Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.4Z: Trapezoid, Rectangle and Triangle"
From LNTwww
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „ {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Signaldarstellung/Gesetzmäßigkeiten der Fouriertransformation }} right| Betrachtet werden drei unt…“) |
m (Text replacement - "”" to """) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Signal_Representation/Fourier_Transform_Laws |
}} | }} | ||
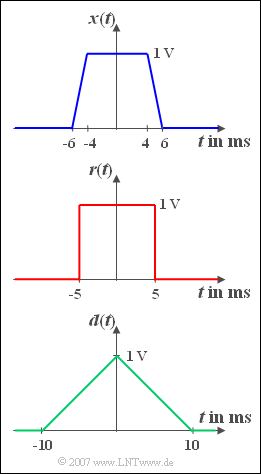
| − | [[File:P_ID510__Sig_Z_3_4.png|right|]] | + | [[File:P_ID510__Sig_Z_3_4.png|right|frame|Trapezoidal pulse and its limiting cases "Rectangle" and "Triangle" ]] |
| − | + | Three different pulse shapes are considered. The pulse ${x(t)}$ is trapezoidal. For $| t | < t_1 = 4 \,\text{ms}$ the time course is constant equal to ${A} = 1\, \text{V}$. Afterwards, ${x(t)}$ drops linearly to the value zero until the time $t_2 = 6\, \text{ms}$. | |
| − | + | The spectral function of the trapezoidal pulse is | |
| − | + | :$$X( f ) = A \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits}( {{\rm \pi} \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} ) \cdot \hspace{0.1cm}{\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits}( {{\rm \pi}\cdot \Delta t \cdot r_t \cdot f} ).$$ | |
| − | :$$\Delta t | ||
| − | + | with the two derived system quantities, namely | |
| − | |||
| − | + | * the [[Signal_Representation/Fourier_Transform_Laws#Reciprocity_Theorem_of_Time_duration_and_Bandwidth|equivalent bandwidth]], | |
| − | :$$ | + | :$$\Delta t = t_1 + t_2,$$ |
| − | |||
| − | + | * and the so-called roll-off factor (in the time domain): | |
| + | :$$r_t = \frac{t_2 - t_1 }{t_2 + t_1 }.$$ | ||
| − | + | Furthermore, the rectangular pulse ${r(t)}$ and the triangular pulse ${d(t)}$ are also shown in the graph, both of which can be interpreted as limiting cases of the trapezoidal pulse ${x(t)}$. | |
| − | |||
| − | === | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''Hints:'' | ||
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Signal_Representation/Fourier_Transform_Theorems|Fourier Transform Theorems]]. | ||
| + | *You can check your results using the two interactive applets | ||
| + | :[[Applets:Pulses_and_Spectra|Pulses and Spectra]], | ||
| + | :[[Applets:Frequency_%26_Impulse_Responses|Frequency & Impulse Responses]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the equivalent pulse duration and the rolloff factor of ${x(t)}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\Delta t$ | + | $\Delta t \ = \ $ { 10 3% } $\text{ms}$ |
| − | $r_t$ | + | $r_t\hspace{0.3cm} = \ $ { 0.2 3% } |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true regarding the spectral function ${X(f)}$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The spectral value at frequency $f = 0$ is equal to $20 \,\text{mV/Hz}$. |
| − | + | + | + For the phase function the values $0$ and $\pi$ $(180^{\circ})$ are possible. |
| − | + $ | + | + ${X(f)}$ only has zeros at all multiples of $100 \,\text{Hz}$. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true regarding the spectral function ${R(f)}$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The spectral value at frequency $f = 0$ is equal to ${X(f = 0)}$. |
| − | + | + | + The values $0$ and $\pi$ $(180^{\circ})$ are possible for the phase function. |
| − | + $ | + | + ${R(f)}$ only has zeros at all multiples of $100 \,\text{Hz}$. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true regarding the spectral function ${D(f)}$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The spectral value at frequency $f = 0$ is equal to ${X(f = 0)}$. |
| − | - | + | - The values $0$ and $\pi$ $(180^{\circ})$ are possible for the phase function. |
| − | + $ | + | + ${D(f)}$ only has zeros at all multiples of $100 \,\text{Hz}$. |
| Line 58: | Line 67: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''1 | + | '''(1)''' The equivalent pulse duration is $\Delta t = t_1 + t_2 \;\underline{= 10 \,\text{ms}}$ and the rolloff factor is $r_t = 2/10 \;\underline{= 0.2}$. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' Proposed <u>solutions 2 and 3</u> are correct: | ||
| + | *The spectral value at $f = 0$ is $A \cdot \Delta t = 10 \,\text{mV/Hz}$. | ||
| + | *Since ${X(f)}$ is real and can assume both positive and negative values, only the two phase values $0$ und $\pi$ are possible. | ||
| + | *Zeros exist due to the first si–function at all multiples of $1/\Delta t = 100\, \text{Hz}$. | ||
| + | *The second si–function leads to zero crossings at intervals of $1/(r_t \cdot \Delta t) = 500 \,\text{Hz}$. These coincide exactly with the zeros of the first si–function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''(3)''' <u>All proposed solutions</u> are correct: |
| + | *With the equivalent pulse duration $\Delta t = 10 \,\text{ms}$ and the rolloff factor $r_t = 0$ one obtains: $R( f ) = A \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {{\rm{\pi }} \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} ).$ | ||
| + | *It follows that $R( f = 0) = A \cdot \Delta t = X( f = 0).$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''4 | + | '''(4)''' Proposed <u>solutions 2 and 3</u> are correct: |
| − | + | *For the triangular pulse, the rolloff factor is $r_t = 1$. | |
| − | + | *The equivalent pulse duration is $\Delta t = 10 \,\text{ms}$. It follows that $D( f ) = A \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ^2 ( {{\rm{\pi }} \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} )$ and $D( f = 0) = A \cdot \Delta t = X( f = 0)$. | |
| + | *Since ${D(f)}$ cannot become negative, the phase $[{\rm arc} \; {D(f)}]$ is always zero. The phase value $\pi$ $(180°)$ is therefore not possible with the triangular pulse. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
__NOEDITSECTION__ | __NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Signal Representation: Exercises|^3.3 Fourier Transform Theorems^]] |
Latest revision as of 15:39, 28 May 2021
Three different pulse shapes are considered. The pulse ${x(t)}$ is trapezoidal. For $| t | < t_1 = 4 \,\text{ms}$ the time course is constant equal to ${A} = 1\, \text{V}$. Afterwards, ${x(t)}$ drops linearly to the value zero until the time $t_2 = 6\, \text{ms}$.
The spectral function of the trapezoidal pulse is
- $$X( f ) = A \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits}( {{\rm \pi} \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} ) \cdot \hspace{0.1cm}{\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits}( {{\rm \pi}\cdot \Delta t \cdot r_t \cdot f} ).$$
with the two derived system quantities, namely
- the equivalent bandwidth,
- $$\Delta t = t_1 + t_2,$$
- and the so-called roll-off factor (in the time domain):
- $$r_t = \frac{t_2 - t_1 }{t_2 + t_1 }.$$
Furthermore, the rectangular pulse ${r(t)}$ and the triangular pulse ${d(t)}$ are also shown in the graph, both of which can be interpreted as limiting cases of the trapezoidal pulse ${x(t)}$.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Fourier Transform Theorems.
- You can check your results using the two interactive applets
Questions
Solution
(1) The equivalent pulse duration is $\Delta t = t_1 + t_2 \;\underline{= 10 \,\text{ms}}$ and the rolloff factor is $r_t = 2/10 \;\underline{= 0.2}$.
(2) Proposed solutions 2 and 3 are correct:
- The spectral value at $f = 0$ is $A \cdot \Delta t = 10 \,\text{mV/Hz}$.
- Since ${X(f)}$ is real and can assume both positive and negative values, only the two phase values $0$ und $\pi$ are possible.
- Zeros exist due to the first si–function at all multiples of $1/\Delta t = 100\, \text{Hz}$.
- The second si–function leads to zero crossings at intervals of $1/(r_t \cdot \Delta t) = 500 \,\text{Hz}$. These coincide exactly with the zeros of the first si–function.
(3) All proposed solutions are correct:
- With the equivalent pulse duration $\Delta t = 10 \,\text{ms}$ and the rolloff factor $r_t = 0$ one obtains: $R( f ) = A \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {{\rm{\pi }} \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} ).$
- It follows that $R( f = 0) = A \cdot \Delta t = X( f = 0).$
(4) Proposed solutions 2 and 3 are correct:
- For the triangular pulse, the rolloff factor is $r_t = 1$.
- The equivalent pulse duration is $\Delta t = 10 \,\text{ms}$. It follows that $D( f ) = A \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ^2 ( {{\rm{\pi }} \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} )$ and $D( f = 0) = A \cdot \Delta t = X( f = 0)$.
- Since ${D(f)}$ cannot become negative, the phase $[{\rm arc} \; {D(f)}]$ is always zero. The phase value $\pi$ $(180°)$ is therefore not possible with the triangular pulse.