Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.15: Optimal Signal Space Allocation"
| (15 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Digital_Signal_Transmission/Carrier_Frequency_Systems_with_Coherent_Demodulation}} |
| − | [[File:P_ID2069__Dig_A_4_15.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2069__Dig_A_4_15.png|right|frame|Considered "8–QAM"]] |
| − | + | A signal space constellation with $M = 8$ signal space points is considered here: | |
| − | * | + | * Four points lie on a circle with radius $r = 1$. |
| − | * | + | |
| + | * Four further points lie offset by $45^\circ$ on a second circle with radius $R$, where the following shall hold: | ||
:$$R_{\rm min} \le R \le R_{\rm max}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} R_{\rm min}= \frac{ \sqrt{3}-1}{ \sqrt{2}} \approx 0.518 | :$$R_{\rm min} \le R \le R_{\rm max}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} R_{\rm min}= \frac{ \sqrt{3}-1}{ \sqrt{2}} \approx 0.518 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} | \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} | ||
R_{\rm max}= \frac{ \sqrt{3}+1}{ \sqrt{2}} \approx 1.932\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | R_{\rm max}= \frac{ \sqrt{3}+1}{ \sqrt{2}} \approx 1.932\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Let the two axes ("basis functions") be normalized respectively and denoted $I$ and $Q$ for simplicity. For further simplification, $E = 1$ can be set. | |
| − | + | In the question section, we speak of "blue" and "red" points. According to the diagram, the blue points lie on the circle with radius $r = 1$, the red points on the circle with radius $R$. The case $R = R_{\rm max}$ is drawn. | |
| − | + | The system parameter $R$ is to be determined in this exercise in such a way that the quotient | |
:$$\eta = \frac{ (d_{\rm min}/2)^2}{ E_{\rm B}} $$ | :$$\eta = \frac{ (d_{\rm min}/2)^2}{ E_{\rm B}} $$ | ||
| − | + | becomes maximum. $\eta$ is a measure for the quality of a modulation alphabet at given transmission energy per bit ("power efficiency"). It is calculated from | |
| − | * | + | * the minimum distance $d_{\rm min}$, and |
| − | |||
| + | * the average bit energy $E_{\rm B}$. | ||
| − | |||
| + | It must be ensured that $d_{\rm min}^2$ and $E_{\rm B}$ are normalized in the same way, but this is already implicit in the exercise. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | |
| + | Notes: | ||
| + | * The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Carrier_Frequency_Systems_with_Coherent_Demodulation|"Carrier Frequency Systems with Coherent Demodulation"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Reference is made in particular to the sections [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Carrier_Frequency_Systems_with_Coherent_Demodulation#Quadrature_amplitude_modulation_.28M-QAM.29|"Quadrature amplitude modulation"]] and [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Carrier_Frequency_Systems_with_Coherent_Demodulation#M.E2.80.93level_amplitude_shift_keying_.28M.E2.80.93ASK.29|"Multi-level phase modulation"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the average energy $E_{\rm B}$ per bit depending on $R$, in particular for $R = 1$ and $R = \sqrt{2}$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$R = 1 \text{:} \hspace{0.55cm} E_{\rm B}\ = \ $ { 0.333 3% } | $R = 1 \text{:} \hspace{0.55cm} E_{\rm B}\ = \ $ { 0.333 3% } | ||
$R = \sqrt{2} \text{:} \hspace{0.2cm} E_{\rm B}\ = \ $ { 0.5 3% } | $R = \sqrt{2} \text{:} \hspace{0.2cm} E_{\rm B}\ = \ $ { 0.5 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the minimum distance between two signal space points? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + For $R < R_{\rm min}$, the minimum distance occurs between two red points. |
| − | + | + | + For $R > R_{\rm max}$, the minimum distance occurs between two blue points. |
| − | + | + | + For $R_{\rm min} ≤ R ≤ R_{\rm max}$, the minimum distance occurs between "red" and "blue". |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the minimum distance depending on $R$, in particular for |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$R = 1 \text{:} \hspace{0.55cm} d_{\rm min}\ = \ $ { 0.765 3% } | $R = 1 \text{:} \hspace{0.55cm} d_{\rm min}\ = \ $ { 0.765 3% } | ||
$R = \sqrt{2} \text{:} \hspace{0.2cm} d_{\rm min}\ = \ $ { 1 3% } | $R = \sqrt{2} \text{:} \hspace{0.2cm} d_{\rm min}\ = \ $ { 1 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Give the power efficiency $\eta$ in general terms. What $\eta$ results for $R = 1$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\eta\ = \ $ { 0.439 3% } | $\eta\ = \ $ { 0.439 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {What power efficiency values result for $R = R_{\rm min}$ and $R = R_{\rm max}$? Interpretation. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$R = R_{\rm min} \text{:} \hspace{0.35cm} \eta\ = \ ${ 0.634 3% } | $R = R_{\rm min} \text{:} \hspace{0.35cm} \eta\ = \ ${ 0.634 3% } | ||
| Line 60: | Line 66: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | [[File:P_ID2073__Dig_A_4_15a.png|right|frame|Special cases of "8–QAM"]] |
| − | :$$E_{\rm S} = {1}/{8 } \cdot ( 4 \cdot r^2 + 4 \cdot R^2) = ({1 + R^2})/{2 } | + | '''(1)''' Because of $M = 8$ ⇒ $b = 3$, the average signal energy per bit is $E_{\rm B} = E_{\rm S}/3$, where the average signal energy per symbol $(E_{\rm S})$ is to be calculated as the mean square distance of the signal space points from the origin. With $r = 1$ one obtains: |
| − | + | :$$E_{\rm S} = {1}/{8 } \cdot ( 4 \cdot r^2 + 4 \cdot R^2) = ({1 + R^2})/{2 }$$ | |
| + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} E_{\rm B} = {E_{\rm S}}/{3} = ({1 + R^2})/{6} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | In particular: | |
| + | * For $R = 1$, there is an "8–PSK" ⇒ $E_{\rm S} = 1$ and $E_{\rm B} \ \underline {= 0.333}$ (see left graph). | ||
| − | + | * The right graph is valid for $R = \sqrt{2}$. In this case, $E_{\rm B} \ \underline {= 0.5}$. | |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Note that these energies actually still have to be multiplied by the normalization energy $E$. | |
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | '''(2)''' <u>All statements are true</u>: | ||
| + | [[File:P_ID2074__Dig_A_4_15c.png|right|frame|To calculate minimum distance]] | ||
| + | *In the drawn example on the front page with $R = R_{\rm max}$, the distance between two neighboring blue points is exactly the same as the distance between a red (outer) and a blue (inner) point. | ||
| − | + | *For $R > R_{\rm max}$, the distance between two blue points is the smallest. | |
| + | *For $R < R_{\rm min}$, the minimum distance occurs between two red points. | ||
| − | '''(3)''' | + | |
| − | :$$d_{\rm min}^2 =(R/\sqrt{2})^2 + (R/\sqrt{2}-1)^2 = 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2 | + | |
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}d_{\rm min} = \sqrt{ 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2} | + | '''(3)''' The graphic illustrates the geometric calculation. With "Pythagoras" one obtains: |
| + | :$$d_{\rm min}^2 =(R/\sqrt{2})^2 + (R/\sqrt{2}-1)^2 = 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2$$ | ||
| + | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}d_{\rm min} = \sqrt{ 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *In particular, for $R = 1$ ("8–PSK"): | |
:$$d_{\rm min} = \sqrt{ 2 - \sqrt{2} } \hspace{0.1cm} \underline{= 0.765} \hspace{0.1cm} (= 2 \cdot \sin (22.5^{\circ}) ) | :$$d_{\rm min} = \sqrt{ 2 - \sqrt{2} } \hspace{0.1cm} \underline{= 0.765} \hspace{0.1cm} (= 2 \cdot \sin (22.5^{\circ}) ) | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *In contrast, for $\underline {R = \sqrt{2}}$ corresponding to the right graph for subtask '''(1)''', the minimum distance is $d_{\rm min} \ \underline {= 1}$. | |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Using the results of '''(1)''' and '''(3)''', we obtain in general or for $R = 1$ ("8–PSK"): |
:$$\eta = \frac{ d_{\rm min}^2}{ 4 \cdot E_{\rm B}} = \frac{ 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2}{ 4 \cdot (1 + R^2)/6} | :$$\eta = \frac{ d_{\rm min}^2}{ 4 \cdot E_{\rm B}} = \frac{ 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2}{ 4 \cdot (1 + R^2)/6} | ||
| − | = \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2)}{ 1 + R^2} | + | = \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2)}{ 1 + R^2}\hspace{0.3cm} |
| − | + | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} R = 1: \hspace{0.2cm}\eta = | |
\frac{ 3/2 \cdot(2 - \sqrt{2}) }{ 2} = 3/4 \cdot(2 - \sqrt{2})\hspace{0.1cm} \underline{\approx 0.439}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(2 - \sqrt{2}) }{ 2} = 3/4 \cdot(2 - \sqrt{2})\hspace{0.1cm} \underline{\approx 0.439}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(5)''' | + | |
| + | '''(5)''' For $R = R_{\rm min} = (\sqrt{3}-1)/\sqrt{2}$, the following value is obtained: | ||
:$$\eta = \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2)}{ 1 + R^2} = 3/2 \cdot \left [ 1 - \frac{ \sqrt{2} \cdot R }{ 1 + R^2}\right ]\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$\eta = \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2)}{ 1 + R^2} = 3/2 \cdot \left [ 1 - \frac{ \sqrt{2} \cdot R }{ 1 + R^2}\right ]\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
:$$\sqrt{2} \cdot R = \sqrt{3}- 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} 1 + R^2 = 3 - \sqrt{3} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | :$$\sqrt{2} \cdot R = \sqrt{3}- 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} 1 + R^2 = 3 - \sqrt{3} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\eta = 3/2 \cdot \left [ 1 - \frac{ \sqrt{3}- 1 }{ 3 - \sqrt{3}}\right ]\hspace{0.1cm} \underline{\approx 0.634}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \eta = 3/2 \cdot \left [ 1 - \frac{ \sqrt{3}- 1 }{ 3 - \sqrt{3}}\right ]\hspace{0.1cm} \underline{\approx 0.634}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *For $R = R_{\rm max}= (\sqrt{3}+1)/\sqrt{2}$ exactly the same value results. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | #The (always desired) maximum of the power efficiency $\eta$ results e.g. for $R = R_{\rm max}$ – i.e. for the signal space constellation in the information section. | |
| + | #In this case all triangles of two neighboring blue points and the red point in between are equilateral. | ||
| + | #Also for $R = R_{\rm min}$ there are equilateral triangles, but now each formed by two red and one blue point. | ||
| + | #In this case the edge length $d_{\rm min}$ is clearly smaller, but at the same time a smaller $E_{\rm B}$ results, so that the power efficiency $\eta$ has the same value. | ||
| + | #The previously considered special cases $R = 1$ ("8–PSK", left graph in the first subtask) and $R = \sqrt{2}$ (right graph) have a noticeably smaller $\eta$ with $\eta = 0.439$ and $\eta = 0.5$, resp. $($compared to $\eta = 0.634)$. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Digital Signal Transmission: Exercises|^4.4 Coherent Demodulation^]] |
Latest revision as of 16:06, 1 October 2022
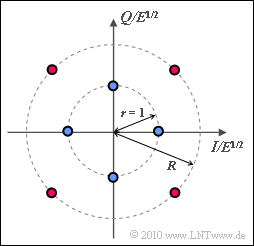
A signal space constellation with $M = 8$ signal space points is considered here:
- Four points lie on a circle with radius $r = 1$.
- Four further points lie offset by $45^\circ$ on a second circle with radius $R$, where the following shall hold:
- $$R_{\rm min} \le R \le R_{\rm max}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} R_{\rm min}= \frac{ \sqrt{3}-1}{ \sqrt{2}} \approx 0.518 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} R_{\rm max}= \frac{ \sqrt{3}+1}{ \sqrt{2}} \approx 1.932\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Let the two axes ("basis functions") be normalized respectively and denoted $I$ and $Q$ for simplicity. For further simplification, $E = 1$ can be set.
In the question section, we speak of "blue" and "red" points. According to the diagram, the blue points lie on the circle with radius $r = 1$, the red points on the circle with radius $R$. The case $R = R_{\rm max}$ is drawn.
The system parameter $R$ is to be determined in this exercise in such a way that the quotient
- $$\eta = \frac{ (d_{\rm min}/2)^2}{ E_{\rm B}} $$
becomes maximum. $\eta$ is a measure for the quality of a modulation alphabet at given transmission energy per bit ("power efficiency"). It is calculated from
- the minimum distance $d_{\rm min}$, and
- the average bit energy $E_{\rm B}$.
It must be ensured that $d_{\rm min}^2$ and $E_{\rm B}$ are normalized in the same way, but this is already implicit in the exercise.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Carrier Frequency Systems with Coherent Demodulation".
- Reference is made in particular to the sections "Quadrature amplitude modulation" and "Multi-level phase modulation".
Questions
Solution
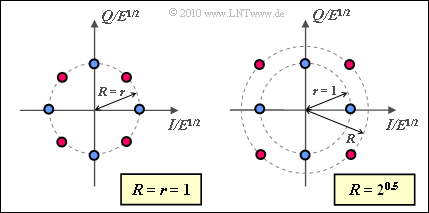
(1) Because of $M = 8$ ⇒ $b = 3$, the average signal energy per bit is $E_{\rm B} = E_{\rm S}/3$, where the average signal energy per symbol $(E_{\rm S})$ is to be calculated as the mean square distance of the signal space points from the origin. With $r = 1$ one obtains:
- $$E_{\rm S} = {1}/{8 } \cdot ( 4 \cdot r^2 + 4 \cdot R^2) = ({1 + R^2})/{2 }$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} E_{\rm B} = {E_{\rm S}}/{3} = ({1 + R^2})/{6} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In particular:
- For $R = 1$, there is an "8–PSK" ⇒ $E_{\rm S} = 1$ and $E_{\rm B} \ \underline {= 0.333}$ (see left graph).
- The right graph is valid for $R = \sqrt{2}$. In this case, $E_{\rm B} \ \underline {= 0.5}$.
Note that these energies actually still have to be multiplied by the normalization energy $E$.
(2) All statements are true:
- In the drawn example on the front page with $R = R_{\rm max}$, the distance between two neighboring blue points is exactly the same as the distance between a red (outer) and a blue (inner) point.
- For $R > R_{\rm max}$, the distance between two blue points is the smallest.
- For $R < R_{\rm min}$, the minimum distance occurs between two red points.
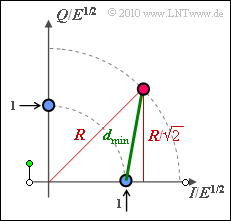
(3) The graphic illustrates the geometric calculation. With "Pythagoras" one obtains:
- $$d_{\rm min}^2 =(R/\sqrt{2})^2 + (R/\sqrt{2}-1)^2 = 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}d_{\rm min} = \sqrt{ 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In particular, for $R = 1$ ("8–PSK"):
- $$d_{\rm min} = \sqrt{ 2 - \sqrt{2} } \hspace{0.1cm} \underline{= 0.765} \hspace{0.1cm} (= 2 \cdot \sin (22.5^{\circ}) ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In contrast, for $\underline {R = \sqrt{2}}$ corresponding to the right graph for subtask (1), the minimum distance is $d_{\rm min} \ \underline {= 1}$.
(4) Using the results of (1) and (3), we obtain in general or for $R = 1$ ("8–PSK"):
- $$\eta = \frac{ d_{\rm min}^2}{ 4 \cdot E_{\rm B}} = \frac{ 1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2}{ 4 \cdot (1 + R^2)/6} = \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2)}{ 1 + R^2}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} R = 1: \hspace{0.2cm}\eta = \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(2 - \sqrt{2}) }{ 2} = 3/4 \cdot(2 - \sqrt{2})\hspace{0.1cm} \underline{\approx 0.439}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) For $R = R_{\rm min} = (\sqrt{3}-1)/\sqrt{2}$, the following value is obtained:
- $$\eta = \frac{ 3/2 \cdot(1 - \sqrt{2} \cdot R + R^2)}{ 1 + R^2} = 3/2 \cdot \left [ 1 - \frac{ \sqrt{2} \cdot R }{ 1 + R^2}\right ]\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\sqrt{2} \cdot R = \sqrt{3}- 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} 1 + R^2 = 3 - \sqrt{3} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \eta = 3/2 \cdot \left [ 1 - \frac{ \sqrt{3}- 1 }{ 3 - \sqrt{3}}\right ]\hspace{0.1cm} \underline{\approx 0.634}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- For $R = R_{\rm max}= (\sqrt{3}+1)/\sqrt{2}$ exactly the same value results.
- The (always desired) maximum of the power efficiency $\eta$ results e.g. for $R = R_{\rm max}$ – i.e. for the signal space constellation in the information section.
- In this case all triangles of two neighboring blue points and the red point in between are equilateral.
- Also for $R = R_{\rm min}$ there are equilateral triangles, but now each formed by two red and one blue point.
- In this case the edge length $d_{\rm min}$ is clearly smaller, but at the same time a smaller $E_{\rm B}$ results, so that the power efficiency $\eta$ has the same value.
- The previously considered special cases $R = 1$ ("8–PSK", left graph in the first subtask) and $R = \sqrt{2}$ (right graph) have a noticeably smaller $\eta$ with $\eta = 0.439$ and $\eta = 0.5$, resp. $($compared to $\eta = 0.634)$.