Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.5: PM and FM for Rectangular Signals"
m |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/Frequency_Modulation_(FM) |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1099__Mod_A_3_5.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1099__Mod_A_3_5.png|right|frame|Two signal waveforms in angle modulation]] |
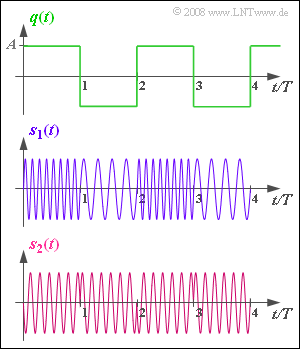
Assume a bipolar and rectangular source signal $q(t)$ , as shown in the upper diagram. This signal can only take on the two signal values $±A = ±2 \ \rm V$ and the duration of the positive and negative rectangles are each $T = 1 \ \rm ms$. The period of $q(t)$ is therefore $T_0 = 2 \ \rm ms$. | Assume a bipolar and rectangular source signal $q(t)$ , as shown in the upper diagram. This signal can only take on the two signal values $±A = ±2 \ \rm V$ and the duration of the positive and negative rectangles are each $T = 1 \ \rm ms$. The period of $q(t)$ is therefore $T_0 = 2 \ \rm ms$. | ||
| − | The signals $s_1(t)$ and $s_2(t)$ display two | + | The signals $s_1(t)$ and $s_2(t)$ display two transmitted signals with angle modulation $\rm (WM)$, each of which can be represented as |
:$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.05cm}\big [\psi (t) \big ]$$ | :$$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.05cm}\big [\psi (t) \big ]$$ | ||
Here, we distinguish between phase modulation $\rm (PM)$ with the angular function | Here, we distinguish between phase modulation $\rm (PM)$ with the angular function | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{Which of the signals is due to phase modulation and which is due to frquency modulation? | {Which of the signals is due to phase modulation and which is due to frquency modulation? | ||
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - $s_1(t)$ | + | - $s_1(t)$ represents a phase modulation. |
| − | + $s_1(t)$ | + | + $s_1(t)$ represents a frequency modulation. |
{What is the carrier phase $ϕ_{\rm T}$ that could be measured without a message signal ⇒ $q(t) \equiv 0$ ? | {What is the carrier phase $ϕ_{\rm T}$ that could be measured without a message signal ⇒ $q(t) \equiv 0$ ? | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
'''(1)''' <u>Answer 2</u> is correct: | '''(1)''' <u>Answer 2</u> is correct: | ||
*For a rectangular (digital) source signal, phase modulation (PM) can be recognised by the typical phase jumps – see the signal waveform $s_2(t)$. | *For a rectangular (digital) source signal, phase modulation (PM) can be recognised by the typical phase jumps – see the signal waveform $s_2(t)$. | ||
| − | *Frequency modulation (FM), on the other hand, has | + | *Frequency modulation (FM), on the other hand, has diverse instantaneous frequencies at different times, as in $s_1(t)$. |
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
*By counting the oscillations of $s_2(t)$ in the time interval $T$ , it can be seen that $f_{\rm T} · T\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 6}$ was used. | *By counting the oscillations of $s_2(t)$ in the time interval $T$ , it can be seen that $f_{\rm T} · T\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 6}$ was used. | ||
*When frequency modulating a bipolar source signal, $f_{\rm T}$ does not occur directly. | *When frequency modulating a bipolar source signal, $f_{\rm T}$ does not occur directly. | ||
| − | * | + | *However, the graphs do indicate that $f_{\rm T} · T = 6$ is also used here. |
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' The frequency deviation can also be represented as follows: |
:$$\Delta f_{\rm A} = \frac {K_{\rm FM}}{2\pi}\cdot A \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\Delta f_{\rm A} = \frac {K_{\rm FM}}{2\pi}\cdot A \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *With $Δf_{\rm A} · {\rm A} = 2$ we thus get: |
:$$K_{\rm FM} = \frac {2 \cdot 2\pi}{A \cdot T}= \frac {4\pi}{2\,{\rm V} \cdot 1\,{\rm ms}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 6283 \,{\rm V}^{-1}{\rm s}^{-1}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$K_{\rm FM} = \frac {2 \cdot 2\pi}{A \cdot T}= \frac {4\pi}{2\,{\rm V} \cdot 1\,{\rm ms}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 6283 \,{\rm V}^{-1}{\rm s}^{-1}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
Latest revision as of 16:19, 23 January 2023
Assume a bipolar and rectangular source signal $q(t)$ , as shown in the upper diagram. This signal can only take on the two signal values $±A = ±2 \ \rm V$ and the duration of the positive and negative rectangles are each $T = 1 \ \rm ms$. The period of $q(t)$ is therefore $T_0 = 2 \ \rm ms$.
The signals $s_1(t)$ and $s_2(t)$ display two transmitted signals with angle modulation $\rm (WM)$, each of which can be represented as
- $$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.05cm}\big [\psi (t) \big ]$$
Here, we distinguish between phase modulation $\rm (PM)$ with the angular function
- $$\psi(t) = \omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \phi(t) = \omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + K_{\rm PM} \cdot q(t)$$
and frequency modulation $\rm (FM)$, where the instantaneous freqiency is linearly related to $q(t)$:
- $$f_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{\omega_{\rm A}(t)}{2\pi}, \hspace{0.3cm} \omega_{\rm A}(t) = \frac{{\rm d}\hspace{0.03cm}\psi(t)}{{\rm d}t}= \omega_{\rm T} + K_{\rm FM} \cdot q(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$K_{\rm PM}$ and $K_{\rm FM}$ denote the dimensionally constrained constants given by the realizations of the PM and FM modulators, respectively. The frequency deviation $Δf_{\rm A}$ indicates the maximum deviation of the instantaneous frequency from the carrier frequency.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Frequency Modulation.
- Reference is also made to the chapter Phase Modulation.
- In anticipation of the fourth chapter, it should be mentioned that phase modulation with a digital input signal is also called Phase Shift Keying $\rm (PSK)$ and frequency modulation is analogously called Frequency Shift Keying $\rm (FSK)$ .
Questions
Solution
- For a rectangular (digital) source signal, phase modulation (PM) can be recognised by the typical phase jumps – see the signal waveform $s_2(t)$.
- Frequency modulation (FM), on the other hand, has diverse instantaneous frequencies at different times, as in $s_1(t)$.
(2) When $q(t) = 0$ , the equations provided for both PM and FM give
- $$s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos (\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t ) \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} \phi_{\rm T} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) The carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$ can be directly determined only from the PM signal $s_2(t)$ .
- By counting the oscillations of $s_2(t)$ in the time interval $T$ , it can be seen that $f_{\rm T} · T\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 6}$ was used.
- When frequency modulating a bipolar source signal, $f_{\rm T}$ does not occur directly.
- However, the graphs do indicate that $f_{\rm T} · T = 6$ is also used here.
(4) The amplitude value $A = 2 \ \rm V$ results in the phase $90^\circ$ or $π/2$ (minus sine wave). This gives:
- $$K_{\rm PM} = \frac {\pi /2}{2\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.785\,{\rm V}^{-1}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) The graph for $s_1(t)$ shows that either four or eight oscillations arise within a time interval $T$ : $4 \le f_{\rm A}(t) \cdot T \le 8\hspace{0.05cm}.$
- Considering the (normalized) carrier frequency $f_{\rm T} · T = 6$ , the (normalized) frequency deviation is:
- $$\Delta f_{\rm A} \cdot T \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {=2}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) The frequency deviation can also be represented as follows:
- $$\Delta f_{\rm A} = \frac {K_{\rm FM}}{2\pi}\cdot A \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- With $Δf_{\rm A} · {\rm A} = 2$ we thus get:
- $$K_{\rm FM} = \frac {2 \cdot 2\pi}{A \cdot T}= \frac {4\pi}{2\,{\rm V} \cdot 1\,{\rm ms}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 6283 \,{\rm V}^{-1}{\rm s}^{-1}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$