Difference between revisions of "Theory of Stochastic Signals/Binomial Distribution"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The '''binomial distribution''' represents an important special case for the occurrence probabilities of a discrete random variable. | The '''binomial distribution''' represents an important special case for the occurrence probabilities of a discrete random variable. | ||
| − | + | To derive the binomial distribution, we assume that $I$ binary and statistically independent random variables $b_i$ each can achieve | |
| − | To derive the binomial distribution, we assume that $I$ binary and statistically independent random variables $b_i$ each can achieve | ||
*the value $1$ with probability ${\rm Pr}(b_i = 1) = p$, and | *the value $1$ with probability ${\rm Pr}(b_i = 1) = p$, and | ||
*the value $0$ with probability ${\rm Pr}(b_i = 0) = 1-p$. | *the value $0$ with probability ${\rm Pr}(b_i = 0) = 1-p$. | ||
| − | + | Then the sum $z$ is also a discrete random variable with the symbol set $\{0, \ 1, \ 2,\hspace{0.1cm}\text{ ...} \hspace{0.1cm}, \ I\}$, which is called binomially distributed: | |
| − | Then the sum $z$ is also a discrete random variable with the symbol set $\{0, \ 1, \ 2,\hspace{0.1cm}\text{ ...} \hspace{0.1cm}, \ I\}$, | ||
:$$z=\sum_{i=1}^{I}b_i.$$ | :$$z=\sum_{i=1}^{I}b_i.$$ | ||
| − | Thus, the symbol size is $M = I + 1.$ }} | + | Thus, the symbol set size is $M = I + 1.$ }} |
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
$\text{Example 1:}$ | $\text{Example 1:}$ | ||
| − | The binomial distribution finds manifold applications in | + | The binomial distribution finds manifold applications in Communications Engineering as well as in other disciplines: |
# It describes the distribution of rejects in statistical quality control. | # It describes the distribution of rejects in statistical quality control. | ||
# It allows the calculation of the residual error probability in blockwise coding. | # It allows the calculation of the residual error probability in blockwise coding. | ||
| − | # | + | # The bit error rate of a digital transmission system obtained by simulation is actually a binomially distributed random quantity.}} |
| − | |||
==Probabilities of the binomial distribution== | ==Probabilities of the binomial distribution== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 35: | ||
For the '''probabilities of the binomial distribution''' with $μ = 0, \hspace{0.1cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}, \ I$: | For the '''probabilities of the binomial distribution''' with $μ = 0, \hspace{0.1cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}, \ I$: | ||
:$$p_\mu = {\rm Pr}(z=\mu)={I \choose \mu}\cdot p\hspace{0.05cm}^\mu\cdot ({\rm 1}-p)\hspace{0.05cm}^{I-\mu}.$$ | :$$p_\mu = {\rm Pr}(z=\mu)={I \choose \mu}\cdot p\hspace{0.05cm}^\mu\cdot ({\rm 1}-p)\hspace{0.05cm}^{I-\mu}.$$ | ||
| − | The first term here indicates the number of combinations $($read: $I\ \text{ over }\ μ)$: | + | *The first term here indicates the number of combinations $($read: $I\ \text{ over }\ μ)$: |
:$${I \choose \mu}=\frac{I !}{\mu !\cdot (I-\mu) !}=\frac{ {I\cdot (I- 1) \cdot \ \cdots \ \cdot (I-\mu+ 1)} }{ 1\cdot 2\cdot \ \cdots \ \cdot \mu}.$$}} | :$${I \choose \mu}=\frac{I !}{\mu !\cdot (I-\mu) !}=\frac{ {I\cdot (I- 1) \cdot \ \cdots \ \cdot (I-\mu+ 1)} }{ 1\cdot 2\cdot \ \cdots \ \cdot \mu}.$$}} | ||
| − | + | Additional notes: | |
| − | *For very large values of $I$ | + | *For very large values of $I$, the binomial distribution can be approximated by the [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Poisson_Distribution|Poisson distribution]] described in the next section. |
| − | *If at the same time the product $I · p \gg 1$, | + | *If at the same time the product $I · p \gg 1$, then according to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De_Moivre%E2%80%93Laplace_theorem de Moivre–Laplace's (central limit) theorem], the Poisson distribution (and hence the binomial distribution) transitions to a discrete [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Gaussian_Distributed_Random_Variables|Gaussian distribution]]. |
| − | |||
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
$\text{Example 2:}$ | $\text{Example 2:}$ | ||
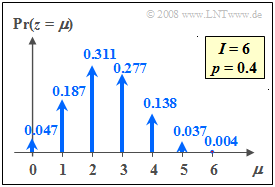
| − | The graph shows the probabilities of the binomial distribution are for $I =6$ and $p =0.4$. Thus $M = I+1=7$ probabilities are different from zero. | + | The graph shows the probabilities of the binomial distribution are for $I =6$ and $p =0.4$. |
| + | [[File:P_ID203__Sto_T_2_3_S2_neu.png |frame|Binomial distribution probabilites]] | ||
| + | *Thus $M = I+1=7$ probabilities are different from zero. | ||
| − | In contrast, for $I = 6$ and $p = 0.5$, the binomial | + | *In contrast, for $I = 6$ and $p = 0.5$, the probabilities of the binomial distribution are as follows: |
:$$\begin{align*}{\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}0) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}6)\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm} 1/64\hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm}0.015625 ,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}1) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}5) \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm}6/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}=\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.09375,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}2) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}4)\hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm}15/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm}0.234375 ,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}3) & = 20/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm} 0.3125 .\end{align*}$$ | :$$\begin{align*}{\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}0) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}6)\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm} 1/64\hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm}0.015625 ,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}1) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}5) \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm}6/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}=\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.09375,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}2) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}4)\hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm}15/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm}0.234375 ,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}3) & = 20/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm} 0.3125 .\end{align*}$$ | ||
| − | These are symmetrical with respect to the abscissa value $\mu = I/2 = 3$.}} | + | *These are symmetrical with respect to the abscissa value $\mu = I/2 = 3$.}} |
| − | Another example of the application of the binomial distribution is the ''' | + | {{GraueBox|TEXT= |
| + | $\text{Example 3:}$ Another example of the application of the binomial distribution is the '''Calculation of the block error probability in Digital Signal Transmission'''. | ||
| − | + | If one transmits blocks each of $I =10$ binary symbols over a channel | |
| − | + | *with probability $p = 0.01$ that one symbol is corrupted ⇒ random variable $e_i = 1$, and | |
| − | If one transmits blocks of $I =10$ binary symbols | + | *correspondingly with probability $1 - p = 0.99$ for a uncorrupted symbol ⇒ random variable $e_i = 0$, |
| − | *with probability $p = 0.01$ one symbol is corrupted ⇒ random variable $e_i = 1$, and | ||
| − | *correspondingly with probability $1 - p = 0.99$ | ||
| − | then the new random variable $f$ | + | then the new random variable $f$ ⇒ "number of block error" is: |
:$$f=\sum_{i=1}^{I}e_i.$$ | :$$f=\sum_{i=1}^{I}e_i.$$ | ||
| − | This random variable $f$ can | + | This random variable $f$ can take all integer values between $0$ (no symbol is corrupted) and $I$ (all symbols symbol are corrupted) . |
| − | *The case where all $I$ symbols are correctly transmitted occurs with probability $p_0 = 0.99^{10} ≈ 0.9044$ . This also follows from the binomial formula for $μ = 0$ considering definition $10\, \text{ over }\, 0 = 1$. | + | *We denote the probabilities for $\mu$ corruptions by $p_μ$. |
| + | *The case where all $I$ symbols are correctly transmitted occurs with probability $p_0 = 0.99^{10} ≈ 0.9044$ . | ||
| + | *This also follows from the binomial formula for $μ = 0$ considering the definition $10\, \text{ over }\, 0 = 1$. | ||
*A single symbol error $(f = 1)$ occurs with the following probability: | *A single symbol error $(f = 1)$ occurs with the following probability: | ||
:$$p_1 = \rm 10\cdot 0.01\cdot 0.99^9\approx 0.0914.$$ | :$$p_1 = \rm 10\cdot 0.01\cdot 0.99^9\approx 0.0914.$$ | ||
| − | :The first factor considers that there are exactly $10\, \text{ over }\, 1 = 10$ possibilities for the position of a single error. The other two factors take into account that one symbol must be corrupted and nine must be transmitted correctly if $f =1$ is to hold. | + | ::The first factor considers that there are exactly $10\, \text{ over }\, 1 = 10$ possibilities for the position of a single error. |
| − | *For $f =2$ there are clearly more combinations, namely $10\, \text{ over }\, 2 = 45$, and we get | + | ::The other two factors take into account that one symbol must be corrupted and nine must be transmitted correctly if $f =1$ is to hold. |
| + | *For $f =2$ there are clearly more combinations, namely $10\, \text{ over }\, 2 = 45$, and we get | ||
:$$p_2 = \rm 45\cdot 0.01^2\cdot 0.99^8\approx 0.0041.$$ | :$$p_2 = \rm 45\cdot 0.01^2\cdot 0.99^8\approx 0.0041.$$ | ||
| − | If a block code can correct up to two errors, the | + | If a block code can correct up to two errors, the block error probability is |
| − | :$$p_{\rm | + | :$$p_{\rm block} = \it p_{\rm 3} \rm +\hspace{0.1cm}\text{ ...} \hspace{0.1cm} \rm + \it p_{\rm 10}\approx \rm 10^{-4},$$ |
| − | + | or | |
| − | :$$p_{\rm | + | :$$p_{\rm block} = \rm 1-\it p_{\rm 0}-\it p_{\rm 1}-p_{\rm 2}\approx \rm 10^{-4}.$$ |
| − | *One can see that | + | *One can see that for large values of $I$ the second possibility of calculation via the complement leads faster to the goal. |
| − | *However, one could also consider | + | *However, one could also consider that for these numerical values $p_{\rm block} ≈ p_3$ holds as an approximation. }} |
| − | Use the interactive applet [[Applets:Binomial-_und_Poissonverteilung_(Applet)|Binomial and Poisson distribution]] to find the binomial probabilities for any $I$ and $p$ . | + | Use the interactive HTML5/JS applet [[Applets:Binomial-_und_Poissonverteilung_(Applet)|Binomial and Poisson distribution]] to find the binomial probabilities for any $I$ and $p$ . |
Revision as of 11:01, 11 December 2021
Contents
General description of the binomial distribution
$\text{Definition:}$ The binomial distribution represents an important special case for the occurrence probabilities of a discrete random variable.
To derive the binomial distribution, we assume that $I$ binary and statistically independent random variables $b_i$ each can achieve
- the value $1$ with probability ${\rm Pr}(b_i = 1) = p$, and
- the value $0$ with probability ${\rm Pr}(b_i = 0) = 1-p$.
Then the sum $z$ is also a discrete random variable with the symbol set $\{0, \ 1, \ 2,\hspace{0.1cm}\text{ ...} \hspace{0.1cm}, \ I\}$, which is called binomially distributed:
- $$z=\sum_{i=1}^{I}b_i.$$
Thus, the symbol set size is $M = I + 1.$
$\text{Example 1:}$ The binomial distribution finds manifold applications in Communications Engineering as well as in other disciplines:
- It describes the distribution of rejects in statistical quality control.
- It allows the calculation of the residual error probability in blockwise coding.
- The bit error rate of a digital transmission system obtained by simulation is actually a binomially distributed random quantity.
Probabilities of the binomial distribution
$\text{Calculation rule:}$ For the probabilities of the binomial distribution with $μ = 0, \hspace{0.1cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm}, \ I$:
- $$p_\mu = {\rm Pr}(z=\mu)={I \choose \mu}\cdot p\hspace{0.05cm}^\mu\cdot ({\rm 1}-p)\hspace{0.05cm}^{I-\mu}.$$
- The first term here indicates the number of combinations $($read: $I\ \text{ over }\ μ)$:
- $${I \choose \mu}=\frac{I !}{\mu !\cdot (I-\mu) !}=\frac{ {I\cdot (I- 1) \cdot \ \cdots \ \cdot (I-\mu+ 1)} }{ 1\cdot 2\cdot \ \cdots \ \cdot \mu}.$$
Additional notes:
- For very large values of $I$, the binomial distribution can be approximated by the Poisson distribution described in the next section.
- If at the same time the product $I · p \gg 1$, then according to de Moivre–Laplace's (central limit) theorem, the Poisson distribution (and hence the binomial distribution) transitions to a discrete Gaussian distribution.
$\text{Example 2:}$ The graph shows the probabilities of the binomial distribution are for $I =6$ and $p =0.4$.
- Thus $M = I+1=7$ probabilities are different from zero.
- In contrast, for $I = 6$ and $p = 0.5$, the probabilities of the binomial distribution are as follows:
- $$\begin{align*}{\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}0) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}6)\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm} 1/64\hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm}0.015625 ,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}1) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}5) \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm}6/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}=\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.09375,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}2) & = {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}4)\hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-0.05cm}15/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm}0.234375 ,\\ {\rm Pr}(z\hspace{-0.05cm} =\hspace{-0.05cm}3) & = 20/64 \hspace{-0.05cm}= \hspace{-0.05cm} 0.3125 .\end{align*}$$
- These are symmetrical with respect to the abscissa value $\mu = I/2 = 3$.
$\text{Example 3:}$ Another example of the application of the binomial distribution is the Calculation of the block error probability in Digital Signal Transmission.
If one transmits blocks each of $I =10$ binary symbols over a channel
- with probability $p = 0.01$ that one symbol is corrupted ⇒ random variable $e_i = 1$, and
- correspondingly with probability $1 - p = 0.99$ for a uncorrupted symbol ⇒ random variable $e_i = 0$,
then the new random variable $f$ ⇒ "number of block error" is:
- $$f=\sum_{i=1}^{I}e_i.$$
This random variable $f$ can take all integer values between $0$ (no symbol is corrupted) and $I$ (all symbols symbol are corrupted) .
- We denote the probabilities for $\mu$ corruptions by $p_μ$.
- The case where all $I$ symbols are correctly transmitted occurs with probability $p_0 = 0.99^{10} ≈ 0.9044$ .
- This also follows from the binomial formula for $μ = 0$ considering the definition $10\, \text{ over }\, 0 = 1$.
- A single symbol error $(f = 1)$ occurs with the following probability:
- $$p_1 = \rm 10\cdot 0.01\cdot 0.99^9\approx 0.0914.$$
- The first factor considers that there are exactly $10\, \text{ over }\, 1 = 10$ possibilities for the position of a single error.
- The other two factors take into account that one symbol must be corrupted and nine must be transmitted correctly if $f =1$ is to hold.
- For $f =2$ there are clearly more combinations, namely $10\, \text{ over }\, 2 = 45$, and we get
- $$p_2 = \rm 45\cdot 0.01^2\cdot 0.99^8\approx 0.0041.$$
If a block code can correct up to two errors, the block error probability is
- $$p_{\rm block} = \it p_{\rm 3} \rm +\hspace{0.1cm}\text{ ...} \hspace{0.1cm} \rm + \it p_{\rm 10}\approx \rm 10^{-4},$$
or
- $$p_{\rm block} = \rm 1-\it p_{\rm 0}-\it p_{\rm 1}-p_{\rm 2}\approx \rm 10^{-4}.$$
- One can see that for large values of $I$ the second possibility of calculation via the complement leads faster to the goal.
- However, one could also consider that for these numerical values $p_{\rm block} ≈ p_3$ holds as an approximation.
Use the interactive HTML5/JS applet Binomial and Poisson distribution to find the binomial probabilities for any $I$ and $p$ .
Moments of the binomial distribution
You can calculate the moments in general using the equations in the chapters Moments of a discrete random variable and probabilities of the binomial distribution .
$\text{Calculation rules:} $ For the $k$-th order moment of a binomially distributed random variable, the general rule is:
- $$m_k={\rm E}\big[z^k\big]=\sum_{\mu={\rm 0} }^{I}\mu^k\cdot{I \choose \mu}\cdot p\hspace{0.05cm}^\mu\cdot ({\rm 1}-p)\hspace{0.05cm}^{I-\mu}.$$
From this, after some transformations, we obtain for
- the linear mean value:
- $$m_1 ={\rm E}\big[z\big]= I\cdot p,$$
- the rms value:
- $$m_2 ={\rm E}\big[z^2\big]= (I^2-I)\cdot p^2+I\cdot p.$$
The variance and standard deviation are obtained by applyings "Steiner's theorem":
- $$\sigma^2 = {m_2-m_1^2} = {I \cdot p\cdot (1-p)} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \sigma = \sqrt{I \cdot p\cdot (1-p)}.$$
The maximum variance $σ^2 = I/4$ is obtained for the "characteristic probability" $p = 1/2$. In this case, the probabilities are symmetric around the mean $m_1 = I/2 \ ⇒ \ p_μ = p_{I–μ}$.
The more the characteristic probability $p$ deviates from the value $1/2$ ,
- the smaller is the standard deviation $σ$, and
- the more asymmetric the probabilities become around the mean $m_1 = I · p$.
$\text{Example 4:}$ As in $\text{example 3}$ , we consider a block of $I =10$ binary symbols, each of which is independently corrupted with probability $p = 0.01$ . Then holds:
- The mean number of block errors is equal to $m_f = {\rm E}\big[ f\big] = I · p = 0.1$.
- Der standard deviation of the random variable $f$ is $σ_f = \sqrt{0.1 \cdot 0.99}≈ 0.315$.
In contrast, in the completely corrupted channel ⇒ falsification probability (*besseres Wort als falsification für Verfälschung?*) $p = 1/2$ results in the values
- $m_f = 5$ ⇒ on average, five of the ten bits within a block are wrong,
- $σ_f = \sqrt{I}/2 ≈1.581$ ⇒ maximum standard deviation $I = 10$.
Exercises for the chapter
Exercise 2.3: Algebraic Sum of Binary Numbers
Exercise 2.4: Number Lottery (6 from 49)