Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.2: Entropy of Ternary Sources"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the entropy $H$ of the source $\rm \underline{Q_1}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$H \ = \ $ { 1.46 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | $H \ = \ $ { 1.46 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements are true if $\rm R$, $\rm G$ and $\rm S$ are represented by the numerical values $-1$, $0$ and $+1$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The result is a smaller entropy. |
| − | + | + | + The entropy remains the same. |
| − | - | + | - The result is a greater entropy. |
| − | { | + | {Determine the entropy of the source $\rm \underline{Q_2}$ using the binary entropy function $H_{\rm bin}(p)$. What value results for $\underline{p = 0.5}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$H \ = \ $ { 1.5 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | $H \ = \ $ { 1.5 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | ||
| − | { | + | {For whic $p$–value der Quelle $\rm \underline{Q_2}$ does the maximum entropy result: $H → H_\text{max}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$p \ = \ $ { 0.333 3% } | $p \ = \ $ { 0.333 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the entropy of the message source $\text{Roulette 1}$, i.e. with respect to the events $\rm R$ed, $\rm S$chwarz and $\rm G$reen (the „zero”)? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$H \ = \ $ { 1.152 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | $H \ = \ $ { 1.152 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the entropy of $\text{Roulette 2}$ , i.e. with regard to the numbers $0$, ... , $36$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$H \ = \ $ { 5.209 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | $H \ = \ $ { 5.209 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
'''(1)''' Mit den Auftrittswahrscheinlichkeiten $1/2$, $1/3$ und $1/6$ erhält man folgenden Entropiewert: | '''(1)''' Mit den Auftrittswahrscheinlichkeiten $1/2$, $1/3$ und $1/6$ erhält man folgenden Entropiewert: | ||
Revision as of 21:57, 7 May 2021
The entropy of a discrete-value memoryless message source with $M$ possible symbols is:
- $$H = \sum_{\mu = 1}^M p_{\mu} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{p_\mu}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} {\rm pseudo unit\hspace{-0.15cm}: \hspace{0.15cm}bit}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Here, the $p_\mu$ denote the occurrence probabilities of the individual symbols or events. n the present example, the events are denoted by $\rm R$(ed), $\rm G$(reen) and $\rm S$(chwarz) with Schwarz being the German word for black.
- For a binary source with the occurrence probabilities $p$ and $1-p$ this can be written:
- $$H = H_{\rm bin}(p) = p \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{p}+ (1-p) \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} {\rm pseudo unit\hspace{-0.15cm}: \hspace{0.15cm}bit}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The entropy of a multilevel source can often be expressed with this „binary entropy function” $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ .
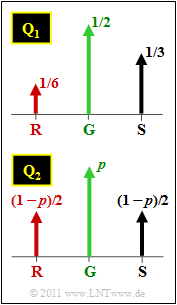
In this task, two ternary sources with the symbol probabilities according to the above graph are considered:
- source $\rm Q_1$ with $p_{\rm G }= 1/2$, $p_{\rm S }= 1/3$ and $p_{\rm R }= 1/6$,
- source $\rm Q_2$ with $p_{\rm G }= p$ and $p_{\rm S } = p_{\rm R } = (1-p)/2$.
The ternary source $\rm Q_2$ can also be applied to roulette when a player bets only on the squares $\rm R$, $\rm S$chwarz and $\rm G$reen (the „zero”). This type of game is referred to as $\text{Roulette 1}$ in the question section.
In contrast, $\text{Roulette 2}$ indicates that the player bets on single numbers $(0$, ... , $36)$ .
Hint:
- The task belongs to the chapter Discrete Memoryless Sources.
Questions
Solution
- $$H \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} 1/2 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(2) +1/3 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(3) +1/6 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(6) =(1/2 + 1/6)\cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(2) + (1/3 + 1/6)\cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(3) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 1.46 \, {\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Richtig ist der Lösungsvorschlag 2:
- Die Entropie hängt nur von den Auftrittswahrscheinlichkeiten ab.
- Es ist dabei egal, welche Zahlenwerte oder physikalische Größen man den einzelnen Symbolen zuordnet.
- Anders ist es bei Mittelwerten oder der AKF–Berechnung. Werden nur Symbole angegeben, so kann man hierfür keine Momente angeben.
- Außerdem hängen die Mittelwerte, Autokorrelation, usw. davon ab, ob man die Zuordnung bipolar $(-1, \hspace{0.10cm}0, \hspace{0.05cm}+1)$ oder unipolar $(0, \hspace{0.05cm}1, \hspace{0.05cm}2)$ vereinbart.
(3) Die Entropie der Quelle $\rm Q_2$ lässt sich wie folgt ausdrücken:
- $$H \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}\frac {1}{p}+ 2 \cdot \frac{1-p}{2} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}\frac {2}{1-p}= p \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}\frac {1}{p}+ (1-p) \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}\frac {1}{1-p} + (1-p)\cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(2)= H_{\rm bin}(p) + 1-p \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Für $p = 0.5$ ⇒ $H_{\rm bin}(p) = 1$ ergibt sich $\underline{H = 1.5\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit}$.
(4) Die maximale Entropie einer gedächtnislosen Quelle mit dem Symbolumfang $M$ ergibt sich, wenn alle $M$ Symbole gleichwahrscheinlich sind.
- Für den Sonderfall $M=3$ folgt daraus:
- $$p_{\rm R} + p_{\rm G} + p_{\rm S} = 1 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \underline {p = 1/3 \approx 0.333}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Damit erhält man mit dem Ergebnis der Teilaufgabe (3) die folgende Entropie:
- $$H = H_{\rm bin}(1/3) + 1-1/3 = 1/3 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(3) + 2/3 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(3/2) + 2/3 $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H = 1/3 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(3) + 2/3 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(3) - 2/3 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(2)+ 2/3 = {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(3) = {1.585 \, {\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) Das System $\text{Roulette 1}$ ist informationstheoretisch gleich der Konfiguration $\rm Q_2$ mit $p = 1/37$:
- $$p_{\rm G} = p = \frac{1}{37}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} p_{\rm R} = p_{\rm S} = \frac{1-p}{2} = \frac{18}{37} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Damit erhält man mit dem Ergebnis der Teilaufgabe (3):
- $$H = H_{\rm bin}(1/37) + \frac{36}{37} = \frac{1}{37} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(37) + \frac{36}{37} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(37) - \frac{36}{37} \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}36 + \frac{36}{37} = {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(37) + \frac{36}{37} \cdot ( 1- {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(36)) = 5.209 - 4.057 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline { = 1.152 \, {\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) Setzt man bei Roulette auf einzelne Zahlen ⇒ Konfiguration $\text{Roulette 2}$, so sind alle Zahlen von $0$ bis $36$ gleichwahrscheinlich und man erhält:
- $$H = {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(37) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline { = 5.209 \, {\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$