Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.13Z: AMI Code"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
${\it \Phi}_c(f = 0) \ = \ $ { 0. } $\ \cdot 10^{-6} \ \rm 1/Hz$ | ${\it \Phi}_c(f = 0) \ = \ $ { 0. } $\ \cdot 10^{-6} \ \rm 1/Hz$ | ||
${\it \Phi}_c(f = 500 \hspace{0.08cm} \rm kHz)\ = \ $ { 0.405 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-6} \ \rm 1/Hz$ | ${\it \Phi}_c(f = 500 \hspace{0.08cm} \rm kHz)\ = \ $ { 0.405 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-6} \ \rm 1/Hz$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' The discrete ACF value for $k = 0$ gives | + | '''(1)''' The discrete ACF value for $k = 0$ gives the variance of the source symbols. |
| − | *Since $q_\nu$ can only take the values $-1$ and $+1$ | + | *Since $q_\nu$ can only take the values $-1$ and $+1$ ⇒ $\varphi_q(k=0)\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}$. |
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
*The discrete-time ACF and its Fourier transform are: | *The discrete-time ACF and its Fourier transform are: | ||
:$${\rm A} \{ \varphi_q ( \tau ) \} = \varphi_q ( k = 0) \cdot T \cdot \delta (\tau) \hspace{0.3cm} \circ\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\bullet\, \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm P} \{{\it \Phi_q}( f) \} = \varphi_q ( k = 0) \cdot T = T.$$ | :$${\rm A} \{ \varphi_q ( \tau ) \} = \varphi_q ( k = 0) \cdot T \cdot \delta (\tau) \hspace{0.3cm} \circ\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\bullet\, \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm P} \{{\it \Phi_q}( f) \} = \varphi_q ( k = 0) \cdot T = T.$$ | ||
| − | *It is considered that $\varphi_q(k=0)= \sigma_q^2= 1$ This means: | + | *It is considered that $\varphi_q(k=0)= \sigma_q^2= 1$. This means: The periodic continuation of ${\rm P} \{ {\it \Phi}_q(f) \}$ thus gives the same value for all frequencies. |
| − | |||
*In contrast, the continuous-time ACF can be represented as follows: | *In contrast, the continuous-time ACF can be represented as follows: | ||
:$$ \varphi_q ( \tau ) = {\rm A} \{ \varphi_q ( \tau ) \} \star ( {\rm \delta} ( \tau) / T ).$$ | :$$ \varphi_q ( \tau ) = {\rm A} \{ \varphi_q ( \tau ) \} \star ( {\rm \delta} ( \tau) / T ).$$ | ||
| − | *The associated | + | *The associated power-spectral density (Fourier transform of the ACF) is then the product of the Fourier transforms of the two convolution terms: |
| − | :$$ {\it \Phi_q} ( f) = {\rm P} \{ {\it \Phi_q}( f) \} \cdot {\rm | + | :$$ {\it \Phi_q} ( f) = {\rm P} \{ {\it \Phi_q}( f) \} \cdot {\rm sinc}^2 (f T ) = T \cdot {\rm sinc}^2 (f T ) .$$ |
| − | *Based on the chosen ACF interpolation (with straight line intercepts) from their samples, a $\rm | + | *Based on the chosen ACF interpolation (with straight line intercepts) from their samples, a $\rm sinc^2$-shaped PSD is obtained. |
| − | *A rectangular spectrum according to the proposed solution | + | *A rectangular spectrum according to the second proposed solution would only occur with $\rm sinc$-shaped interpolation. |
| − | '''(3)''' The coded sequence is: $\langle +1, \ 0, -1, +1, \ 0, -1, +1, \ 0, \ 0, \ 0 \rangle$. Thus the 6th symbol is $c_6\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -1}$. | + | '''(3)''' The coded sequence is: $\langle +1, \ 0, -1, +1, \ 0, -1, +1, \ 0, \ 0, \ 0 \rangle$. Thus the 6th code symbol is $c_6\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -1}$. |
| − | '''(4)''' The probabilities | + | '''(4)''' The occurrence probabilities of the values $-1$, $\ 0$ and $+1$ are $0.25, 0.5, 0.25$. It follows: |
:$$\varphi_c ( k = 0) = 0.25 \cdot (-1)^2 + 0.5 \cdot 0^2 +0.25 \cdot (+1)^2\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0.5}. $$ | :$$\varphi_c ( k = 0) = 0.25 \cdot (-1)^2 + 0.5 \cdot 0^2 +0.25 \cdot (+1)^2\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0.5}. $$ | ||
| − | '''(5)''' For the ACF value at $k = 1$ consider the product $c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1}$. The combinations shown | + | '''(5)''' For the ACF value at $k = 1$ consider the product $c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1}$. The combinations shown in the table are obtained. |
*Only products $c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1} \ne 0$ with ${\rm Pr}\big[c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1}\big] \ne 0$: | *Only products $c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1} \ne 0$ with ${\rm Pr}\big[c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1}\big] \ne 0$: | ||
:$$\varphi_c ( k = 1) = {\rm Pr} \big [( c_{\nu} = +1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1) \big ] \cdot (+1) \cdot (-1) + {\rm Pr} \big [ ( c_{\nu} = -1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = +1) \big ] \cdot (-1) \cdot (+1).$$ | :$$\varphi_c ( k = 1) = {\rm Pr} \big [( c_{\nu} = +1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1) \big ] \cdot (+1) \cdot (-1) + {\rm Pr} \big [ ( c_{\nu} = -1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = +1) \big ] \cdot (-1) \cdot (+1).$$ | ||
[[File:P_ID428__Sto_Z_4_13_e.png|right|frame|For ACF calculation of AMI code]] | [[File:P_ID428__Sto_Z_4_13_e.png|right|frame|For ACF calculation of AMI code]] | ||
| − | *In the table, these terms are marked in red. Further: | + | *In the table, these terms are marked in red. Further: |
:$$ {\rm Pr} \big [ ( c_{\nu} = +1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1) \big ] = $$ | :$$ {\rm Pr} \big [ ( c_{\nu} = +1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1) \big ] = $$ | ||
:$$ = {\rm Pr} ( c_{\nu} = +1) \cdot {\rm Pr} \left ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1 | c_{\nu } = +1) \right ) = \frac{1}{4} \cdot \frac{1}{2}= \frac{1}{8} . $$ | :$$ = {\rm Pr} ( c_{\nu} = +1) \cdot {\rm Pr} \left ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1 | c_{\nu } = +1) \right ) = \frac{1}{4} \cdot \frac{1}{2}= \frac{1}{8} . $$ | ||
| − | : | + | :It is assumed that $+1$ occurs with probability $0.25$ and is followed by $-1$ only in half of the cases. |
| − | |||
*The same result is obtained for the second contribution. Thus applies: | *The same result is obtained for the second contribution. Thus applies: | ||
| − | $$varphi_c ( k = 1) = \frac {1}{8} \cdot (+1)\cdot (-1) + \frac {1}{8} \cdot (-1)\cdot (+1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -0.25}.$$ | + | :$$\varphi_c ( k = 1) = \frac {1}{8} \cdot (+1)\cdot (-1) + \frac {1}{8} \cdot (-1)\cdot (+1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -0.25}.$$ |
:$$\varphi_c ( k = -1) = \varphi_c ( k = 1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -0.25}.$$ | :$$\varphi_c ( k = -1) = \varphi_c ( k = 1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -0.25}.$$ | ||
*To calculate $\varphi_c ( k = 2)$ it is necessary to average over $3^3 = 27$ combinations. The result is zero. | *To calculate $\varphi_c ( k = 2)$ it is necessary to average over $3^3 = 27$ combinations. The result is zero. | ||
| Line 133: | Line 131: | ||
:$$P \{{\it \Phi_c}( f) \} = T\cdot \varphi_c ( k = 0) +2T \cdot \varphi_c ( k = 1) \cdot {\rm cos} ( 2 \pi f T ).$$ | :$$P \{{\it \Phi_c}( f) \} = T\cdot \varphi_c ( k = 0) +2T \cdot \varphi_c ( k = 1) \cdot {\rm cos} ( 2 \pi f T ).$$ | ||
| − | *With the result of the last subtask, it follows: | + | *With the result of the last subtask, it follows: |
:$$P \{{\it \Phi}_c( f) \} = \frac {T}{2} (1 - {\rm cos} ( 2 \pi f T ) )= T \cdot {\rm sin}^2 ( \pi f T ).$$ | :$$P \{{\it \Phi}_c( f) \} = \frac {T}{2} (1 - {\rm cos} ( 2 \pi f T ) )= T \cdot {\rm sin}^2 ( \pi f T ).$$ | ||
| − | *As shown in item '''(2)''' | + | *As shown in item '''(2)''': For the PSD – that is, the Fourier transform of $\varphi_c(\tau)$: |
| − | :$${\it \Phi_c}( f) = T \cdot {\rm sin}^2 ( \pi f T ) \cdot {\rm | + | :$${\it \Phi_c}( f) = T \cdot {\rm sin}^2 ( \pi f T ) \cdot {\rm sinc}^2 ( f T ) = T \cdot \frac {{\rm sin}^4 ( \pi f T )}{( \pi f T )^2 } .$$ |
:$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\it \Phi_c}( f = 0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0}, \hspace{0.8cm} | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\it \Phi_c}( f = 0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0}, \hspace{0.8cm} | ||
{\it \Phi_c}( f = {\rm500 \hspace{0.1cm}kHz}) = T \cdot \frac {{\rm sin}^4 ( \pi /2 )}{( \pi /2 )^2 } = \frac {4 T}{\pi^2} \rm \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.405 \cdot 10^{-6} \ {1}/{Hz}}.$$ | {\it \Phi_c}( f = {\rm500 \hspace{0.1cm}kHz}) = T \cdot \frac {{\rm sin}^4 ( \pi /2 )}{( \pi /2 )^2 } = \frac {4 T}{\pi^2} \rm \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.405 \cdot 10^{-6} \ {1}/{Hz}}.$$ | ||
Latest revision as of 17:33, 25 March 2022
For spectral adaptation (shaping) of a digital signal to the characteristics of the channel, one uses so-called "pseudo-ternary codes". With these codes, the binary source symbol sequence $\langle q_\nu \rangle$ is converted to a sequence $\langle c_\nu \rangle$ of ternary symbols according to a fixed rule:
- $$q_{\nu} \in \{ -1,\hspace{0.1cm} +1 \} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} c_{\nu} \in \{ -1, \hspace{0.1cm}0, \hspace{0.1cm}+1 \} .$$
The best known representative of this code class is the AMI code (from "Alternate Mark Inversion"). Here
- the binary value $q_\nu = -1$ is always mapped to $c_\nu = 0$ ,
- while $q_\nu = +1$ is alternately represented by the ternary values $c_\nu = +1$ and $c_\nu = -1$.
By convention, the ternary symbol $c_\nu = +1$ shall be selected at the first occurrence of $q_\nu = +1$ .
It is further assumed that
- the two possible source symbols are each equally probable and
- the source symbol sequence $\langle q_\nu \rangle $ has no internal statistical bindings.
Thus, all discrete ACF values are zero except $\varphi_q(k=0)$:
- $$\varphi_q ( k \cdot T) = 0 \hspace{0.5cm} {\rm if} \hspace{0.5cm} k \not= 0.$$
Here $T$ denotes the time distance between the source symbols. Use $T = 1 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm µ s$. The code symbols have the same spacing.
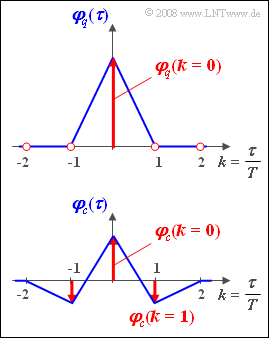
The graphic shows the given auto-correlation functions. Please note:
- In red are respectively the discrete-time representations ${\rm A} \{ \varphi_q(\tau) \}$ and ${\rm A} \{ \varphi_c(\tau) \}$ of the auto-correlation functions, each with the reference value $T$.
- The functions shown in blue indicate the continuous-time progressions $\varphi_q(\tau)$ and $\varphi_c(\tau)$ of the ACF, assuming square-wave pulses.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Power-Spectral Density.
- Reference is also made to the chapter Auto-Correlation Function as well as to the page Numerical PSD determination.
- Use the following Fourier correspondence, where ${\rm \Delta} (t)$ denotes a triangular pulse symmetric about $t = 0$ with ${\rm \Delta} (t= 0) = 1$ and ${\rm \Delta} (t) = 0$ for $|t| \ge T$:
- $${\rm \Delta} (t) \hspace{0.3cm} \circ\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\bullet\, \hspace{0.3cm} T \cdot {\rm si}^2 ( \pi f T).$$
Questions
Solution
- Since $q_\nu$ can only take the values $-1$ and $+1$ ⇒ $\varphi_q(k=0)\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}$.
(2) Correct are the proposed solutions 1 and 3:
- The discrete-time ACF and its Fourier transform are:
- $${\rm A} \{ \varphi_q ( \tau ) \} = \varphi_q ( k = 0) \cdot T \cdot \delta (\tau) \hspace{0.3cm} \circ\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\bullet\, \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm P} \{{\it \Phi_q}( f) \} = \varphi_q ( k = 0) \cdot T = T.$$
- It is considered that $\varphi_q(k=0)= \sigma_q^2= 1$. This means: The periodic continuation of ${\rm P} \{ {\it \Phi}_q(f) \}$ thus gives the same value for all frequencies.
- In contrast, the continuous-time ACF can be represented as follows:
- $$ \varphi_q ( \tau ) = {\rm A} \{ \varphi_q ( \tau ) \} \star ( {\rm \delta} ( \tau) / T ).$$
- The associated power-spectral density (Fourier transform of the ACF) is then the product of the Fourier transforms of the two convolution terms:
- $$ {\it \Phi_q} ( f) = {\rm P} \{ {\it \Phi_q}( f) \} \cdot {\rm sinc}^2 (f T ) = T \cdot {\rm sinc}^2 (f T ) .$$
- Based on the chosen ACF interpolation (with straight line intercepts) from their samples, a $\rm sinc^2$-shaped PSD is obtained.
- A rectangular spectrum according to the second proposed solution would only occur with $\rm sinc$-shaped interpolation.
(3) The coded sequence is: $\langle +1, \ 0, -1, +1, \ 0, -1, +1, \ 0, \ 0, \ 0 \rangle$. Thus the 6th code symbol is $c_6\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -1}$.
(4) The occurrence probabilities of the values $-1$, $\ 0$ and $+1$ are $0.25, 0.5, 0.25$. It follows:
- $$\varphi_c ( k = 0) = 0.25 \cdot (-1)^2 + 0.5 \cdot 0^2 +0.25 \cdot (+1)^2\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0.5}. $$
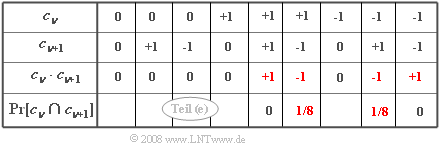
(5) For the ACF value at $k = 1$ consider the product $c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1}$. The combinations shown in the table are obtained.
- Only products $c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1} \ne 0$ with ${\rm Pr}\big[c_{\nu} \cdot c_{\nu+1}\big] \ne 0$:
- $$\varphi_c ( k = 1) = {\rm Pr} \big [( c_{\nu} = +1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1) \big ] \cdot (+1) \cdot (-1) + {\rm Pr} \big [ ( c_{\nu} = -1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = +1) \big ] \cdot (-1) \cdot (+1).$$
- In the table, these terms are marked in red. Further:
- $$ {\rm Pr} \big [ ( c_{\nu} = +1) \cap ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1) \big ] = $$
- $$ = {\rm Pr} ( c_{\nu} = +1) \cdot {\rm Pr} \left ( c_{\nu + 1} = -1 | c_{\nu } = +1) \right ) = \frac{1}{4} \cdot \frac{1}{2}= \frac{1}{8} . $$
- It is assumed that $+1$ occurs with probability $0.25$ and is followed by $-1$ only in half of the cases.
- The same result is obtained for the second contribution. Thus applies:
- $$\varphi_c ( k = 1) = \frac {1}{8} \cdot (+1)\cdot (-1) + \frac {1}{8} \cdot (-1)\cdot (+1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -0.25}.$$
- $$\varphi_c ( k = -1) = \varphi_c ( k = 1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -0.25}.$$
- To calculate $\varphi_c ( k = 2)$ it is necessary to average over $3^3 = 27$ combinations. The result is zero.
(6) The Fourier transform of the discrete-time ACF ${\rm A} \{ \varphi_c(\tau) \}$ is:
- $$P \{{\it \Phi_c}( f) \} = T\cdot \varphi_c ( k = 0) +2T \cdot \varphi_c ( k = 1) \cdot {\rm cos} ( 2 \pi f T ).$$
- With the result of the last subtask, it follows:
- $$P \{{\it \Phi}_c( f) \} = \frac {T}{2} (1 - {\rm cos} ( 2 \pi f T ) )= T \cdot {\rm sin}^2 ( \pi f T ).$$
- As shown in item (2): For the PSD – that is, the Fourier transform of $\varphi_c(\tau)$:
- $${\it \Phi_c}( f) = T \cdot {\rm sin}^2 ( \pi f T ) \cdot {\rm sinc}^2 ( f T ) = T \cdot \frac {{\rm sin}^4 ( \pi f T )}{( \pi f T )^2 } .$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\it \Phi_c}( f = 0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0}, \hspace{0.8cm} {\it \Phi_c}( f = {\rm500 \hspace{0.1cm}kHz}) = T \cdot \frac {{\rm sin}^4 ( \pi /2 )}{( \pi /2 )^2 } = \frac {4 T}{\pi^2} \rm \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.405 \cdot 10^{-6} \ {1}/{Hz}}.$$