Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.1Z: Sum Signal"
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
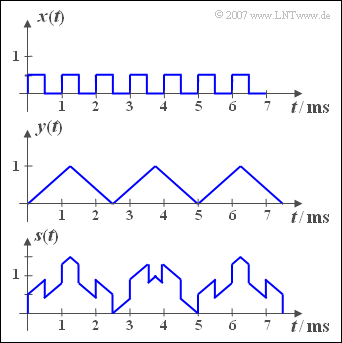
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The following applies to the square wave signal: $T_x = 1 \,\text{ms}$ ⇒ $f_x \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1 \, \text{kHz}}$. |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' The following applies to the triangular signal: $T_y = 2.5 \,\text{ms}$ und $f_y \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.4\, \text{kHz}}$. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' The base frequency $f_s$ of the sum signal $s(t)$ is the greatest common divisor $f_x = 1 \,\text{kHz}$ and $f_y = 0.4 \,\text{kHz}$. |
*Daraus folgt $f_s = 200 \,\text{Hz}$ und die Periodendauer $T_s\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 5 \,\text{ms}}$, wie auch aus der grafischen Darstellung des Signals ${s(t)}$ auf der Angabenseite hervorgeht. | *Daraus folgt $f_s = 200 \,\text{Hz}$ und die Periodendauer $T_s\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 5 \,\text{ms}}$, wie auch aus der grafischen Darstellung des Signals ${s(t)}$ auf der Angabenseite hervorgeht. | ||
Revision as of 00:55, 27 December 2020
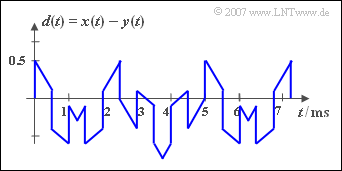
The adjacent diagram shows the two periodic signals ${x(t)}$ and ${y(t)}$ , from which the sum signal ${s(t)}$ – sketched in the lower picture – and the difference signal ${d(t)}$ are formed.
Furthermore, in this task we consider the signa ${w(t)}$, which results from the sum of the two periodic signals ${u(t)}$ und $v(t)$ . The base frequencies of the signals are
- $f_u = 998 \,\text{Hz},$
- $f_v = 1002 \,\text{Hz}.$
That is all we know about the signals ${u(t)}$ and $v(t)$ .
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Signal_Representation/General_Description|General description of periodic signals].
- With the interactive applet Periodendauer periodischer Signale the resulting period duration of two harmonic oscillations can be determined.
Questions
Solution
(2) The following applies to the triangular signal: $T_y = 2.5 \,\text{ms}$ und $f_y \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.4\, \text{kHz}}$.
(3) The base frequency $f_s$ of the sum signal $s(t)$ is the greatest common divisor $f_x = 1 \,\text{kHz}$ and $f_y = 0.4 \,\text{kHz}$.
- Daraus folgt $f_s = 200 \,\text{Hz}$ und die Periodendauer $T_s\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 5 \,\text{ms}}$, wie auch aus der grafischen Darstellung des Signals ${s(t)}$ auf der Angabenseite hervorgeht.
(4) Die Periodendauer $T_d$ ändert sich gegenüber der Periodendauer $T_s$ nicht, wenn das Signal ${y(t)}$ nicht addiert, sondern subtrahiert wird: $T_d = T_s \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 5\, \text{ms}}$.
(5) Der größte gemeinsame Teiler von $f_u = 998 \,\text{Hz}$ und $f_{v} = 1002 \,\text{Hz}$ ist $f_w = 2 \,\text{Hz}$.
- Der Kehrwert hiervon ergibt die Periodendauer $T_w \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 500 \,\text{ms}}$.