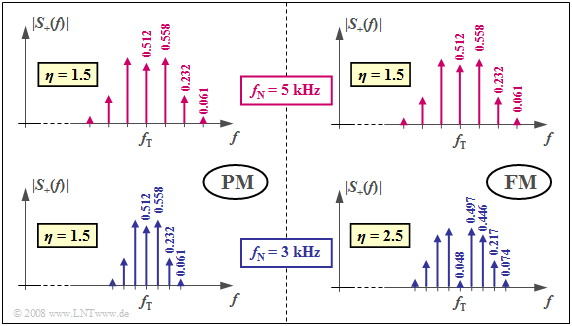
$\text{Example 3:}$ Let us again consider a harmonic oscillation, here with amplitude $A_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm V$ according to
- phase modulation $\rm (PM)$ with $K_{\rm PM} = \rm 0.5 \ \rm V^{–1}$,
- frequency modulation $\rm (FM)$ with $K_{\rm FM} = \rm 15708 \ \rm V^{–1}s^{–1}$.
The corresponding signal characteristics are shown in $\text{Example 2}$.
- For both transmission systems, a Bessel spectrum with modulation index $η = 1.5$ is obtained for $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$.
- The identical magnitude spectra of the analytical signal (positive frequencies only) are shown in the two upper diagrams.
- Bessel lines with values smaller than $0.03$ are ignored in both cases.
The lower diagrams are valid for the message frequency $f_{\rm N} = 3 \ \rm kHz$:
- In PM, there is a narrower spectrum compared to $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$, since the spacing of the Bessel lines is only $3 \ \rm kHz$ (left diagram).
- Since the modulation index $η = 1.5$ does not changes, we get the same Bessel weights as for $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ (upper diagram).
- Also in FM, the Bessel lines now occur at $3 \ \rm kHz$ spacing (lower graph on the right). However, there are significantly more Bessel lines than in the upper right graph (valid for $η = 1.5$ ) due to the larger modulation index $η = 2.5$ .
- This follows from the fact that for FM, the index $η$ is inversely proportional to $f_{\rm N}$ .
Influence of band-limiting in angle modulation
Let us briefly summarize some previous results of this section, by assuming an example with
- carrier frequency $f_{\rm T} = 100 \ \rm kHz$,
- message frequency $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ and
- modulation index $η = π/2 \approx 1.5$:
- The spectrum of an angle-modulated oscillation consists of Bessel lines around the carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$ at a distance $f_{\rm N}$ between neighboring samplesand is infinitely extended in theory.
- Even if we ignore all spectral lines with magnitudes smaller than $0.01$, the now finite bandwidth for $η = π/2$ is still $B_{\rm HF} = 8 · f_{\rm N} = 40 \ \rm kHz$.
- The locus curve – i.e., the course of the equivalent low-pass signal in the complex plane – is ideally a circular arc with an opening angle of $±1.57 \ {\rm rad} = ±90^\circ$.
- However, this circular arc after vector summation results only if all Bessel lines on the locus rotate with the correct pointer lengths, the correct phase positions and the correct angular frequencies.
- Logically, the circular locus curve is altered when the spectral lines are distorted (e.g. by linear channel distortions) or missing altogether (e.g. by band-limiting).
- Since the ideal angle demodulator detects the phase $ϕ_r(t)$ of the received signal and obtains the sink signal $v(t)$ from it, the demodulator causes non-linear distortions. This means: The distortions are irreversible and cannot be compensated for by a linear filter.
- At the same time, this means: Due to linear distortions in the channel, nonlinear distortions occur in the demodulated signal $v(t)$.
- As a result, new frequencies ("harmonics") are created, which were not in the original source signal $q(t)$.
- The smaller the available bandwidth $B_{\rm HF}$ and the larger the chosen modulation index $η$, the larger becomes the distortion factor $K$, which captures nonlinear distortions.
- As a rule of thumb for the required high-frequency bandwidth for a desired distortion factor $K$, one can use the so-called »Carson Rule«:
- $$K < 10\%\text{:}\hspace{0.6cm} B_{\rm HF} \ge 2 \cdot f_{\rm N} \cdot (\eta +1)\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$K < 1\%\text{:}\hspace{0.72cm} B_{\rm HF} \ge 2 \cdot f_{\rm N} \cdot(\eta +2)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\text{Example 4:}$ We continue to assume the system parameters $f_{\rm T} = 100 \ \rm kHz$, $f_{\rm N} = 5 \ \rm kHz$ and $η = π/2$. For this case, the graph displays the magnitude spectrum $ \vert S_{\rm TP}(f) \vert$ of the equivalent low-pass signal on the left and the corresponding complex time function $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ on the right.
- According to Carson's rule to limit the harmonic distortion to the value $K < 1\%$, an RF bandwidth of $B_{1 \%} ≈ 36 \ \rm kHz$ is required.
- The equivalent low-pass signal is composed of the constant $D_0$ and three clockwise $(D_1,\ D_2,\ D_3)$ and three counterclockwise $(D_{-1},\ D_{-2},\ D_{-3})$ rotating pointers:
- $$\begin{align*}s_{\rm TP}(t) & = \sum_{n = - 3}^{+3}D_n \cdot{\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}n \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\omega_{\rm N} \hspace{0.02cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t }\end{align*}$$
- The ochre curve in the time domain plot makes it clear that the equivalent low-pass signal differs only slightly from the distortion-free semicircle (thin black line) due to this bandwidth limitation.
If one is satisfied with a distortion factor $K < 10\%$ , the RF bandwidth $B_{10 \%} ≈ 26\ \rm kHz$ is already sufficient.
- This also truncates the two Fourier coefficients $D_3$ and $D_{-3}$ and so the locus curve shown in purple represents a section of a parabola.
- The simulation of this case study yields a distortion factor of $K ≈ 6\%$.
- Evidently, Carson's Rule often gives a somewhat overly pessimistic result $(10\%$ instead of $6\%)$.
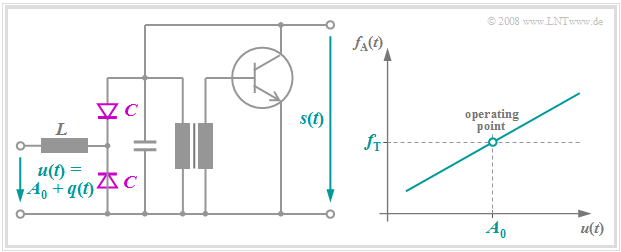
Realization of a FM modulator
A frequency modulation $s(t)$ is obtained when the oscillation frequency of an oscillator is changed to the rhythm of the modulating signal $u(t)$. RC elements or oscillating circuits usually serve as frequency-determining elements. The left graph shows the form of a possible circuit realization; the exact circuit description can be found in [Mäu 88][1]. The idealized frequency-voltage characteristic is shown on the right.
Only a few remarks should be made here:
- The applied voltage $u(t)$ is additively composed of the source signal $q(t)$ and a DC component $A_0$ which defines the operating point.
- The capacitance $C$ of the capacitance diode is approximately proportional to $1/u^{2}(t)$, so the oscillation frequency of the LC oscillator changes depending on $q(t)$.
- When the change in frequency is small, $u(t)$ and $f_{\rm A}(t)$ are linearly dependent. Thus, the instantaneous angular frequency with slope $K_{\rm FM}$ of the modulator characteristic is given as
- $$\omega_{\rm A}(t) = \omega_{\rm T} + K_{\rm FM} \cdot q(t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The push-pull circuit consisting of both capacitance diodes is used, among other things, to compensate for imbalances and thus reduce quadratic distortion.
- With an input of $A_0+{\rm d}q(t)/{\rm d}t$, the frequency-modulated signal $s(t)$ is obtained at the output.
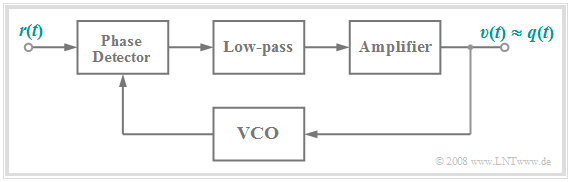
PLL realization of FM demodulator
The following diagram shows a second possible realization of an FM demodulator. A detailed circuit description of the PLL FM demodulator and further demodulators – for example, using an edge discriminator – can be found in [Mäu 88][1].
In short, this circuit, which operates as a $($"Phase–Locked–Loop", $\rm PLL)$, can be described as follows:
- The phase detector determines the phase differences (distances of zero crossings) between the received signal $r(t)$ and the comparison signal provided by the VCO.
- After low-pass filtering and amplification, the output signal $v(t)$ is approximately equal to the source signal $q(t)$ if it has been FM-modulated at the transmit end.
- The output signal $v(t)$ is simultaneously applied to the input of the "Voltage Controlled Oscillator", abbreviated as "$\rm VCO$".
- The VCO output signal is permanently readjusted in such a way that its frequency corresponds as closely to the instantaneous frequency $f_{\rm A}(t)$ of the received signal $r(t)$.
Exercises for the chapter
Exercise 3.5: PM and FM for Rectangular Signals
Exercise 3.5Z: Phase Modulation of a Trapezoidal Signal
Exercise 3.6: PM or FM? Or AM?
Exercise 3.7: Angular Modulation of a Harmonic Oscillation
Exercise 3.8: Modulation Index and Bandwidth
Exercise 3.9: Circular Arc and Parabola
References