Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.1: Rectification"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File:P_ID239__Sig_A_2_1.png|250px|right|frame|Periodisches Dreiecksignal]] | [[File:P_ID239__Sig_A_2_1.png|250px|right|frame|Periodisches Dreiecksignal]] | ||
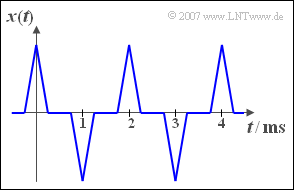
| − | + | The graph shows the periodic signal $x(t)$. If $x(t)$ is applied to the input of a non-linearity with the characteristic curve | |
:$$y=g(x)=\left\{ {x \; \rm f\ddot{u}r\; \it x \geq \rm 0, \atop {\rm 0 \;\;\; \rm sonst,}}\right.$$ | :$$y=g(x)=\left\{ {x \; \rm f\ddot{u}r\; \it x \geq \rm 0, \atop {\rm 0 \;\;\; \rm sonst,}}\right.$$ | ||
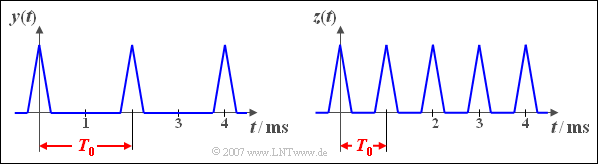
| − | + | the signall $y(t)$ is obtained at the output. A second non-linear characteristic | |
:$$z=h(x)=|x|$$ | :$$z=h(x)=|x|$$ | ||
| − | + | delivers the signal $z(t)$. | |
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Hint:'' |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Signal_Representation/General_Description|General description of periodic signals]]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements are true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+$y = g(x)$ beschreibt einen Einweggleichrichter. | +$y = g(x)$ beschreibt einen Einweggleichrichter. | ||
Revision as of 23:57, 26 December 2020
The graph shows the periodic signal $x(t)$. If $x(t)$ is applied to the input of a non-linearity with the characteristic curve
- $$y=g(x)=\left\{ {x \; \rm f\ddot{u}r\; \it x \geq \rm 0, \atop {\rm 0 \;\;\; \rm sonst,}}\right.$$
the signall $y(t)$ is obtained at the output. A second non-linear characteristic
- $$z=h(x)=|x|$$
delivers the signal $z(t)$.
Hint:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter General description of periodic signals.
Questions
Musterlösung
- Die nichtlineare Kennlinie $y = g(x)$ beschreibt einen Einweggleichrichter.
- $z = h(x) = |x|$ beschreibt einen Zweiweggleichrichter.
(2) Die Periodendauer des gegebenen Signals $x(t)$ beträgt $T_0 = 2\,\text{ms}$. Der Kehrwert hiervon ergibt die Grundfrequenz $f_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{ = 500\,\text{Hz}}$.
(3) Die Einweggleichrichtung ändert nichts an der Periodendauer, siehe linke Skizze. Somit gilt weiterhin $T_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 2\,\text{ms}}$.
(4) Das Signal $z(t)$ nach der Doppelweggleichrichtung hat dagegen die doppelte Frequenz (siehe rechte Darstellung). Hier gelten folgende Werte:
- $$T_0 = 1\,\text{ms}, \hspace{0.5cm} f_0 = 1\,\text{kHz}, \hspace{0.5cm} \omega_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 6283\,\text{1/s}}.$$