Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.4: Trapezoidal Spectrum and Pulse"
m (Oezdemir moved page Aufgabe 3.4: Trapezspektrum bzw. -impuls to Exercise 3.4: Trapezoidal Spectrum and Pulse) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:P_ID508__Sig_A_3_4.png|250px|right|frame|Trapezspektrum & Trapezimpuls]] | [[File:P_ID508__Sig_A_3_4.png|250px|right|frame|Trapezspektrum & Trapezimpuls]] | ||
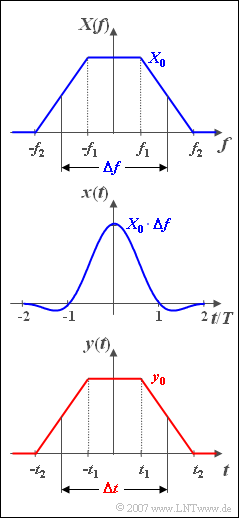
| − | + | We consider here a trapezoidal spectral function $X(f)$ according to the upper graph, which is completely described by the three parameters $X_0$, $f_1$ and $f_2$ . For the two corner frequencies, $f_2 > 0$ and $0 \leq f_1 \leq f_2$ always apply. | |
| − | + | Instead of the corner frequencies $f_1$ and $f_2$ , the following two descriptive variables can also be used: | |
| − | * | + | *the [[Signal_Representation/Fourier_Transform_Laws#Reciprocity_Theorem_of_Time_duration_and_Bandwidth|equivalent bandwidth]]: |
:$$\Delta f = f_1 + f_2,$$ | :$$\Delta f = f_1 + f_2,$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *the so-called [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Einige_systemtheoretische_Tiefpassfunktionen#Trapez.E2.80.93Tiefpass|rolloff factor]] (in the frequency domain): |
:$$r_f = \frac{ {f_2 - f_1 }}{ {f_2 + f_1 }}.$$ | :$$r_f = \frac{ {f_2 - f_1 }}{ {f_2 + f_1 }}.$$ | ||
| − | + | With these quantities, the associated time function (see middle graph) is:- | |
:$$x( t ) = X_0 \cdot \Delta f \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm \pi} \cdot \Delta f \cdot t} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm \pi} \cdot r_f \cdot \Delta f\cdot t} ).$$ | :$$x( t ) = X_0 \cdot \Delta f \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm \pi} \cdot \Delta f \cdot t} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm \pi} \cdot r_f \cdot \Delta f\cdot t} ).$$ | ||
| − | + | Here $\text{si}(x) = \text{sin}(x)/x$ is the so-called splitting function. | |
| − | In | + | In this example, the numerical values $X_0 = 10^{–3}\,\text{V/Hz}$, $f_1 = 1\,\text{kHz}$ and $f_2 = 3\,\text{kHz}$ are to be used. The time $T = 1/\Delta f$ is only used for standardisation purposes. |
| + | From subtask '''(3)''' a trapezoidal signal $y(t)$ is considered, which is identical in shape to the spectrum $X(f)$ . | ||
| − | + | The following can be used here as descriptive variables: | |
| − | + | *the pulse amplitude $y_0 = y(t = 0)$, | |
| − | + | *the [[Signal_Representation/Fourier_Transform_Laws#Reciprocity_Theorem_of_Time_duration_and_Bandwidth|equivalent pulse duration]] (defined via the rectangle with the same area): | |
| − | * | ||
| − | * | ||
:$$\Delta t = t_1 + t_2,$$ | :$$\Delta t = t_1 + t_2,$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *the rolloff factor (in the time domain) with comparable definition as $r_f$: |
:$$r_t = \frac{ {t_2 - t_1 }}{ {t_2 + t_1 }}.$$ | :$$r_t = \frac{ {t_2 - t_1 }}{ {t_2 + t_1 }}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Let $y_0 = 4\,\text{V}$, $\Delta t = 1\,\text{ms}$ and $r_t = 0.5$. | |
Revision as of 19:36, 23 January 2021
We consider here a trapezoidal spectral function $X(f)$ according to the upper graph, which is completely described by the three parameters $X_0$, $f_1$ and $f_2$ . For the two corner frequencies, $f_2 > 0$ and $0 \leq f_1 \leq f_2$ always apply.
Instead of the corner frequencies $f_1$ and $f_2$ , the following two descriptive variables can also be used:
- the equivalent bandwidth:
- $$\Delta f = f_1 + f_2,$$
- the so-called rolloff factor (in the frequency domain):
- $$r_f = \frac{ {f_2 - f_1 }}{ {f_2 + f_1 }}.$$
With these quantities, the associated time function (see middle graph) is:-
- $$x( t ) = X_0 \cdot \Delta f \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm \pi} \cdot \Delta f \cdot t} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm \pi} \cdot r_f \cdot \Delta f\cdot t} ).$$
Here $\text{si}(x) = \text{sin}(x)/x$ is the so-called splitting function.
In this example, the numerical values $X_0 = 10^{–3}\,\text{V/Hz}$, $f_1 = 1\,\text{kHz}$ and $f_2 = 3\,\text{kHz}$ are to be used. The time $T = 1/\Delta f$ is only used for standardisation purposes. From subtask (3) a trapezoidal signal $y(t)$ is considered, which is identical in shape to the spectrum $X(f)$ .
The following can be used here as descriptive variables:
- the pulse amplitude $y_0 = y(t = 0)$,
- the equivalent pulse duration (defined via the rectangle with the same area):
- $$\Delta t = t_1 + t_2,$$
- the rolloff factor (in the time domain) with comparable definition as $r_f$:
- $$r_t = \frac{ {t_2 - t_1 }}{ {t_2 + t_1 }}.$$
Let $y_0 = 4\,\text{V}$, $\Delta t = 1\,\text{ms}$ and $r_t = 0.5$.
Hinweise:
- Die Aufgabe gehört zum Kapitel Gesetzmäßigkeiten der Fouriertransformation.
- Verwenden Sie zur Lösung den Vertauschungssatz und den Ähnlichkeitssatz.
- Sie können Ihre Ergebnisse anhand der beiden interaktiven Applets Impulse und Spektren sowie Frequenzgang und Impulsantwort überprüfen.
Fragebogen
Musterlösung
- $$\Delta f = f_1 + f_2 \hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{= 4\;{\rm{kHz}}}{\rm{.}}$$
- Für den Rolloff-Faktor gilt:
- $${ {r_f = }}\frac{ {f_2 - f_1 }}{ {f_2 + f_1 }}\hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{ = 0.5}.$$
(2) Der Maximalwert des Impulses $x(t)$ tritt zum Zeitpunkt $t = 0$ auf:
- $$x_0 = x(t = 0) = X_0 \cdot \Delta f \hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{= 4\, \text{V}}.$$
- Zum Zeitpunkt $t = T = 1/\Delta f$ gilt aufgrund von $\text{si}(\pi) = 0$:
- $$x( {t = T} ) = x_0 \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {\rm{\pi }} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { { {\rm{\pi }}}/{2}} )\hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{ = 0}.$$
- Auch bei allen Vielfachen von $T$ weist $x(t)$ Nulldurchgänge auf. Zum Zeitpunkt $t = T/2$ gilt:
- $$x( {t = T/2} ) = x_0 \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { { {\rm{\pi }}}/{2}} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits}( { { {\rm{\pi }}}/{4}} ) = x_0 \cdot \frac{ { 1 \cdot \sqrt 2 /2}}{ { {\rm{\pi /}}2 \cdot {\rm{\pi /4}}}} = x_0 \cdot \frac{ {4 \cdot \sqrt 2 }}{ { {\rm{\pi }}^{\rm{2}} }} \hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{= 2.293\;{\rm{V}}}{\rm{.}}$$
(3) Die zum trapezförmigen Spektrum $X(f)$ zugehörige Zeitfunktion lautet entsprechend der Angabe:
- $$x( t ) = X_0 \cdot \Delta f \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm{\pi }} \cdot \Delta f \cdot t} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm{\pi }} \cdot r_f \cdot \Delta f \cdot t} ).$$
- Da sowohl $X(f)$ als auch $x(t)$ reell sind und zudem $y(t)$ formgleich mit $X(f)$ ist, erhält man unter Berücksichtigung aller Äquivalenzen für die Spektralfunktion des Trapezimpulses:
- $$Y( f ) = y_0 \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm{\pi }} \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( { {\rm{\pi }} \cdot r_t \cdot \Delta t \cdot f} ).$$
- Insbesondere gilt:
- $$Y( {f = 0} ) = y_0 \cdot \Delta t \hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{= 4 \;{\rm{mV/Hz}}}{\rm{,}}$$
- $$Y( {f = 0.5\;{\rm{kHz}}} ) = y_0 \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {{ {\rm{\pi }}}/{2}} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {{ {\rm{\pi }}}/{4}} ) \hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{= 2.293 \;{\rm{mV/Hz}}}{\rm{,}}$$
- $$Y( {f = 1\;{\rm{kHz}}} ) = y_0 \cdot \Delta t \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {\rm{\pi }} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {{ {\rm{\pi }}}/{2}} )\hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{ = 0}\;{\rm{.}}$$
(4) Der Spektralwert bei der Frequenz $f = 0$ wird nicht verändert:
- $$Y_0 = y_0 \cdot \Delta t \hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{= 4 \,\rm{mV/Hz}}.$$
- Da nun aber die Zeitfunktion nur halb so breit ist, verbreitert sich das Spektrum um den Faktor $2$:
- $$Y( {f = 1\;{\rm{kHz}}} ) = Y_0 \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {{ {\rm{\pi }}}/{2}} ) \cdot {\mathop{\rm si}\nolimits} ( {{ {\rm{\pi }}}/{4}} ) \hspace{0.15 cm}\underline{= 2.293\,{\rm{mV/Hz}}}{\rm{.}}$$
- In der Teilaufgabe (3) ist dieser Spektralwert bei der Frequenz $f = 0.5\,\rm{kHz}$ aufgetreten.