Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.9: Huffman Decoding after Errors"
From LNTwww
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Information_Theory/Entropy_Coding_According_to_Huffman |
}} | }} | ||
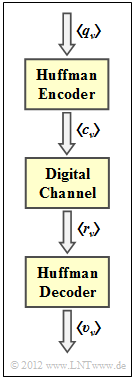
| − | [[File:EN_Inf_A_2_9.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:EN_Inf_A_2_9.png|right|frame|Overall system with "Huffman"]] |
We consider Huffman coding according to the following assignment: | We consider Huffman coding according to the following assignment: | ||
: $\rm A$ → <b>1</b>, $\rm B$ → <b>01</b>, $\rm C$ → <b>001</b>, $\rm D$ → <b>000</b>. | : $\rm A$ → <b>1</b>, $\rm B$ → <b>01</b>, $\rm C$ → <b>001</b>, $\rm D$ → <b>000</b>. | ||
| − | Huffman coding is always < | + | Huffman coding is always <u>lossless</u>. This means: |
| − | *If the | + | *If the encoded sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle$ is immediately decoded again after the Huffman encoder, the decoding result $\langle v_\nu \rangle$ is equal to the source symbol sequence $\langle q_\nu \rangle$. |
| − | *If, on the other hand, the | + | *If, on the other hand, the reception sequence $\langle r_\nu \rangle$ does not match the generated code sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle$ due to errors during transmission <br>$($<b>0</b> → <b>1</b>, <b>1</b> → <b>0</b>$)$, error propagation may occur. |
*A single bit error can then lead to (almost) all subsequent characters being decoded incorrectly. | *A single bit error can then lead to (almost) all subsequent characters being decoded incorrectly. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| − | + | <u>Hints:</u> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Hints: | ||
*The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Entropiecodierung_nach_Huffman|Entropy coding according to Huffman]]. | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Entropiecodierung_nach_Huffman|Entropy coding according to Huffman]]. | ||
*In particular, reference is made to the page [[Information_Theory/Entropiecodierung_nach_Huffman#Influence_of_transmission_errors_on_decoding|Influence of transmission errors on decoding]] . | *In particular, reference is made to the page [[Information_Theory/Entropiecodierung_nach_Huffman#Influence_of_transmission_errors_on_decoding|Influence of transmission errors on decoding]] . | ||
| Line 32: | Line 29: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {We consider the | + | {We consider the encoded sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 10100100011000010011 \rangle$. What is the corresponding source symbol sequence? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- $\langle q_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \rm CCDAADBCA \rangle$, | - $\langle q_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \rm CCDAADBCA \rangle$, | ||
| Line 40: | Line 37: | ||
| − | {Which sequence $\langle v_\nu \rangle$ results after decoding if the first bit is | + | {Which sequence $\langle v_\nu \rangle$ results after decoding if the first bit is falsified $\rm (1 → 0)$? <br> $\langle c_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 10100100011000010011 \rangle$ ⇒ $\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \underline{0}0100100011000010011 \rangle$. |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
+ $\langle v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \rm CCDAADBCA \rangle$, | + $\langle v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \rm CCDAADBCA \rangle$, | ||
| Line 56: | Line 53: | ||
| − | {Which sequence $\langle v_\nu \rangle$ results after decoding if the sixth bit is | + | {Which sequence $\langle v_\nu \rangle$ results after decoding if the sixth bit is falsified $\rm (1 → 0)$? <br> $\langle c_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 10100100011000010011 \rangle$ ⇒ $\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 10100\underline{0}00011000010011 \rangle$. |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- $\langle v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \rm CCDAADBCA \rangle$, | - $\langle v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \rm CCDAADBCA \rangle$, | ||
| Line 69: | Line 66: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' <u> | + | '''(1)''' <u>Solution suggestion 3</u> is correct: |
| − | *Below you can see the | + | *Below you can see the encoded sequence divided by inverted commas: |
:$$\langle c_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 1'01'001'000'1'1'000'01'001'1 \rangle .$$ | :$$\langle c_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 1'01'001'000'1'1'000'01'001'1 \rangle .$$ | ||
*This belongs to the following source symbol sequence: | *This belongs to the following source symbol sequence: | ||
| − | :$$\langle | + | :$$\langle q_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle ABCDAADBCA \rangle .$$ |
| Line 87: | Line 84: | ||
Interpretation: | Interpretation: | ||
*$\rm AB$ is replaced by $\rm C$ , the further text $\rm CDAADBCA$ is unchanged, but shifted by one position. | *$\rm AB$ is replaced by $\rm C$ , the further text $\rm CDAADBCA$ is unchanged, but shifted by one position. | ||
| − | *However, if you compare the first nine symbols of the original with the decoding < | + | *However, if you compare the first nine symbols of the original with the decoding result <u>position by position</u>, as an automaton would do, you will recognise eight different symbols. |
| Line 93: | Line 90: | ||
'''(3)''' The correct <u>answers are 1 and 3</u>: | '''(3)''' The correct <u>answers are 1 and 3</u>: | ||
| − | * An additional bit error at position 2 $\rm (0 → 1)$ falsifies $\rm AB$ to $\rm BA$ | + | * An additional bit error at position 2 $\rm (0 → 1)$ falsifies $\rm AB$ to $\rm BA$, but all further symbols are recognised correctly again. |
* An additional bit error at position 15 $\rm (0 → 1)$ leads to | * An additional bit error at position 15 $\rm (0 → 1)$ leads to | ||
:$$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm {\langle \underline{0}01'001'000'1'1'000'\underline{1}'1'001'1 \rangle} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\langle \it v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \underline{C}CDAAD\underline{AA}CA \rangle .$$ | :$$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm {\langle \underline{0}01'001'000'1'1'000'\underline{1}'1'001'1 \rangle} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\langle \it v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \underline{C}CDAAD\underline{AA}CA \rangle .$$ | ||
| − | ::Due to the bit error at position 1 $\rm (1 → 0)$ , $\rm AB$ | + | ::Due to the bit error at position 1 $\rm (1 → 0)$ , $\rm AB$ is falsified to $\rm C$ , i.e. a character is "swallowed". The additional bit error at position 15 $\rm (0 → 1)$ turns $\rm B$ into the tuple $\rm AA$. After that, all symbols in the correct position are recognised correctly, starting with $\rm CA$. |
* An additional bit error at position 10 $\rm (1 → 0)$ on the other hand, leads to | * An additional bit error at position 10 $\rm (1 → 0)$ on the other hand, leads to | ||
| Line 110: | Line 107: | ||
:$$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 101'00\underline{0}'000'1'000'0'1'001'1 \rangle \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\langle \it v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle AB\underline{D}DAADBCA \rangle .$$ | :$$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 101'00\underline{0}'000'1'000'0'1'001'1 \rangle \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\langle \it v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle AB\underline{D}DAADBCA \rangle .$$ | ||
| − | *The first $\rm C$ becomes a $\rm D$. All other symbols are decoded correctly. | + | *The first $\rm C$ becomes a $\rm D$. All other symbols are decoded correctly. |
Latest revision as of 16:29, 23 January 2023
We consider Huffman coding according to the following assignment:
- $\rm A$ → 1, $\rm B$ → 01, $\rm C$ → 001, $\rm D$ → 000.
Huffman coding is always lossless. This means:
- If the encoded sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle$ is immediately decoded again after the Huffman encoder, the decoding result $\langle v_\nu \rangle$ is equal to the source symbol sequence $\langle q_\nu \rangle$.
- If, on the other hand, the reception sequence $\langle r_\nu \rangle$ does not match the generated code sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle$ due to errors during transmission
$($0 → 1, 1 → 0$)$, error propagation may occur. - A single bit error can then lead to (almost) all subsequent characters being decoded incorrectly.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Entropy coding according to Huffman.
- In particular, reference is made to the page Influence of transmission errors on decoding .
Questions
Solution
(1) Solution suggestion 3 is correct:
- Below you can see the encoded sequence divided by inverted commas:
- $$\langle c_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 1'01'001'000'1'1'000'01'001'1 \rangle .$$
- This belongs to the following source symbol sequence:
- $$\langle q_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle ABCDAADBCA \rangle .$$
(2) Solution suggestion 1 is correct:
- With a bit error at position 1, one obtains for the reception sequence:
- $$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 00100100011000010011 \rangle .$$
- The inverted commas clarify the individual blocks of decoding:
- $$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 001'001'000'1'1'000'01'001'1 \rangle .$$
- This leads to the following sink symbol sequence:
- $$\langle v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle CCDAADBCA \rangle .$$
Interpretation:
- $\rm AB$ is replaced by $\rm C$ , the further text $\rm CDAADBCA$ is unchanged, but shifted by one position.
- However, if you compare the first nine symbols of the original with the decoding result position by position, as an automaton would do, you will recognise eight different symbols.
(3) The correct answers are 1 and 3:
- An additional bit error at position 2 $\rm (0 → 1)$ falsifies $\rm AB$ to $\rm BA$, but all further symbols are recognised correctly again.
- An additional bit error at position 15 $\rm (0 → 1)$ leads to
- $$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm {\langle \underline{0}01'001'000'1'1'000'\underline{1}'1'001'1 \rangle} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\langle \it v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \underline{C}CDAAD\underline{AA}CA \rangle .$$
- Due to the bit error at position 1 $\rm (1 → 0)$ , $\rm AB$ is falsified to $\rm C$ , i.e. a character is "swallowed". The additional bit error at position 15 $\rm (0 → 1)$ turns $\rm B$ into the tuple $\rm AA$. After that, all symbols in the correct position are recognised correctly, starting with $\rm CA$.
- An additional bit error at position 10 $\rm (1 → 0)$ on the other hand, leads to
- $$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \underline{0}01'001'000'\underline{0}'1'000'0'1'001'1 \rangle \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\langle \it v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle \underline{C}CDAAD\underline{B}CA \rangle .$$
- The bit error at position 10 turns $\rm AA$ into $\rm B$. The decoder thus swallows a total of two characters. All subsequently decoded characters are then not in the correct position.
(4) Solution suggestion 2 is correct:
- The first bit error at position 6 $\rm (1 → 0)$ yields
- $$\langle r_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle 101'00\underline{0}'000'1'000'0'1'001'1 \rangle \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\langle \it v_\nu \rangle = \rm \langle AB\underline{D}DAADBCA \rangle .$$
- The first $\rm C$ becomes a $\rm D$. All other symbols are decoded correctly.