Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.11Z: Arithmetic Coding once again"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:EN_Inf_Z_2_11_v2.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:EN_Inf_Z_2_11_v2.png|right|frame|Preset interval ranges]] |
| − | + | Here we consider arithmetic coding $(\rm AC)$. All necessary information about this type of entropy coding can be found in [[Aufgaben:2.11_Arithmetische_Codierung|Exercise 2.11]]. | |
| − | + | The graph is also the result of Exercise 2.11. The numerical values for coding steps 3 and 7 that are important for the current task are highlighted in colour: | |
| − | * | + | * The interval for $N= 3$ $($symbol sequence $\rm XXY)$ starts at $B_3 = 0.343$ and goes up to $E_3 = 0.392$. |
| − | * | + | * The interval limits for $N= 7$ $($symbol sequence $\rm XXYXXXZ)$ are $B_7 = 0.3564456$ and $E_7 =0.359807$. |
| − | + | This task is only about assigning binary sequences to the selected intervals. Procedure: | |
| − | * | + | * The interval $I$ is determined by the beginning $B$, the end $E$, the interval width ${\it \Delta} = E-B$ sowie die Intervallmitte $M = (B+E)/2$. |
| − | * | + | * The interval $I$ is characterised by the binary representation (with limited resolution) of any real number value $r \in I$. For example, one chooses $r \approx M$. |
| − | * | + | * The required number of bits results from the interval width according to the following equation (the open square brackets mean "round up"): |
:$$N_{\rm Bit} = \left\lceil{\rm log_2} \hspace{0.15cm} 1/{\it \Delta} \right\rceil+1\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | :$$N_{\rm Bit} = \left\lceil{\rm log_2} \hspace{0.15cm} 1/{\it \Delta} \right\rceil+1\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | ||
| − | + | For example, for $N_{\rm Bit} = 5$ the binary code <b>01001</b> stands for the following real-valued number $r$: | |
:$$r = 0 \cdot 2^{-1}+1 \cdot 2^{-2}+0 \cdot 2^{-3}+0 \cdot 2^{-4}+1 \cdot 2^{-5} = 0.28125 | :$$r = 0 \cdot 2^{-1}+1 \cdot 2^{-2}+0 \cdot 2^{-3}+0 \cdot 2^{-4}+1 \cdot 2^{-5} = 0.28125 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | \hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | * | + | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Weitere_Quellencodierverfahren|Other source coding methods]]. |
| − | * | + | *In particular, reference is made to the page [[Information_Theory/Weitere_Quellencodierverfahren#Arithmetische_Codierung|Arithmetic coding]]. |
| − | * | + | *Further information on the topic can also be found in this [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arithmetic_coding Wikipedia article]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {How many bits are used to represent the source symbol sequence $\rm XXY$ ⇒ $N = 3$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$N_\text{Bit} \ = \ $ { 6 } | $N_\text{Bit} \ = \ $ { 6 } | ||
| − | { | + | {Which arithmetic code $\rm (AC)$ applies to this case? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- $\rm AC = $ <b>01011</b>, | - $\rm AC = $ <b>01011</b>, | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
| − | { | + | {How many bits are used to represent the source symbol sequence $\rm XXYXXXZ$ ⇒ $N = 7$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$N_\text{Bit} \ = \ $ { 11 } | $N_\text{Bit} \ = \ $ { 11 } | ||
| − | { | + | {Is <b>01011100001</b> a valid code for the source symbol sequence $\rm XXYXXXZ$? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - | + | - Yes. |
| − | + | + | + No. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements apply to arithmetic coding in general? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + It is a common coding of entire sequences. |
| − | + | + | + A 32 Bit–computer architecture limits the sequence length $N$. |
| − | + | + | + This problem can be circumvented by integer realisation. |
| − | + | + | + Integer realisation increases the coding speed. |
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
'''(1)''' Das ausgewählte Intervall beginnt bei $B_3 = 0.343$ und endet bei $E_3 = 0.392$. | '''(1)''' Das ausgewählte Intervall beginnt bei $B_3 = 0.343$ und endet bei $E_3 = 0.392$. | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 7 August 2021
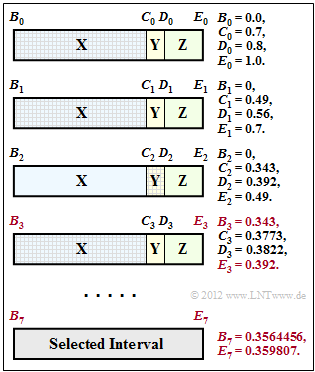
Here we consider arithmetic coding $(\rm AC)$. All necessary information about this type of entropy coding can be found in Exercise 2.11.
The graph is also the result of Exercise 2.11. The numerical values for coding steps 3 and 7 that are important for the current task are highlighted in colour:
- The interval for $N= 3$ $($symbol sequence $\rm XXY)$ starts at $B_3 = 0.343$ and goes up to $E_3 = 0.392$.
- The interval limits for $N= 7$ $($symbol sequence $\rm XXYXXXZ)$ are $B_7 = 0.3564456$ and $E_7 =0.359807$.
This task is only about assigning binary sequences to the selected intervals. Procedure:
- The interval $I$ is determined by the beginning $B$, the end $E$, the interval width ${\it \Delta} = E-B$ sowie die Intervallmitte $M = (B+E)/2$.
- The interval $I$ is characterised by the binary representation (with limited resolution) of any real number value $r \in I$. For example, one chooses $r \approx M$.
- The required number of bits results from the interval width according to the following equation (the open square brackets mean "round up"):
- $$N_{\rm Bit} = \left\lceil{\rm log_2} \hspace{0.15cm} 1/{\it \Delta} \right\rceil+1\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
For example, for $N_{\rm Bit} = 5$ the binary code 01001 stands for the following real-valued number $r$:
- $$r = 0 \cdot 2^{-1}+1 \cdot 2^{-2}+0 \cdot 2^{-3}+0 \cdot 2^{-4}+1 \cdot 2^{-5} = 0.28125 \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
Hints:
- The task belongs to the chapter Other source coding methods.
- In particular, reference is made to the page Arithmetic coding.
- Further information on the topic can also be found in this Wikipedia article.
Questions
Solution
- Die Intervallbreite ist somit ${\it \Delta}_3 = 0.049$ und damit gilt mit dem Logarithmus dualis:
- $$N_{\rm Bit} = {\rm log_2} \hspace{0.15cm} \left\lceil \frac{1}{0.049}\right\rceil+1\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 6} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Das ausgewählte Intervall ergibt sich zu $I = \big[0.343, \ 0.392\big)$.
- Die Mitte liegt bei $M_3 = 0.3675$.
- Zur Bestimmung des arithmetischen Codes versuchen wir, die Intervallmitte durch eine Binärdarstellung möglichst gut zu erreichen.
- Da uns gerade kein entsprechendes Tool zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe zur Verfügung steht, gehen wir von folgenden Nebenrechnungen aus:
- $H_4 = 2^{-2} + 2^{-2} = 0.3125$ ⇒ gehört nicht zum Intervall $I$.
- $H_5 = H_4 +2^{-5} = 0.34375 \in I$ ⇒ Binärdarstellung: 0.01011 ⇒ Code: 01011.
- $H_6 = H_5 +2^{-6} = 0.359375 \in I$ ⇒ Binärdarstellung: 0.010111 ⇒ Code: 010111.
- $H_7 = H_6 +2^{-7} = 0.3671875 \in I$ ⇒ Binärdarstellung: 0.0101111 ⇒ Code: 0101111.
- $H_{12} = H_7 +2^{-12} = 0.3674316406 \in I$ ⇒ Binärdarstellung: 0.010111100001 ⇒ Code: 010111100001.
Der entsprechende 6 Bit–Code lautet somit $\rm AC =$ 010111 ⇒ Richtig ist der Lösungsvorschlag 2.
(3) Hier ergibt sich mit dem Beginn $B_7 = 0.3564456$ und dem Ende $E_7 = 0.359807$ die Intervallbreite ${\it \Delta}_7 = 0.0033614$ und damit
- $$N_{\rm Bit} = \left\lceil {\rm log_2} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{1}{0.0033614} \right\rceil + 1\hspace{0.15cm} = \left\lceil {\rm log_2} \hspace{0.15cm} 297.5 \right\rceil + 1\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 11} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Die Binärdarstellung des Codes 01011100001 ergibt
- $$2^{-2}+ 2^{-4}+ 2^{-5}+ 2^{-6}+ 2^{-11} = 0.3598632813 > E_7 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Richtig ist also NEIN. Der gültige arithmetische Code ist $\rm AC =$ 01011011101, wegen
- $$2^{-2}+ 2^{-4}+ 2^{-5}+ 2^{-7}+ 2^{-8}+ 2^{-9}+ 2^{-11} =0.3579101563 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} B_7 \le 0.3579101563 < E_7.$$
(5) Alle Aussagen sind richtig. Siehe auch:
- Bodden, E.; Clasen, M.; Kneis, J.: Algebraische Kodierung. Proseminar, Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV, RWTH Aachen, 2002.