Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.6: Non-Binary Markov Sources"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2253__Inf_A_1_6.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2253__Inf_A_1_6.png|right|frame|Markov sources with <br>$M = 3$ and $M = 4$]] |
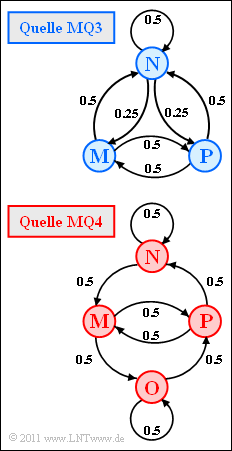
| − | + | The graph shows two ergodic Markov sources $($German: "Markovquellen" ⇒ "$\rm MQ$"$)$: | |
| − | * | + | * The source $\rm MQ3$ is denoted by $M = 3$ states (symbols) $\rm N$, $\rm M$, $\rm P$. Due to stationarity, the probabilities have the following values: |
| − | :$$p_{\rm N} = | + | :$$p_{\rm N} = 1/2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm P} = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | * | + | * For the source $\rm MQ4$ the state $\rm O$ is additionally possible ⇒ $M = 4$. Due to the symmetric transitions, the stationary probabilities are all equal: |
| − | :$$p_{\rm N} = p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm O} = | + | :$$p_{\rm N} = p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm O} = p_{\rm P} = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | In terms of information theory, Markov sources are of particular importance, since with these – and only with these – by | |
| − | * $H_1$ | + | * $H_1$ (first entropy approximation, based only on the symbol probabilities), and |
| − | * $H_2$ ( | + | * $H_2$ (second entropy approximation, computable with the composite probabilities for all two-tuples) |
| − | + | are also determined at the same time: | |
| − | * | + | * the further entropy approximations $H_k$ with $k = 3, \ 4$, ..., and |
| − | * | + | * the actual (final) source entropy $H$. |
| − | + | The following equations of determination apply: | |
:$$H = 2 \cdot H_2 - H_1\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$H = 2 \cdot H_2 - H_1\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
:$$H_k = {1}/{k} \cdot \big [ H_{\rm 1} + (k-1) \cdot H \big ] | :$$H_k = {1}/{k} \cdot \big [ H_{\rm 1} + (k-1) \cdot H \big ] | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| + | ''Hint:'' | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Discrete_Sources_with_Memory|Discrete Sources with Memory]]. | ||
| + | *Reference is made in particular to the page [[Information_Theory/Discrete_Sources_with_Memory#Non-binary_Markov_sources|Non-binary Markov Sources]]. | ||
| + | *For all entropies, add the pseudo-unit "bit/symbol". | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 45: | Line 43: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the entropy approximation $H_1$ of the Markov source $\rm MQ3$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H_1 \ = \ $ | + | $H_1 \ = \ $ { 1.5 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the entropy approximation $H_2$ of the Markov source $\rm MQ3$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H_2 \ = \ | + | $H_2 \ = \ $ { 1.375 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | { | + | {What are the actual source entropy $H$ and the approximations $H_3$ and $H_4$ for $\rm MQ3$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H \ = \ $ | + | $H \ = \ $ { 1.25 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | $H_3 \ = \ $ { 1.333 3% } $\ \rm bit/ | + | $H_3 \ = \ $ { 1.333 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | $H_4 \ = \ $ { 1.3125 3% } $\ \rm bit/ | + | $H_4 \ = \ $ { 1.3125 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | + | {Calculate the entropy approximation $H_1$ of the Markov source $\rm MQ4$. | |
| − | { | ||
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H_1 \ = \ | + | $H_1 \ = \ $ { 2 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the entropy approximation $H_2$ of the Markov source $\rm MQ4$ |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H_2 \ = | + | $H_2 \ = \ $ { 1.5 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$. |
| − | { | + | {What are the actual source entropy $H$ and the approximations $H_3$ and $H_4$ for $\rm MQ4$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H \ = | + | $H \ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | $H_3 \ = | + | $H_3 \ = \ $ { 1.333 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | $H_4 \ = | + | $H_4 \ = \ $ { 1.25 3% } $\ \rm bit/symbol$ |
| − | |||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 21 June 2021
The graph shows two ergodic Markov sources $($German: "Markovquellen" ⇒ "$\rm MQ$"$)$:
- The source $\rm MQ3$ is denoted by $M = 3$ states (symbols) $\rm N$, $\rm M$, $\rm P$. Due to stationarity, the probabilities have the following values:
- $$p_{\rm N} = 1/2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm P} = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- For the source $\rm MQ4$ the state $\rm O$ is additionally possible ⇒ $M = 4$. Due to the symmetric transitions, the stationary probabilities are all equal:
- $$p_{\rm N} = p_{\rm M} = p_{\rm O} = p_{\rm P} = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In terms of information theory, Markov sources are of particular importance, since with these – and only with these – by
- $H_1$ (first entropy approximation, based only on the symbol probabilities), and
- $H_2$ (second entropy approximation, computable with the composite probabilities for all two-tuples)
are also determined at the same time:
- the further entropy approximations $H_k$ with $k = 3, \ 4$, ..., and
- the actual (final) source entropy $H$.
The following equations of determination apply:
- $$H = 2 \cdot H_2 - H_1\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$H_k = {1}/{k} \cdot \big [ H_{\rm 1} + (k-1) \cdot H \big ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hint:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Discrete Sources with Memory.
- Reference is made in particular to the page Non-binary Markov Sources.
- For all entropies, add the pseudo-unit "bit/symbol".
Fragebogen
Musterlösung
- Daraus lässt sich die Entropienäherung $H_1$ berechnen:
- $$H_{\rm 1} = 1/2 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (2) + 2 \cdot 1/4 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}(4 ) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.5 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Die Verbundwahrscheinlichkeit ist $p_{\rm XY} = p_{\rm X} \cdot p_{\rm Y|X}$, wobei $p_{\rm X}$ die Symbolwahrscheinlichkeit von $\rm X$ angibt und $p_{\rm Y|X}$ die bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeit für $\rm Y$, unter der Voraussetzung, dass vorher $\rm X$ aufgetreten ist.
- $\rm X$ und $\rm Y$ sind hier Platzhalter für die Symbole $\rm N$, $\rm P$ und $\rm M$. Dann gilt:
- $$p_{\rm NN} = 1/2 \cdot 1/2 = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm PP} = 1/4 \cdot 0 = 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm MM} = 1/4 \cdot 0 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ p_{\rm NP} = 1/2 \cdot 1/4 = 1/8\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} p_{\rm PM} = 1/4 \cdot 1/2 = 1/8\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm MN} = 1/4 \cdot 1/2 = 1/8 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ p_{\rm NM} = 1/2 \cdot 1/4 = 1/8\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} p_{\rm MP} = 1/4 \cdot 1/2 = 1/8\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}p_{\rm PN} = 1/4 \cdot 1/2 = 1/8$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H_{\rm 2} = {1}/{2} \cdot \big [ 1/4 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm}( 4) + 6 \cdot 1/8 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (8) \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.375 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) $\rm MQ3$ weist Markoveigenschaften auf.
- Deshalb können aus $H_1$ und $H_2$ alle Näherungen $H_3$, $H_4$, ... und auch der Grenzwert $H =H_\infty$ für $k \to \infty$ angegeben werden:
- $$H = 2 \cdot H_2 - H_1 = 2\cdot 1.375 - 1.5 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.250 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ H_3 \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm}= (H_1 + 2 \cdot H)/3 = (1.5 + 2 \cdot 1.25)/3 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.333 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ H_4 = (H_1 + 3 \cdot H)/4 = (1.5 + 3 \cdot 1.25)/4 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.3125 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Die zehnte Entropienäherung unterscheidet sich noch immer vom Endwert $H = 1.25 \, \rm bit/Symbol$, wenn auch nur geringfügig $($um $2\%)$ :
- $$H_{10} = (H_1 + 9 \cdot H)/10 = (1.5 + 9 \cdot 1.25)/10 {= 1.275 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Entsprechend der Angabe sind bei $\rm MQ4$ die $M = 4$ Symbole gleichwahrscheinlich.
- Daraus folgt:
- $$H_{\rm 1} = H_{\rm 0} = {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (4) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 2 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) Von den $M^2 = 16$ möglichen Zweiertupeln sind nun acht Kombinationen nicht möglich:
- $$\rm NP, NO, PP, PO, OM, ON, MM, MN.$$
- Die acht weiteren Kombinationen (Zweiertupel) ergeben jeweils den Verbundwahrscheinlichkeitswert $1/8$, wie an zwei Beispielen gezeigt wird:
- $$p_{\rm NN} = p_{\rm N} \cdot p_{\rm N\hspace{0.01cm}|\hspace{0.01cm}N} = 1/4 \cdot 1/2 = 1/8 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.5cm} p_{\rm MP} = p_{\rm M} \cdot p_{\rm P\hspace{0.01cm}|\hspace{0.01cm}M} = 1/4 \cdot 1/2 = 1/8 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H_2 = {1}/{2} \cdot \big [ 8 \cdot 1/8 \cdot {\rm log}_2\hspace{0.1cm} (8) \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.5 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) Aufgrund der Markoveigenschaft gilt hier:
- $$H = 2 \cdot H_2 - H_1 = 2\cdot 1.5 - 2 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ H_3 = (H_1 + 2 \cdot H)/3 = (2 + 2 \cdot 1)/3 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.333 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ H_4 = (H_1 + 3 \cdot H)/4 = (2 + 3 \cdot 1)/4 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 1.250 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Auch hier unterscheidet sich die zehnte Näherung noch deutlich vom Endwert, nämlich um $10\%$:
- $$H_{10} = (H_1 + 9 \cdot H)/10 = (2 + 9 \cdot 1)/10 {= 1.1 \,{\rm bit/Symbol}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Eine Abweichung um nur $2\%$ ergibt sich hier erst für $k = 50$. Zum Vergleich: Bei der Markovquelle $\rm MQ3$ wurde diese Annäherung bereits mit $k = 10$ erreicht.