Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.12: Regular and Irregular Tanner Graph"
m (Guenter moved page Aufgabe 4.12: Regulärer und irregulärer Tanner–Graph to Exercise 4.12: Regular and Irregular Tanner Graph) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/The_Basics_of_Low-Density_Parity_Check_Codes}} |
| − | [[File:P_ID3072__KC_A_4_12_v1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID3072__KC_A_4_12_v1.png|right|frame|Given Tanner graph for code $\rm A$]] |
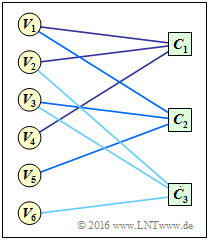
Dargestellt ist ein Tanner–Graph eines Codes $\rm A$ mit | Dargestellt ist ein Tanner–Graph eines Codes $\rm A$ mit | ||
| − | * | + | * the <i>variable nodes</i> (abbreviated VNs) $V_1, \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} , \ V_6$, where $V_i$ denotes the $i$th code word bit (whether information– or parity bit) and corresponds to the $i$th column of the parity-check matrix; |
| − | * | + | * the check nodes</i> (abbreviated CNs) $C_1, \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} , \ C_3$, which represent the rows of the $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ matrix and hence the parity-check equations. |
| − | + | An edge between $V_i$ and $C_j$ indicates that the $i$th code word symbol is involved in the $j$th parity-check equation. In this case, the element $h_{j,\hspace{0.05cm}i}$ of the parity-check matrix is equal $1$. | |
| − | In | + | In the exercise, the relation between the above Tanner–graph $($valid for the code $\rm A)$ and the matrix $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ shall be given. In addition, the Tanner–graph to a parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_{\rm B}$ shall be set up, resulting from $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ adding another row. This is to be determined so that the associated code $\rm B$ is regular. This means: |
| − | * | + | * From all <i>variable nodes</i> $V_i$ $($with $1 ≤ i ≤ n)$ go off equal numbers of edges, likewise from all <i>check nodes</i> $C_j$ $($with $1 ≤ j ≤ m)$. |
| − | * | + | * The Hamming weights of all rows of $\mathbf{H}_{\rm B}$ are each said to be equal $(w_{\rm Z})$, as are the Hamming–weights of all columns $(w_{\rm S})$. |
| − | * | + | * For the rate of the regular code to be constructed $\rm B$ the following lower bound then applies: |
:$$R \ge 1 - \frac{w_{\rm S}}{w_{\rm Z}} | :$$R \ge 1 - \frac{w_{\rm S}}{w_{\rm Z}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/The_Basics_of_Low-Density_Parity_Check_Codes|"Basics of Low–density Parity–check Codes"]]. |
| − | * | + | *Reference is made in particular to the page [[Channel_Coding/The_Basics_of_Low-Density_Parity_Check_Codes#Two-part_LDPC_graph_representation_-_Tanner_graph|"Two-part LDPC graph representation – Tanner graph"]]. |
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {How many rows $(m)$ and columns $(n)$ does the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ have? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$m \hspace{0.18cm} = \ ${ 3 } | $m \hspace{0.18cm} = \ ${ 3 } | ||
$n \hspace{0.3cm} = \ ${ 6 } | $n \hspace{0.3cm} = \ ${ 6 } | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true based on the Tanner graph? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The row 1 of $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$–matrix is "$1 \ 1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0 \ 0$". |
| − | - | + | - The row 2 of $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$–matrix is "$1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0 \ 0 \ 1$". |
| − | + | + | + The row 3 of $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$–matrix is "$0 \ 1 \ 1 \ 0 \ 0 \ 1$". |
| − | { | + | {What are the properties of the code $\rm A$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The code is systematic. |
| − | - | + | - The code is regular. |
| − | + | + | + The code rate is $R = 1/2$. |
| − | - | + | - The code rate is $R = 1/3$. |
| − | { | + | {The matrix $\mathbf{H}_{\rm B}$ is obtained from $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ by adding one more row. By which fourth row does a regular code $\rm B$ result? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | +By adding "$0 \ 0 \ 0 \ 1 \ 1 \ 1$". |
| − | - | + | - By adding "$1 \ 1 \ 1 \ 1 \ 1 \ 1$". |
| − | - | + | - By adding any other row. |
| − | { | + | {What are the properties of the code $\rm B$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The code is systematic. |
| − | + | + | + The code is regular. |
| − | + | + | + The code rate is $R = 1/2$. |
| − | - | + | - The code rate is $R = 1/3$. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solutiojn=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The number of $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$–rows is equal to the number of <i>check nodes</i> $C_j$ in the Tanner graph ⇒ $\underline{m = 3}$, and the number $\underline{n = 6}$ of <i>variable nodes</i> $V_i$ is equal to the column number. |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' Correct are <u>answers 1 and 3</u> in contrast to statement 2: |
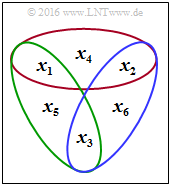
| − | * | + | *The second $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$–row is rather "$1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0$". Thus, this exercise is based on the following parity-check equation: |
| − | [[File:P_ID3073__KC_A_4_12c_v1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID3073__KC_A_4_12c_v1.png|right|frame|Underlying parity-check equations]] |
:$${ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm A} = | :$${ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm A} = | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
\end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *In the diagram, the parity-check equations are illustrated as red (row 1), green (row 2), and blue (row 3) groupings, respectively. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' Correct are <u>solutions 1 and 3</u>: |
| − | * | + | * The $\mathbf{H}$ matrix ends with a $3 × 3$ diagonal matrix ⇒ systematic code. |
| − | * | + | * Thus, the Hamming weights of the last three columns are $w_{\rm S}(4) = w_{\rm S}(5) = w_{\rm S}(6) = 1$. |
| − | * | + | * For the first three columns, $w_{\rm S}(1) = w_{\rm S}(2) = w_{\rm S}(3) = 2$ ⇒ irregular code. |
| − | * | + | * The three matrix rows are linearly independent. Thus $k = n - m = 6 - 3 = 3$ and $R = k/n = 1/2$ holds. |
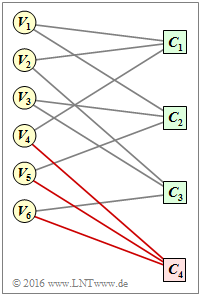
| − | [[File: P_ID3074__KC_A_4_12d_v1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File: P_ID3074__KC_A_4_12d_v1.png|right|frame|Modified Tanner graph for code $\rm B$]] |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Correct is the <u>proposed solution 1</u>: |
| − | * | + | *Looking at the previous Tanner–s graph, one can see the correctness of proposed solution 1. |
| − | * | + | *By adding the row "$0 \ 0 \ 0 \ 1 \ 1 \ 1$" to the $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ matrix, one obtains: |
:$${ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm B} = | :$${ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm B} = | ||
\begin{pmatrix} | \begin{pmatrix} | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
\end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The modifications are marked in red in the adjacent graphic. | |
| − | + | Due to the newly added check node $C_4$ and the connections with $V_4, \ V_5$ and $V_6$, there are now | |
| − | * | + | * from all variable nodes $V_i$ two lines, and |
| − | * | + | * from all Check Nodes $C_j$ uniformly four. |
| − | + | This is the condition for the code $\rm B$ to be regular. | |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' Correct are the <u>solutions 2 and 3</u>: |
| − | * | + | *The construction in subtask (4) yields a regular code. |
| − | * | + | *The Hamming weights of the rows and columns, respectively, are $w_{\rm Z} = 3$ and $w_{\rm S} = 2$. |
| − | * | + | *This gives as lower bound for the code rate: |
:$$R \ge 1 - \frac{w_{\rm S}}{w_{\rm Z}} | :$$R \ge 1 - \frac{w_{\rm S}}{w_{\rm Z}} | ||
= 1 - {2}/{3} = 1/3 | = 1 - {2}/{3} = 1/3 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The $\mathbf{H}$ manipulation does not change the generator matrix $\mathbf{G}$. |
| − | * | + | *The same code is still sent with code rate $R = 1/2$. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Revision as of 21:21, 10 December 2022
Dargestellt ist ein Tanner–Graph eines Codes $\rm A$ mit
- the variable nodes (abbreviated VNs) $V_1, \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} , \ V_6$, where $V_i$ denotes the $i$th code word bit (whether information– or parity bit) and corresponds to the $i$th column of the parity-check matrix;
- the check nodes (abbreviated CNs) $C_1, \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} , \ C_3$, which represent the rows of the $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ matrix and hence the parity-check equations.
An edge between $V_i$ and $C_j$ indicates that the $i$th code word symbol is involved in the $j$th parity-check equation. In this case, the element $h_{j,\hspace{0.05cm}i}$ of the parity-check matrix is equal $1$.
In the exercise, the relation between the above Tanner–graph $($valid for the code $\rm A)$ and the matrix $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ shall be given. In addition, the Tanner–graph to a parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}_{\rm B}$ shall be set up, resulting from $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ adding another row. This is to be determined so that the associated code $\rm B$ is regular. This means:
- From all variable nodes $V_i$ $($with $1 ≤ i ≤ n)$ go off equal numbers of edges, likewise from all check nodes $C_j$ $($with $1 ≤ j ≤ m)$.
- The Hamming weights of all rows of $\mathbf{H}_{\rm B}$ are each said to be equal $(w_{\rm Z})$, as are the Hamming–weights of all columns $(w_{\rm S})$.
- For the rate of the regular code to be constructed $\rm B$ the following lower bound then applies:
- $$R \ge 1 - \frac{w_{\rm S}}{w_{\rm Z}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Basics of Low–density Parity–check Codes".
- Reference is made in particular to the page "Two-part LDPC graph representation – Tanner graph".
Questions
Solutiojn
(2) Correct are answers 1 and 3 in contrast to statement 2:
- The second $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$–row is rather "$1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0 \ 1 \ 0$". Thus, this exercise is based on the following parity-check equation:
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm A} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &1 &0 &1 &0 &0\\ 1 &0 &1 &0 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &0 &0 &1 \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In the diagram, the parity-check equations are illustrated as red (row 1), green (row 2), and blue (row 3) groupings, respectively.
(3) Correct are solutions 1 and 3:
- The $\mathbf{H}$ matrix ends with a $3 × 3$ diagonal matrix ⇒ systematic code.
- Thus, the Hamming weights of the last three columns are $w_{\rm S}(4) = w_{\rm S}(5) = w_{\rm S}(6) = 1$.
- For the first three columns, $w_{\rm S}(1) = w_{\rm S}(2) = w_{\rm S}(3) = 2$ ⇒ irregular code.
- The three matrix rows are linearly independent. Thus $k = n - m = 6 - 3 = 3$ and $R = k/n = 1/2$ holds.
(4) Correct is the proposed solution 1:
- Looking at the previous Tanner–s graph, one can see the correctness of proposed solution 1.
- By adding the row "$0 \ 0 \ 0 \ 1 \ 1 \ 1$" to the $\mathbf{H}_{\rm A}$ matrix, one obtains:
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm B} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 &1 &0 &1 &0 &0\\ 1 &0 &1 &0 &1 &0\\ 0 &1 &1 &0 &0 &1\\ 0 &0 &0 &1 &1 &1 \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The modifications are marked in red in the adjacent graphic.
Due to the newly added check node $C_4$ and the connections with $V_4, \ V_5$ and $V_6$, there are now
- from all variable nodes $V_i$ two lines, and
- from all Check Nodes $C_j$ uniformly four.
This is the condition for the code $\rm B$ to be regular.
(5) Correct are the solutions 2 and 3:
- The construction in subtask (4) yields a regular code.
- The Hamming weights of the rows and columns, respectively, are $w_{\rm Z} = 3$ and $w_{\rm S} = 2$.
- This gives as lower bound for the code rate:
- $$R \ge 1 - \frac{w_{\rm S}}{w_{\rm Z}} = 1 - {2}/{3} = 1/3 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The $\mathbf{H}$ manipulation does not change the generator matrix $\mathbf{G}$.
- The same code is still sent with code rate $R = 1/2$.