Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 5.6: OFDM Spectrum"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/General_Description_of_OFDM |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1659__A_5_6.png|right|frame|Real | + | [[File:P_ID1659__A_5_6.png|right|frame|Real and imaginary part of the OFDM signal]] |
| − | + | In this task, we consider an OFDM system with $N = 4$ carriers. | |
| − | * | + | *For simplicity, we restrict ourselves to a single time interval $T$. |
| − | * | + | *The frame duration is also $T_{\rm R} = T.$ |
| − | * | + | *Accordingly, a guard interval is not used. |
| − | + | With the summary of pulse shaping and modulation by the function | |
| − | :$$ g_\mu (t) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} s_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ {\kern 1pt} {\rm{j2 \pi}} {\kern 1pt} \mu f_0 t} \quad 0 \le t < T, \\ 0 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad {\rm | + | :$$ g_\mu (t) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} s_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ {\kern 1pt} {\rm{j2 \pi}} {\kern 1pt} \mu f_0 t} \quad 0 \le t < T, \\ 0 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad {\rm otherwise} \\ \end{array} \right.$$ |
| − | + | the (complex) OFDM transmit signal in the considered time interval $(0 ≤ t < T)$ results to: | |
:$$ s (t) = \sum\limits_{\mu = 0}^{N - 1} {a_{\mu} \cdot g_\mu (t )}.$$ | :$$ s (t) = \sum\limits_{\mu = 0}^{N - 1} {a_{\mu} \cdot g_\mu (t )}.$$ | ||
| − | + | All carrier coefficients $a_0$, $a_1$, $a_2$ and $a_3$ are either $0$ or $\pm 1$. | |
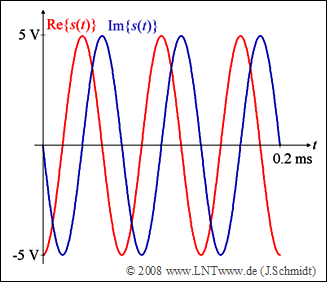
| − | + | The diagram shows the real and imaginary parts of the transmitted signal $s(t)$ for a given combination of $a_0$, ... , $a_3$, <br>which is to be determined in subtask '''(3)'''. | |
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Notes:'' |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Allgemeine_Beschreibung_von_OFDM|General Description of OFDM]]. |
| − | * | + | *Reference is made in particular to the pages |
| − | : [[Modulation_Methods/ | + | : [[Modulation_Methods/General_Description_of_OFDM#The_principle_of_OFDM_-_system_consideration_in_the_time_domain|OFDM - system consideration in the time domain]], |
| − | : [[Modulation_Methods/ | + | : [[Modulation_Methods/General_Description_of_OFDM#System_consideration_in_the_frequency_domain_with_causal_basic_pulse|OFDM-System consideration in the frequency domain with causal basic pulse]]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the amplitude $s_0$ of the transmitted signal? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$s_0 \ = \ $ { 5 3% } $\ \rm V$ | $s_0 \ = \ $ { 5 3% } $\ \rm V$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the symbol duration $T$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$T \ = \ $ { 0.2 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | $T \ = \ $ { 0.2 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Which amplitude coefficients are the basis of the diagram? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$a_0 \ = \ $ { 0. } | $a_0 \ = \ $ { 0. } | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
$a_3 \ = \ ${ -1.01--0.99 } | $a_3 \ = \ ${ -1.01--0.99 } | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true regarding the OFDM magnitude function $|s(t)|$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $|s(t)|$ | + | - $|s(t)|$ is constant without limit. |
| − | + $|s(t)|$ | + | + $|s(t)|$ is constant within the symbol duration $T$. |
| − | - $|s(t)|$ | + | - $|s(t)|$ has a cosine shape. |
| − | - $|s(t)|$ | + | - $|s(t)|$ has a sinusoidal shape. |
| − | { | + | {Now let $a_0 = 0$, $a_1 = +1$, $a_2 = -1$ and $a_3 = +1$. Calculate the spectrum $S(f)$. Which values result for the mentioned frequencies? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$S(f = 0)\ = \ $ { 0. } $\ \rm mV/Hz$ | $S(f = 0)\ = \ $ { 0. } $\ \rm mV/Hz$ | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
$S(f = 15 \ \rm kHz) \ = \ $ { 1 1% } $\ \rm mV/Hz$ | $S(f = 15 \ \rm kHz) \ = \ $ { 1 1% } $\ \rm mV/Hz$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Interpret your results of subtasks '''(3)''' and '''(5)'''. Which statements are true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + OFDM | + | + OFDM satisfies the first Nyquist criterion in the time domain. |
| − | + OFDM | + | + OFDM satisfies the first Nyquist criterion in the frequency domain. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The transmitted signal $s(t)$ is a complex exponential oscillation with only one frequency. |
| − | * | + | *The amplitude $s_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 5\ \rm V}$ can be taken directly from the diagram. |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' Furthermore, the symbol duration $T\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 0.2\ \rm ms}$ can be seen from the diagram. |
| − | * | + | *From this the basic frequency results to $f_0 = 1/T = 5\ \rm kHz$. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' In the example shown, there is only one frequency, namely $3 · f_0$. |
| − | * | + | *From this follows $a_0 = a_1 = a_2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 0}$ and for the range $0 ≤ t < T$: |
:$$s(t) = a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ {\kern 1pt} {\rm{j\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}2 \pi}} \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} 3 f_0 \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} t}= a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \cos ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t) + \rm{j} \cdot a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \sin ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t).$$ | :$$s(t) = a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ {\kern 1pt} {\rm{j\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}2 \pi}} \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} 3 f_0 \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} t}= a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \cos ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t) + \rm{j} \cdot a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \sin ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t).$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Comparison with the sketch $($real part: minus cosine, imaginary part: minus sine$)$ gives the following result: |
:$$a_3\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -1}.$$ | :$$a_3\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -1}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' The <u>second solution</u> is correct: |
| − | * | + | * The magnitude function is: $ |s(t)| = a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \sqrt{\cos^2 ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t) + \sin^2 ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t)}= a_3 \cdot s_0.$ |
| − | * | + | *However, this equation is valid only in the range of symbol duration $T$. |
| − | * | + | *This means: the OFDM principle works only with a time limit on $T$. |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' In general, for the OFDM spectrum: |
:$$S (f) = s_0 \cdot T \cdot \sum\limits_{\mu = 0}^{N - 1} {a_{\mu } \cdot \,} {\rm{si}}(\pi \cdot T \cdot (f - \mu \cdot f_0 )) \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{j\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}2\pi}} \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}{T}/{2}\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} (f - \mu \cdot f_0 )} .$$ | :$$S (f) = s_0 \cdot T \cdot \sum\limits_{\mu = 0}^{N - 1} {a_{\mu } \cdot \,} {\rm{si}}(\pi \cdot T \cdot (f - \mu \cdot f_0 )) \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{j\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}2\pi}} \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}{T}/{2}\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} (f - \mu \cdot f_0 )} .$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The $\rm si$ function results from the time limit on $T$, and the last term in the sum results from the displacement law. |
| − | * | + | *By the zero crossings of the $\rm si$ function at the distance $f_0$ as well as $\rm si(0) = 1$ one obtains |
:$$S(f = μ · f_0) = s_0 · T · a_μ.$$ | :$$S(f = μ · f_0) = s_0 · T · a_μ.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *With $s_0 = 5 \ \rm V$ and $T = 0.2 \ \rm ms$ ⇒ $s_0 · T = 1\ \rm mV/Hz$ it further holds: |
:$$ \mu = 0,\hspace{0.1cm} a_0 = 0\text{:}\hspace{0.95cm} S (f = 0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0},\hspace{8cm}.$$ | :$$ \mu = 0,\hspace{0.1cm} a_0 = 0\text{:}\hspace{0.95cm} S (f = 0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0},\hspace{8cm}.$$ | ||
:$$\mu = 1, \hspace{0.1cm}a_1 = +1\text{:}\hspace{0.55cm} S (f = 5\,\,{\rm{kHz}}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +1\,\,{\rm{mV/Hz}}},$$ | :$$\mu = 1, \hspace{0.1cm}a_1 = +1\text{:}\hspace{0.55cm} S (f = 5\,\,{\rm{kHz}}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +1\,\,{\rm{mV/Hz}}},$$ | ||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
| − | '''(6)''' <u> | + | '''(6)''' <u>Both statements</u> are correct: |
| − | * | + | * The orthogonality with respect to the frequency domain has already been shown in subtask '''(5)'''. |
| − | * | + | *The orthogonality with respect to the time domain results from the limitation of the individual symbols to the time duration $T$. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Revision as of 09:59, 20 December 2021
In this task, we consider an OFDM system with $N = 4$ carriers.
- For simplicity, we restrict ourselves to a single time interval $T$.
- The frame duration is also $T_{\rm R} = T.$
- Accordingly, a guard interval is not used.
With the summary of pulse shaping and modulation by the function
- $$ g_\mu (t) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} s_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ {\kern 1pt} {\rm{j2 \pi}} {\kern 1pt} \mu f_0 t} \quad 0 \le t < T, \\ 0 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad {\rm otherwise} \\ \end{array} \right.$$
the (complex) OFDM transmit signal in the considered time interval $(0 ≤ t < T)$ results to:
- $$ s (t) = \sum\limits_{\mu = 0}^{N - 1} {a_{\mu} \cdot g_\mu (t )}.$$
All carrier coefficients $a_0$, $a_1$, $a_2$ and $a_3$ are either $0$ or $\pm 1$.
The diagram shows the real and imaginary parts of the transmitted signal $s(t)$ for a given combination of $a_0$, ... , $a_3$,
which is to be determined in subtask (3).
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter General Description of OFDM.
- Reference is made in particular to the pages
- OFDM - system consideration in the time domain,
- OFDM-System consideration in the frequency domain with causal basic pulse.
Questions
Solution
- The amplitude $s_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 5\ \rm V}$ can be taken directly from the diagram.
(2) Furthermore, the symbol duration $T\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 0.2\ \rm ms}$ can be seen from the diagram.
- From this the basic frequency results to $f_0 = 1/T = 5\ \rm kHz$.
(3) In the example shown, there is only one frequency, namely $3 · f_0$.
- From this follows $a_0 = a_1 = a_2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 0}$ and for the range $0 ≤ t < T$:
- $$s(t) = a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ {\kern 1pt} {\rm{j\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}2 \pi}} \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} 3 f_0 \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} t}= a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \cos ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t) + \rm{j} \cdot a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \sin ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t).$$
- Comparison with the sketch $($real part: minus cosine, imaginary part: minus sine$)$ gives the following result:
- $$a_3\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -1}.$$
(4) The second solution is correct:
- The magnitude function is: $ |s(t)| = a_3 \cdot s_0 \cdot \sqrt{\cos^2 ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t) + \sin^2 ({\rm{2 \pi}} \cdot 3 f_0 \cdot t)}= a_3 \cdot s_0.$
- However, this equation is valid only in the range of symbol duration $T$.
- This means: the OFDM principle works only with a time limit on $T$.
(5) In general, for the OFDM spectrum:
- $$S (f) = s_0 \cdot T \cdot \sum\limits_{\mu = 0}^{N - 1} {a_{\mu } \cdot \,} {\rm{si}}(\pi \cdot T \cdot (f - \mu \cdot f_0 )) \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{j\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}2\pi}} \hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm}{T}/{2}\hspace{0.04cm}\cdot \hspace{0.04cm} (f - \mu \cdot f_0 )} .$$
- The $\rm si$ function results from the time limit on $T$, and the last term in the sum results from the displacement law.
- By the zero crossings of the $\rm si$ function at the distance $f_0$ as well as $\rm si(0) = 1$ one obtains
- $$S(f = μ · f_0) = s_0 · T · a_μ.$$
- With $s_0 = 5 \ \rm V$ and $T = 0.2 \ \rm ms$ ⇒ $s_0 · T = 1\ \rm mV/Hz$ it further holds:
- $$ \mu = 0,\hspace{0.1cm} a_0 = 0\text{:}\hspace{0.95cm} S (f = 0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0},\hspace{8cm}.$$
- $$\mu = 1, \hspace{0.1cm}a_1 = +1\text{:}\hspace{0.55cm} S (f = 5\,\,{\rm{kHz}}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +1\,\,{\rm{mV/Hz}}},$$
- $$ \mu = 2, \hspace{0.1cm}a_2 = -1\text{:}\hspace{0.55cm} S (f = 10\,\,{\rm{kHz}}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -1\,\,{\rm{mV/Hz}}},$$
- $$ \mu = 3, \hspace{0.1cm}a_3 = +1\text{:}\hspace{0.55cm} S (f = 15\,\,{\rm{kHz}}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +1\,\,{\rm{mV/Hz}}}.$$
(6) Both statements are correct:
- The orthogonality with respect to the frequency domain has already been shown in subtask (5).
- The orthogonality with respect to the time domain results from the limitation of the individual symbols to the time duration $T$.