Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.1Z: Convolution Codes of Rate 1/2"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Basics_of_Convolutional_Coding}} | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Basics_of_Convolutional_Coding}} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2589__KC_Z_3_1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2589__KC_Z_3_1.png|right|frame|Convolutional codes of rate $1/2$ '''Korrektur''']] |
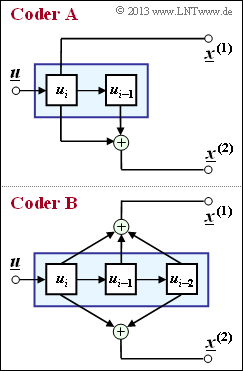
| − | The graphic shows two convolutional encoders of rate $R = 1/2$ | + | The graphic shows two convolutional encoders of rate $R = 1/2$: |
| + | *At the input there is the information sequence $\underline {u} = (u_1, u_2, \ \text{...} \ , u_i, \ \text{...})$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *From this, modulo-2 operations generate the two sequences | ||
:$$\underline{\it x}^{(1)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \big( \hspace{0.05cm}x_1^{(1)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_2^{(1)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} | :$$\underline{\it x}^{(1)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \big( \hspace{0.05cm}x_1^{(1)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_2^{(1)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
x_i^{(1)} \hspace{0.05cm},\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | x_i^{(1)} \hspace{0.05cm},\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| Line 8: | Line 11: | ||
x_i^{(2)} \hspace{0.05cm}, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )$$ | x_i^{(2)} \hspace{0.05cm}, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )$$ | ||
| − | where $x_i^{(j)}$ with $j = 1$ resp. $j = 2$ except from $u_i$ also from the previous information bits $u_{i-1}, \ \text{...} \ , u_{i-m}$ | + | :where $x_i^{(j)}$ with $j = 1$ resp. $j = 2$ may depend except from $u_i$ also from the previous information bits $u_{i-1}, \ \text{...} \ , u_{i-m}$. |
| + | *One refers $m$ as the "memory" and $\nu = m + 1$ as the "influence length" of the code $($or of the encoder$)$. | ||
| + | * The considered encoders $\rm A$ and $\rm B$ differ with respect to these quantities. | ||
| + | <u>Hints:</u> | ||
| + | *The exercise refers to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Basics_of_Convolutional_Coding| "Basics of Convolutional Coding"]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*Not shown in the diagram is the multiplexing of the two subsequences $\underline {x}^{(1)}$ and $\underline {x}^{(2)}$ to the resulting code sequence | *Not shown in the diagram is the multiplexing of the two subsequences $\underline {x}^{(1)}$ and $\underline {x}^{(2)}$ to the resulting code sequence | ||
:$$\underline {x} = (x_1^{(1)}, x_1^{(2)}, x_2^{(1)}, x_2^{(2)}, \ \text{...}).$$ | :$$\underline {x} = (x_1^{(1)}, x_1^{(2)}, x_2^{(1)}, x_2^{(2)}, \ \text{...}).$$ | ||
| − | *In subtasks '''(3)''' to '''(5)''' you are to determine the | + | *In subtasks '''(3)''' to '''(5)''' you are to determine the start of the sequences $\underline {x}^{(1)}, \underline{x}^{(2)}$ and $\underline{x}$ assuming the information sequence |
| + | :$$\underline{u} = (1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, \ \text{. ..}).$$ | ||
| Line 26: | Line 32: | ||
===Questions=== | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {In which code parameters do | + | {In which code parameters do encoder $\rm A$ and encoder $\rm B$ differ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
- $k$: Number of information bits processed per coding step, | - $k$: Number of information bits processed per coding step, | ||
- $n$: Number of code bits output per coding step, | - $n$: Number of code bits output per coding step, | ||
| − | + $m$: memory order of the code | + | + $m$: memory order of the code, |
+ $\nu$: influence length of the code. | + $\nu$: influence length of the code. | ||
| − | {Which encoder exhibits the memory $m = 2$ | + | {Which encoder exhibits the memory $m = 2$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
- Encoder $\rm A$, | - Encoder $\rm A$, | ||
| − | + | + | + encoder $\rm B$. |
{What is the partial code sequence $\underline {x}^{(1)}$ of encoder $\rm B$ for $\underline {u} = (1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, \ \text{...})$? | {What is the partial code sequence $\underline {x}^{(1)}$ of encoder $\rm B$ for $\underline {u} = (1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, \ \text{...})$? | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 6 November 2022
The graphic shows two convolutional encoders of rate $R = 1/2$:
- At the input there is the information sequence $\underline {u} = (u_1, u_2, \ \text{...} \ , u_i, \ \text{...})$.
- From this, modulo-2 operations generate the two sequences
- $$\underline{\it x}^{(1)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \big( \hspace{0.05cm}x_1^{(1)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_2^{(1)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_i^{(1)} \hspace{0.05cm},\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\underline{\it x}^{(2)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \big( \hspace{0.05cm}x_1^{(2)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_2^{(2)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_i^{(2)} \hspace{0.05cm}, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )$$
- where $x_i^{(j)}$ with $j = 1$ resp. $j = 2$ may depend except from $u_i$ also from the previous information bits $u_{i-1}, \ \text{...} \ , u_{i-m}$.
- One refers $m$ as the "memory" and $\nu = m + 1$ as the "influence length" of the code $($or of the encoder$)$.
- The considered encoders $\rm A$ and $\rm B$ differ with respect to these quantities.
Hints:
- The exercise refers to the chapter "Basics of Convolutional Coding".
- Not shown in the diagram is the multiplexing of the two subsequences $\underline {x}^{(1)}$ and $\underline {x}^{(2)}$ to the resulting code sequence
- $$\underline {x} = (x_1^{(1)}, x_1^{(2)}, x_2^{(1)}, x_2^{(2)}, \ \text{...}).$$
- In subtasks (3) to (5) you are to determine the start of the sequences $\underline {x}^{(1)}, \underline{x}^{(2)}$ and $\underline{x}$ assuming the information sequence
- $$\underline{u} = (1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, \ \text{. ..}).$$
Questions
Solution
- The memory $m$ and the influence length $\nu$ are different ⇒ Answers 3 and 4.
(2) The shift register of encoder $\rm A$ does contain two memory cells.
However, since $x_i^{(1)} = u_i$ and $x_i^{(2)} = u_i + u_{i-1}$ is influenced only by the immediately preceding bit $u_{i-1}$ besides the current information bit $u_i$, is
- the memory $m = 1$, and
- the influence length $\nu = m + 1 = 2$.
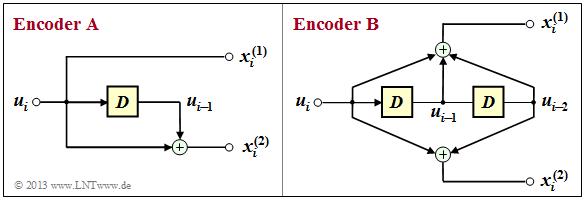
The graphic shows the two coders in another representation, whereby the "memory cells" are highlighted in yellow.
- For the encoder $\rm A$ one recognizes only one such memory ⇒ $m = 1$.
- In contrast, for the encoder $\rm B$ actually $m = 2$ and $\nu = 3$.
- The proposed solution 2 is therefore correct.
(3) For the upper output of encoder $\rm B$ applies in general:
- $$x_i^{(1)} = u_{i} + u_{i-1}+ u_{i-2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Considering the preassignment ($u_0 = u_{-1} = 0$), we obtain with the above data:
- $$x_1^{(1)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u_{1} + u_{0}+ u_{-1} = 1+0+0 = 1 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{1cm}x_2^{(1)} = u_{2} + u_{1}+ u_{0} = 0+1+0 = 1\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$x_3^{(1)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u_{3} + u_{2}+ u_{1} \hspace{0.25cm}= 1+0+1 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{1cm}x_4^{(1)} = u_{4} + u_{3}+ u_{2} = 1+1+0 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$x_5^{(1)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u_{5} + u_{4}+ u_{3} \hspace{0.25cm}= 0+1+1 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{1cm}x_6^{(1)} = u_{6} + u_{5}+ u_{4} = 0+0+1 = 1\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$x_7^{(1)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} x_8^{(1)} = \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}= 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The proposed solution 1 is therefore correct.
- The second solution suggestion ⇒ $\underline {x}^{(1)} = $\underline {u}$ would only be valid for a systematic code (which is not present here). '''(4)''' Analogous to subtask (3), $x_i^{(2)} = u_i + u_{i–2}$ is obtained:
- $$x_1^{(2)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1+0 = 1 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}x_2^{(2)} = 0+0 = 0\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}x_3^{(3)} = 1+1 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}x_4^{(2)} = 1+0 = 1 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$x_5^{(2)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0+1 = 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}x_6^{(2)} = 0+1 = 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} x_7^{(2)} = x_8^{(2)} = \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}= 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The correct solution is therefore proposed solution 2.
(5) For the (entire) code sequence, one can formally write:
- $$\underline{\it x} = \big( \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{\it x}_1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} \underline{\it x}_2\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} \underline{\it x}_i \hspace{0.05cm}, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \underline{\it x}_i = \big( x_i^{(1)}\hspace{0.05cm}, x_i^{(2)} \big) \hspace{0.4cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.4cm} \underline{\it x} = \big( \hspace{0.05cm}x_1^{(1)}\hspace{0.01cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_2^{(1)}\hspace{0.01cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_1^{(2)}\hspace{0.01cm},\hspace{0.05cm} x_2^{(2)}\hspace{0.01cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} \big )\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
A comparison with the solutions of exercises (3) and (4) shows the correctness of proposed solution 1.