Difference between revisions of "Exercise 3.1: GSM Network Components"
m (Guenter verschob die Seite 3.1 GSM–Netzkomponenten nach Aufgabe 3.1: GSM–Netzkomponenten) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_GSM |
}} | }} | ||
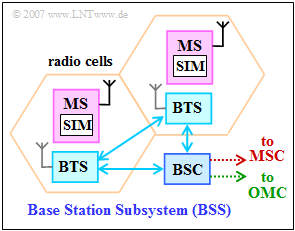
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_Bei_A_3_1.png|right|frame|GSM: Base Station Subsystem]] |
| − | + | The network infrastructure in the 2G mobile communications standard "Global System for Mobile Communications" – $\rm GSM$, for short – includes the following subsystems: | |
| − | * Base Station Subsystem ( | + | * Base Station Subsystem $\rm (BSS)$, |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * Switching & Management Subsystem $\rm (SMSS)$, | ||
| − | + | * Operation & Maintenance Subsystem $\rm (OMSS)$. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The base station subsystem is essentially responsible for the GSM radio network (see diagram), while the SMSS represents the switching network and the OMSS is responsible for operations and maintenance. | ||
| − | + | The following terms continue to be used in the questions for this exercise: | |
| + | #Authentication Center $\rm (AUC)$, | ||
| + | #Base Station Controller $\rm (BSC)$, | ||
| + | #Base Transceiver Station $\rm (BTS)$, | ||
| + | #Gateway Mobile Switching Center $\rm (GMSC)$, | ||
| + | #Home Location Register $\rm (HLR)$, | ||
| + | #Mobile Switching Center $\rm (MSC)$, | ||
| + | #Operation and Maintenance Center $\rm (OMC)$, | ||
| + | #Visitor Location Register $\rm (VLR)$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | |
| + | <u>Hint:</u> This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_GSM|"General Description of GSM"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {With which of the three subsystems does the mobile station communicate? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ BSS, | + BSS, | ||
| Line 37: | Line 40: | ||
- OMSS. | - OMSS. | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for a base transceiver station $\rm (BTS)$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + BTS | + | + BTS is the transmitting and receiving equipment of the base station. |
| − | - | + | - The task of the BTS is the switching of calls. |
| − | + | + | + Usually several BTS are subordinated to a common BSC. |
| − | { | + | {How many channels $($antennas$)$ can a BTS support simultaneously? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$N_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 3 3% } | $N_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 3 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following components are part of the OMSS? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
- GMSC, | - GMSC, | ||
| Line 54: | Line 57: | ||
+ OMC. | + OMC. | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following components are databases? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ AUC, | + AUC, | ||
| Line 63: | Line 66: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' Correct is the <u>proposed solution 1</u>: |
| + | *Each mobile station $\rm (MS)$ is in radio communication with a base transceiver station $\rm (BTS)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *This is part of the base station subsystem $\rm (BSS)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' Correct are the <u>proposed solutions 1 and 3</u>: | ||
| + | *In contrast, proposed solution 2 is incorrect: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The BTS is not responsible for switching tasks, but this is the task of a mobile switching center $\rm (MSC)$, <br>which is a part of the switching and management subsystem $\rm (SMSS)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' In GSM, the individual antennas usually cover $120^\circ$ sectors. | ||
| + | *This also means that a BTS can provide up to <u>three radio channels</u>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | '''( | + | '''(4)''' Correct is <u>the proposed solution 3</u>: |
| + | *Only the operation and management center $\rm (OMC)$ is part of the OMSS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In contrast, MSC and GMSC are components of the mobile switching subsystem $\rm (SMSS)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *With respect to the OMC, a further distinction is made between $\text{OMC-B}$ $($for BSS monitoring$)$ and $\text{OMC-S}$ $($for SMSS monitoring$)$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''(5)''' GMSC | + | '''(5)''' Correct are the <u>proposed solutions 1, 3 and 4</u>: |
| + | *GMSC is a hardware unit responsible for switching between the fixed and mobile networks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The other three terms given describe databases of the SMSS. | ||
| + | #AUC is responsible for storing confidential data and keys. | ||
| + | #HLR is a central register for the entire "Public Land Mobile Network" $\rm (PLMN)$ for managing unencrypted subscriber data, subscribed services, and routing for calls of a mobile operator's own subscribers. | ||
| + | #In contrast, the visitor register $\rm (VLR)$ stores information about the current visitors of other operators who are in the current PLMN. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 79: | Line 108: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Examples of Communication Systems: Exercises|^3.1 General Description of GSM |
^]] | ^]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:51, 7 January 2023
The network infrastructure in the 2G mobile communications standard "Global System for Mobile Communications" – $\rm GSM$, for short – includes the following subsystems:
- Base Station Subsystem $\rm (BSS)$,
- Switching & Management Subsystem $\rm (SMSS)$,
- Operation & Maintenance Subsystem $\rm (OMSS)$.
The base station subsystem is essentially responsible for the GSM radio network (see diagram), while the SMSS represents the switching network and the OMSS is responsible for operations and maintenance.
The following terms continue to be used in the questions for this exercise:
- Authentication Center $\rm (AUC)$,
- Base Station Controller $\rm (BSC)$,
- Base Transceiver Station $\rm (BTS)$,
- Gateway Mobile Switching Center $\rm (GMSC)$,
- Home Location Register $\rm (HLR)$,
- Mobile Switching Center $\rm (MSC)$,
- Operation and Maintenance Center $\rm (OMC)$,
- Visitor Location Register $\rm (VLR)$.
Hint: This exercise belongs to the chapter "General Description of GSM".
Questions
Solution
- Each mobile station $\rm (MS)$ is in radio communication with a base transceiver station $\rm (BTS)$.
- This is part of the base station subsystem $\rm (BSS)$.
(2) Correct are the proposed solutions 1 and 3:
- In contrast, proposed solution 2 is incorrect:
- The BTS is not responsible for switching tasks, but this is the task of a mobile switching center $\rm (MSC)$,
which is a part of the switching and management subsystem $\rm (SMSS)$.
(3) In GSM, the individual antennas usually cover $120^\circ$ sectors.
- This also means that a BTS can provide up to three radio channels.
(4) Correct is the proposed solution 3:
- Only the operation and management center $\rm (OMC)$ is part of the OMSS.
- In contrast, MSC and GMSC are components of the mobile switching subsystem $\rm (SMSS)$.
- With respect to the OMC, a further distinction is made between $\text{OMC-B}$ $($for BSS monitoring$)$ and $\text{OMC-S}$ $($for SMSS monitoring$)$.
(5) Correct are the proposed solutions 1, 3 and 4:
- GMSC is a hardware unit responsible for switching between the fixed and mobile networks.
- The other three terms given describe databases of the SMSS.
- AUC is responsible for storing confidential data and keys.
- HLR is a central register for the entire "Public Land Mobile Network" $\rm (PLMN)$ for managing unencrypted subscriber data, subscribed services, and routing for calls of a mobile operator's own subscribers.
- In contrast, the visitor register $\rm (VLR)$ stores information about the current visitors of other operators who are in the current PLMN.